Coupled Effects of Reservoir Curvature, Thickness, and Well Configuration on Hydrogen Storage Efficiency in Saline Aquifers
选址评估是盐穴储氢研究中的关键步骤,储层几何特征是决定选址评估的关键因素之一。然而,对于具有有效圈闭能力的背斜盐穴储层,储层曲率、厚度和井配置对储氢效率的耦合效应尚不清楚。因此,本文基于鄂尔多斯盆地,设计了不同曲率、厚度和井配置的三维计算模型进行模拟分析。
CMG软件应用情况
本文采用了CMG-GEM(Computer Modelling Group Ltd.的通用状态方程模型)多组分模拟器,进行了三维地质模型的数值模拟,研究了不同曲率、厚度和井配置条件下盐穴储氢的性能表现。通过该软件,作者能够模拟氢气注入、储存和生产过程中的多相流动行为,评估氢气回收率及其影响因素。
结论
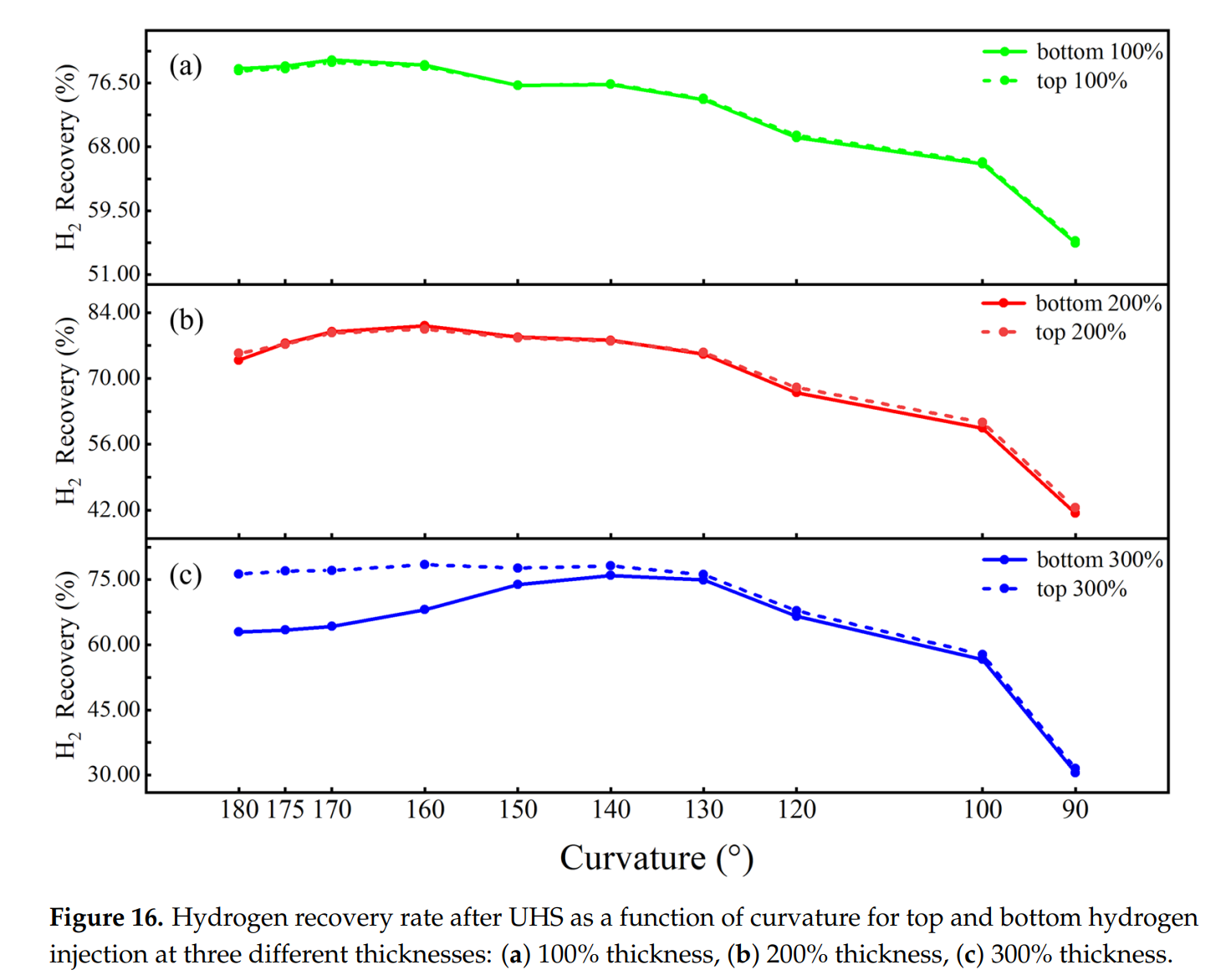
- 背斜储层曲率越大,圈闭效应越强,氢气回采率先升高后降低,170°时回收率最高达79.58%,90°时降至55.17%,主要由于无限边界条件下井底压力过早下降至最低安全阈值。
- 增加储层厚度可抑制氢气横向运移,促进垂向扩散,降低盖层突破风险。厚度为100%、200%、300%时,盖层最大气相饱和度分别为0.12、0.08、0.05,厚度越大,盖层气相饱和度越低。
- 曲率与厚度存在耦合效应,薄储层在小曲率条件下储氢效率更高,厚储层在大曲率条件下表现更佳。厚度100%时,170°曲率回收率最高(79.58%);厚度200%时,160°曲率最佳;厚度300%时,140°曲率最优(75.98%)。
- 顶部注氢显著降低了回收率对曲率和厚度的敏感性。例如,曲率180°至130°时,顶部注氢在300%厚度下回收率波动小于1%;曲率180°至100°时,顶部注氢三种厚度回收率差异仅2.51%,远低于底部注氢的16.20%。
本文简化处理了地层参数,未考虑氢气的生化反应,未来研究应结合更实际的地质特征进行深入分析。
作者单位
中国地质大学(北京)
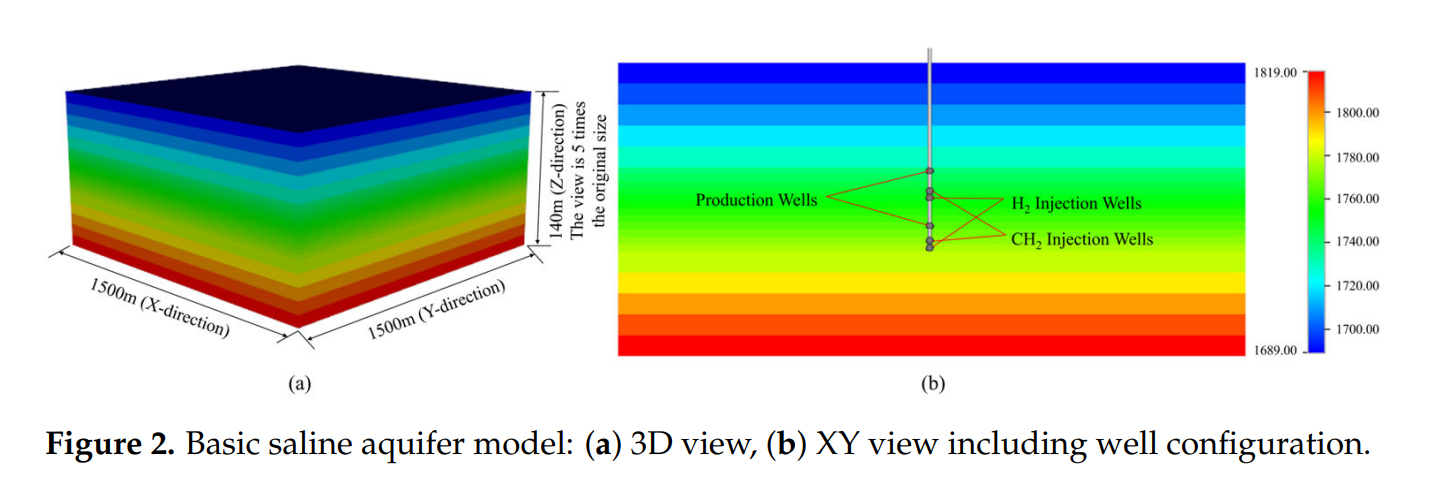
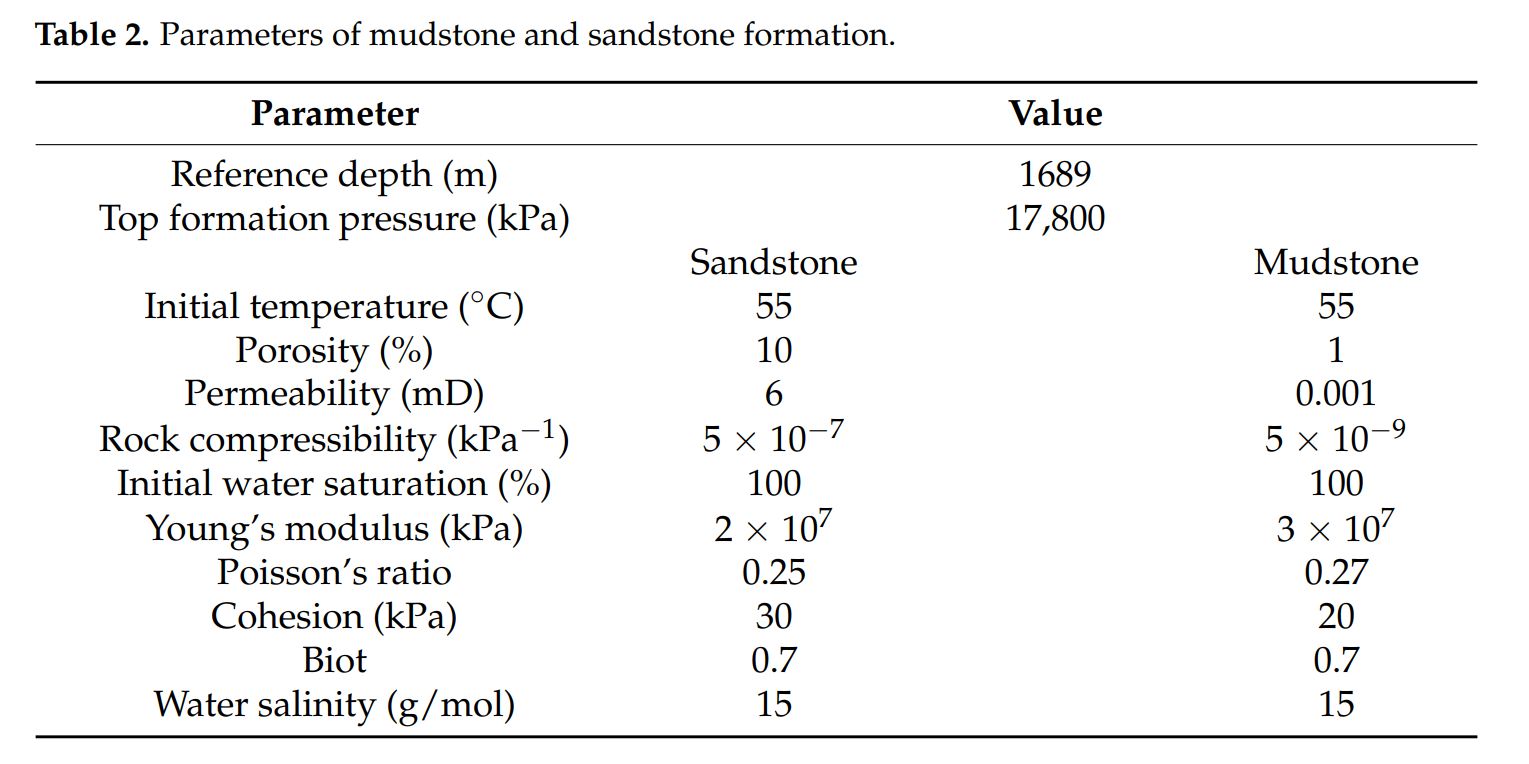
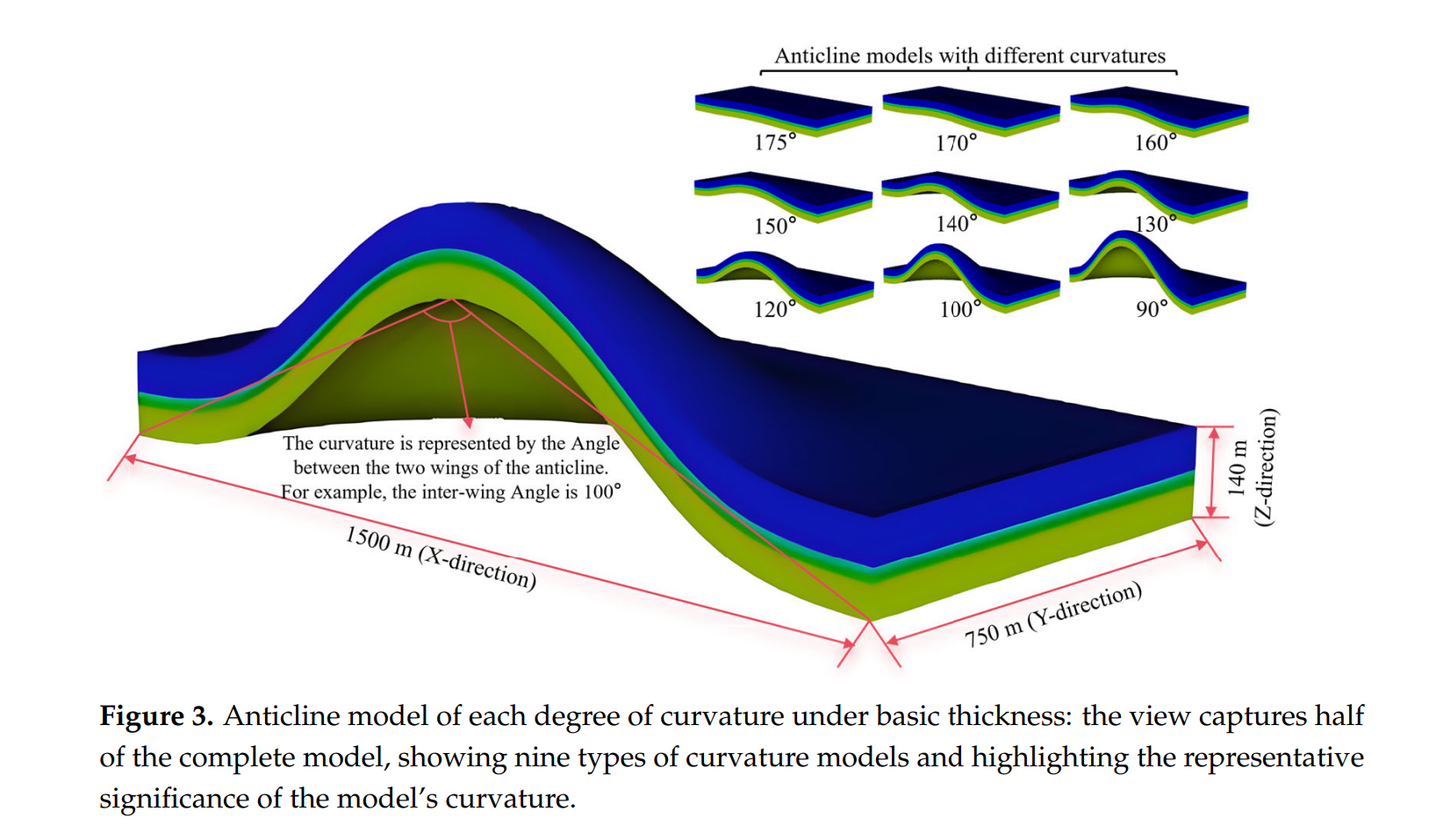
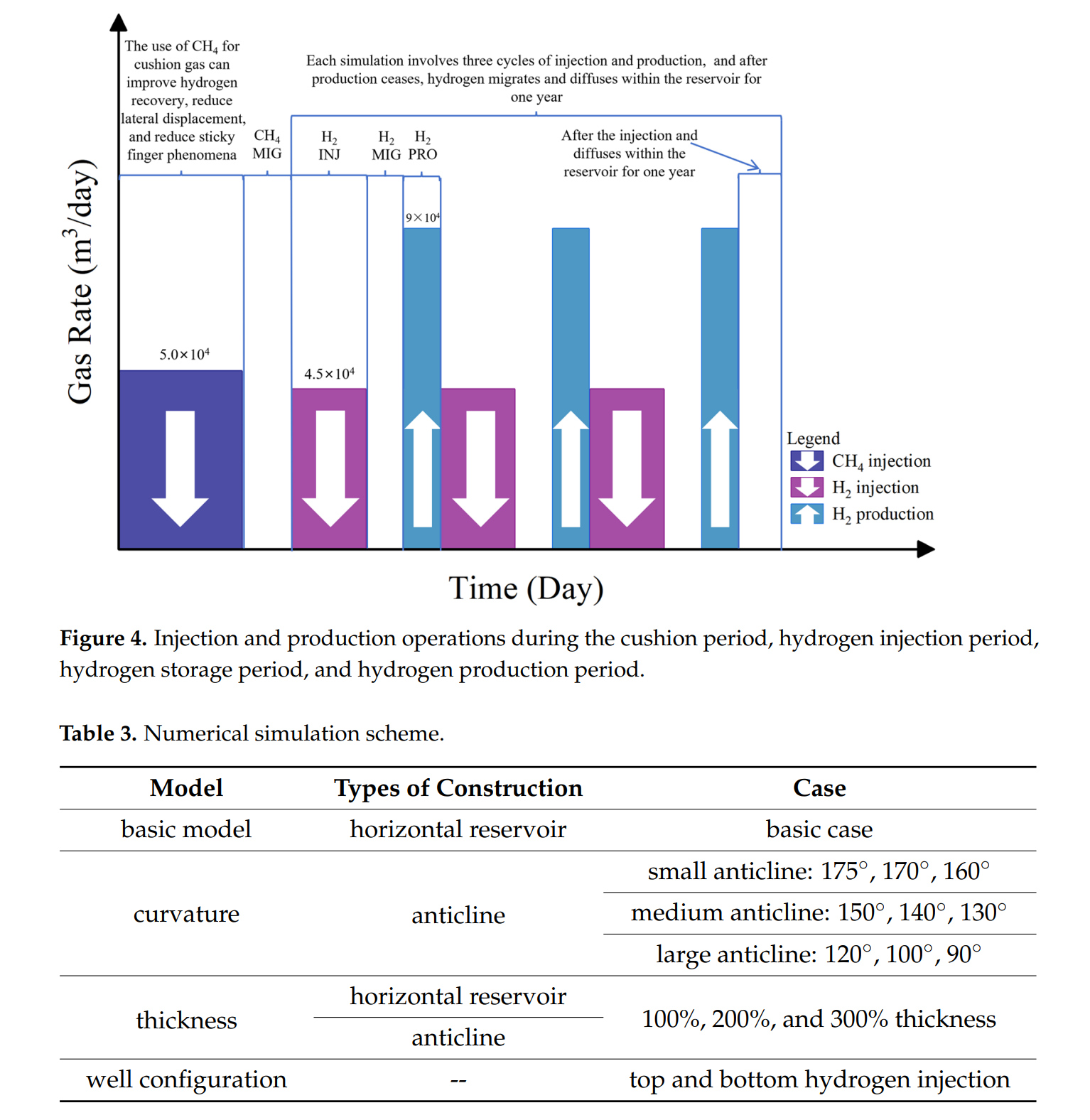

Abstract
Site selection evaluation is a crucial step in the research of hydrogen storage in saline aquifers. Geometric characteristics of the reservoir are one of the key factors determining the site selection evaluation. However, for the anticlinal saline aquifers with effective trap capacity, the coupled effects of reservoir curvature, thickness, and well configuration on hydrogen storage efficiency remain unclear. Thus, based on the Ordos Basin, various 3D computational models with different curvatures, thicknesses, and well configurations are designed to conduct the simulation analysis. The results show that (1) the greater the curvature, the stronger the trap effect. Hydrogen recovery rises first and then declines, reaching a peak of 79.58% at 170° and dropping to 55.17% at 90°. (2) Increasing thickness suppresses lateral hydrogen migration. The maximum gas saturations in the caprock are 0.12, 0.08, and 0.05 for thicknesses of 100%, 200%, and 300%, respectively, indicating that greater thickness reduces gas diffusion into the caprock. (3) The coupling effect between curvature and thickness affects the recovery rate. Thin reservoirs are suitable for small curvatures, while thick reservoirs are more suitable for high curvatures. (4) Top hydrogen injection significantly reduces the sensitivity of the recovery rate to curvature and thickness. When the curvature is between 180° and 100°, lowering recovery differences across thicknesses are lowered from 16.20% under bottom injection to 2.51% under top injection. These results provide support for the site selection and design of hydrogen storage in saline aquifers.
