Prediction of Pressure Build-Up Distribution and Geomechanical Analysis in a CO2 Sequestration Reservoir Using Optimised Artificial Intelligence Models
CO₂ 注入引起的孔隙压力升高会降低有效应力,诱发盖层破裂、断层复活及微震活动,威胁封存安全。本文构建了一套“CMG-GEM 数值模拟 → 混合人工智能代理模型”的完整工作流程:
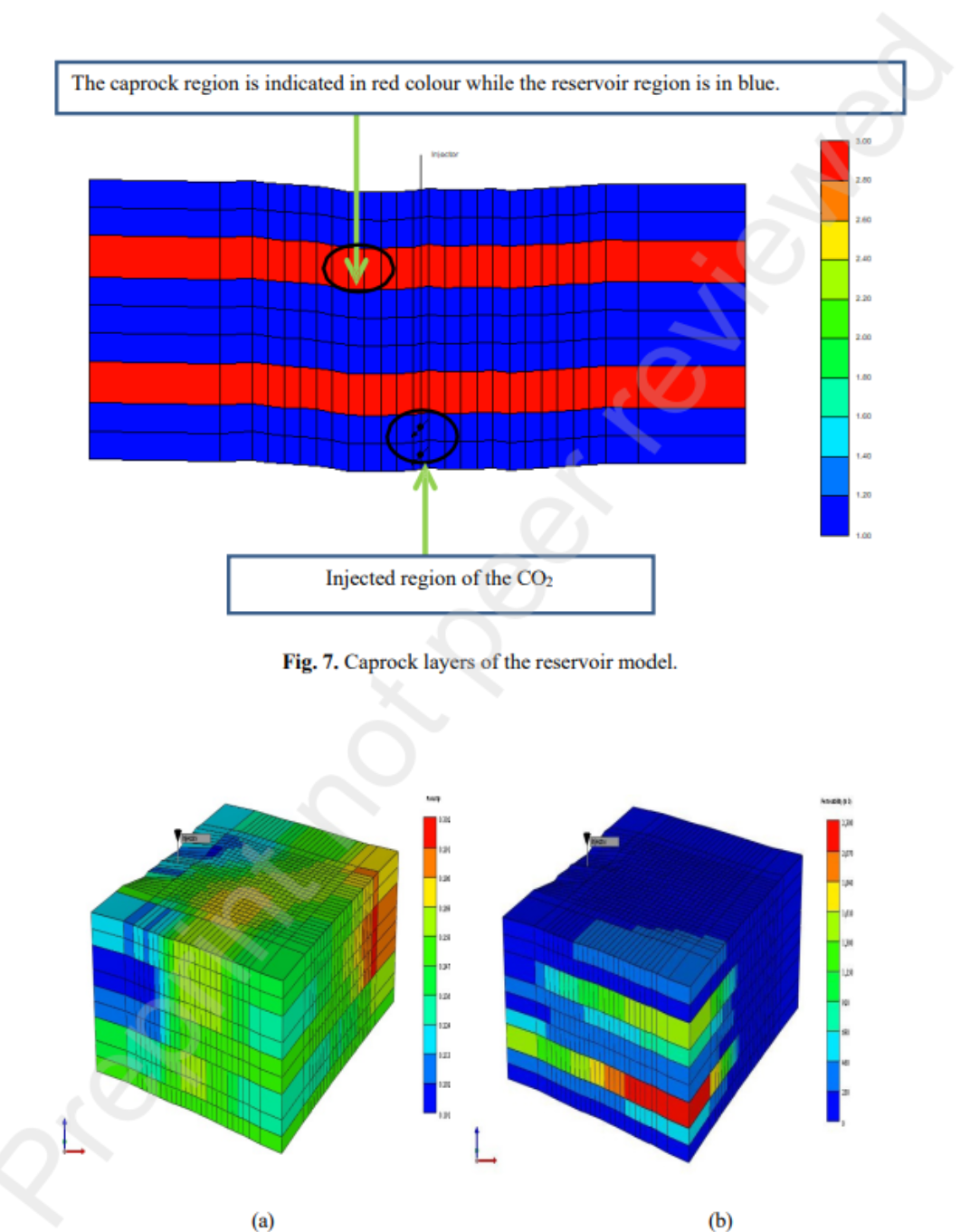
- 以深部咸水层为对象,在 CMG-GEM 中建立双重孔隙-双重渗透率三维模型,连续注入 20 年 CO₂,获得压力、饱和度、有效平均应力(EMS)与微震事件密度等 4 482 组数据集;
- 将人工神经网络(ANN)与四种元启发式算法(鲸鱼 WOA、粒子群 PSO、灰狼 GWO、大猩猩 GTO)及 PINN 耦合,形成五种“混合 AI”代理模型,用于快速预测 EMS;
- 通过交叉验证、敏感性分析与现场案例比对,评估模型在预测精度、计算效率、物理一致性上的综合表现。
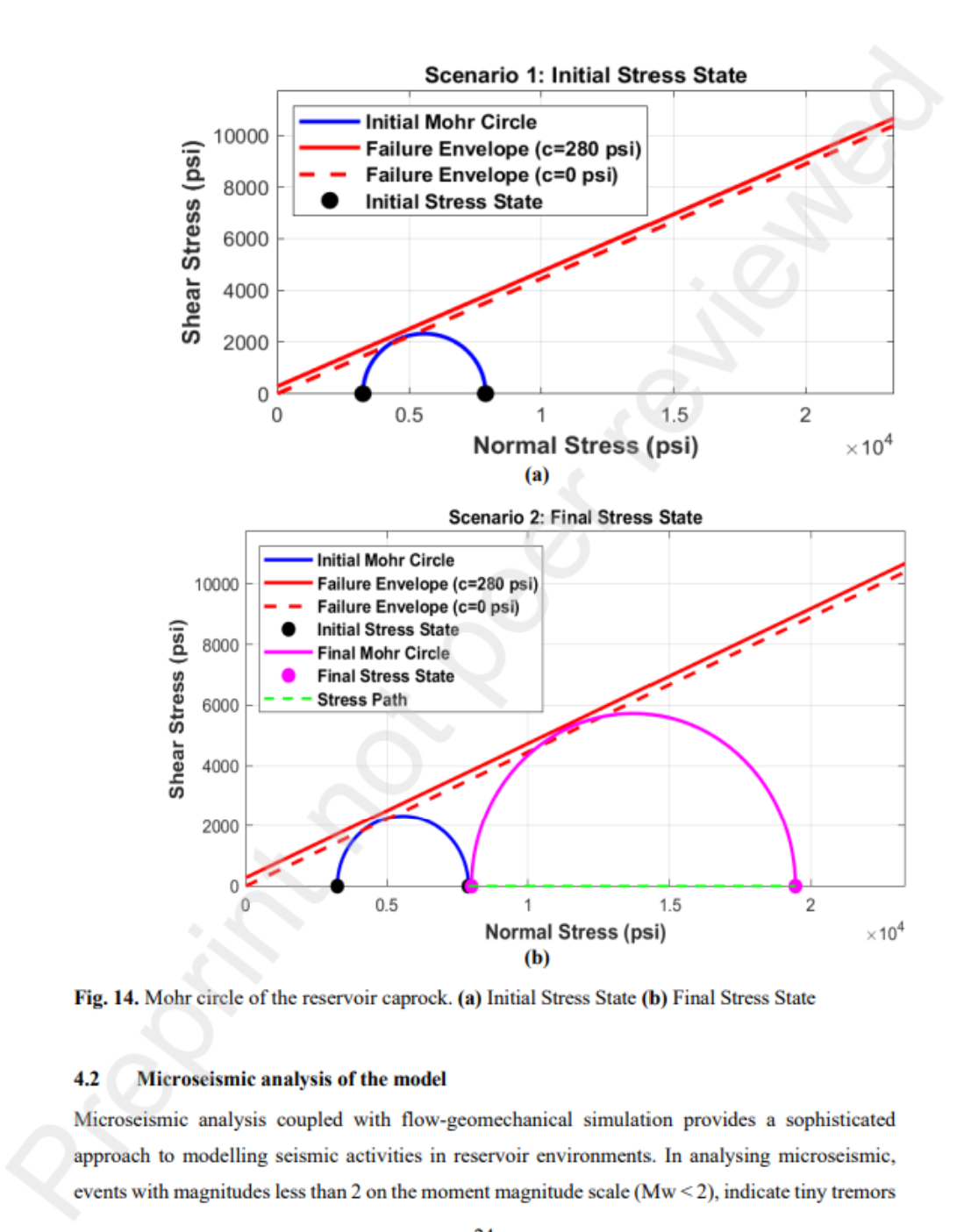
结果表明:ANN-GTO 模型精度最高(测试集 R²=0.99941,MAPE=0.072%);微震事件密度随压力累积呈 0.1–1 增至 30–220 的规律,为泄漏风险提供了可量化代理指标。研究为 CO₂ 封存项目的实时监测、风险预警与注入策略优化提供了高效、可靠的决策工具。
【CMG 软件应用情况】
• 软件版本:CMG-GEM(Generalized Equation-of-State Model)
• 模型规模:29×26×9 网格,4 482 个活动网格块
• 关键功能:
– 建立双重孔隙-双重渗透率三维储层模型;
– 设置 CO₂-卤水两相流动、相对渗透率曲线及岩石压缩性;
– 运行 20 年连续注入,输出压力、饱和度、有效平均应力(EMS)及微地震事件密度;
– 通过拉丁超立方采样(LHS)在孔隙度、渗透率、注入速率等参数空间生成训练数据集。
• 软件接口:CMG-GEM 结果文件直接导入 MATLAB,用于 AI 模型训练与验证。
【主要结论】
- CMG-GEM 数值模拟成功再现了 CO₂ 注入引起的压力积聚、有效应力降低及微震事件时空演化;
- 混合 AI 模型可在秒级完成传统数值模拟需数天才能完成的 EMS 预测,其中 ANN-GTO 精度最高;
- 微震事件密度与压力积聚呈显著正相关,可作为泄漏风险的早期代理指标;
- 与 Sleipner、In Salah、Quest 等现场案例对比,模拟的盖层泄漏模式与观测一致,验证了方法可靠性;
- 建议实际项目采用“混合 AI 快速筛查 + 传统数值模拟精细验证”的协同策略,兼顾效率与物理可信度。
作者单位】
中国地质大学(北京)能源学院)


Abstract
Carbon dioxide injection into geological formations is widely practiced but poses significant geomechanical risks due to pore pressure build-up, which can cause caprock failure, fault reactivation, poroelastic responses, and compromised well integrity. This study presents a predictive model for effective mean stress that directly links reservoir pressure build-up to geomechanical deformation. It introduces a hybrid Artificial Intelligence (AI) workflow that forecasts pressure build-up and its effects on effective stresses without extensive compositional simulations. The study also provides a comparative analysis of hybrid algorithms versus the traditional ADAM optimizer and Physics Informed Neural Network (PINN). Furthermore, it investigates how pressure-induced effective stresses influence CO2injection in reservoir formations. To achieve enhanced predictive accuracy and computational efficiency, the study employs innovative hybrid models that integrate Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) with advanced optimization algorithms-including the Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO), and Gorilla Troops Optimization (GTO). The ANN-GTO model demonstrated superior predictive accuracy with a correlation coefficient of 0.99970 and R2of 0.99941. Microseismic analysis revealed temporal and spatial clustering of induced events, correlating strongly with pressure-driven stress changes, with event densities increasing from 0.1–1 to 30–220 events over the simulation period. These findings provide proxies for leakage risk and proactive leakage risk mitigation. Our results confirm that hybrid ANN models effectively predict leakage risks from pressure build-up and related microseismic activity, thereby enhancing the safety and efficiency of CO2sequestration.
