CARBON DIOXIDE SEQUESTRATION AND ENHANCED OIL RECOVERY CO-OPTIMIZATION
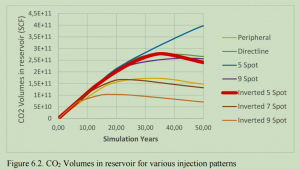
随着全球工业的增长,人为排放导致的大气中温室气体含量持续上升,引发全球温室效应和气候变化。二氧化碳(CO2)作为一种温室气体,其在石油行业中通过提高石油采收率(CO2-EOR)的方式被商业性使用近50年。石油行业的操作旨在最大化回收石油的同时,尽量减少CO2的注入量,以降低成本。为了克服CO2封存在EOR过程中的经济限制,需要采用工程方法同时最大化经济石油回收和石油储层中注入的CO2体积,这一过程被称为协同优化。为此,通过进行不同情景的模拟,以找到可以存储的最大CO2量、可以生产的最石油量,以及同时最大化两者的最佳点。结果表明,使用倒置的5点模式和实施水交替气体(WAG)注入可以显著促进协同优化,而其他参数,如模式区域和注入速率,需要根据具体情况评估,同时考虑经济因素。
CMG软件的应用情况
本研究中,CMG的IMEX软件被用于构建和模拟地质模型,以及进行储层模拟和石油采收率预测。通过CMG的Builder和Results软件,研究者能够模拟不同的注入策略对石油采收率和储层中CO2封存量的影响。这些软件能够处理各种结构复杂的储层、不同网格大小和类型的流体,适用于非常规储层的模拟以及二次和三次采油的恢复。

Abstract
The worldwide growth of industry leads to continuous rise of anthropogenic emission amount into the atmosphere, which causes greenhouse effect all over the world, that is heating up the atmosphere and changing the global climate. On the other hand, carbon dioxide injection into oil reservoirs for the purpose of enhancement of oil recovery (CO2-EOR) has been commercially used for nearly 50 years. The operations in petroleum sector are being carried out in a way to maximize the recovered oil while keeping the amount of CO2 injected at its minimum due to the purchase cost of carbon dioxide. To overcome the economic restrictions for CO2 sequestration during EOR, it is necessary to simultaneously maximize economic oil recovery and the volumes of CO2 injected in oil reservoirs using an engineering approach. This process is named as co-optimization. For this purpose, several simulations for different scenarios are being carried out to find the maximum amount of CO2 that can be stored, maximum amount of oil that can be produced, and an optimal point for simultaneous maximization of both numbers.
Results show, that using inverted 5 spot pattern and implementing water-alternating gas (WAG) injection can significantly contribute to the co-optimization, while other parameters, such as pattern area and injection rate need to be evaluated on case by case basis, considering economical factors as well.
Keywords
Climate Change, CO2, Storage, Sequestration, Enhanced Oil Recovery, Co-Optimization
作者单位
中东技术大学自然与应用科学研究生院,石油与天然气工程系。

