Evaluating reservoir suitability for large-scale hydrogen storage: A preliminary assessment considering reservoir properties
随着清洁能源需求的增长,全球致力于寻找枯竭油气藏中大规模地下储氢(UHS)的理想选址。在注入氢气前对储层进行全面的初步评估,对 UHS 的成功与安全至关重要。近期 UHS 标准常强调经济和化学因素,却忽视了关键的储层物性。
本研究引入了一个全面的储层尺度初步评估框架,专门针对枯竭气藏中的长期储存。评估标准涵盖储层几何形状、岩石物理性质、构造和地层流体等关键要素。
为展示该方法的实际应用,我们评估了 Barnett 页岩气藏的储层参数,评估分三个关键阶段:(1)依据综合筛选标准对储层特性进行系统评估,以确定其对储存的适用性;(2)运用均质和多层气藏模型,探讨储存的可行性和效率,此阶段涉及深入研究注入阶段的储层行为;(3)通过敏感性分析研究不同储层尺寸和注入 / 生产压力的影响,以增强对 UHS 性能的理解。
研究结果显示:(a)尽管存在储层压实和含水层支撑等潜在挑战,该储层仍有望成为储存地点;(b)注入阶段储层压力显著增加,尤其是均质储层;(c)在保持厚度一致的情况下增加储层尺寸,可优化注入 – 开采循环效率。为确保向实施阶段顺利过渡,建议开展进一步的综合研究,包括实验和数值研究,以解决注入性问题并探索储存地点的开发。该评估框架为评估枯竭气藏大规模储氢潜力提供了宝贵工具,有助于推动全球环保能源系统的发展。
CMG 软件应用情况:
本文使用 CMG 软件建立了 3D 储层模型,通过该模型对均质和多层储层进行模拟,分析了储层压力响应、氢气浓度变化、氢气存储效率等,以评估 Barnett 页岩储层对大规模氢气存储的适用性。
研究内容:
- 方法
- 初步评估标准:筛选标准旨在确定枯竭气藏用于大规模储氢的适用性,分为几何形状、岩石物理、构造和储层流体四类,涵盖储层厚度、孔隙度、断层特征、流体性质等参数,为储氢选址提供依据。
- 案例研究
- Barnett 页岩特征:位于德克萨斯州中北部,面积广阔,厚度和深度适宜,储层特性如孔隙度、渗透率等有利于天然气存储,岩石主要由硅质页岩、石灰岩等组成,矿物成分多样,具备一定的储氢潜力。
- 模拟方法
- 均质储层模型:基于 Barnett 页岩储层数据建立,考虑水力压裂,模拟注入和生产压力,分析氢气存储效率和储层压力响应。
- 多层储层模型:考虑地层非均质性,通过不同层的孔隙度和渗透率赋值模拟氢气在多层储层中的相行为,研究其对氢气存储的影响。
- 周期存储模拟方案:模拟氢气存储的四个循环阶段,包括储层衰竭、缓冲气注入、氢气注入和开采,以评估储层在不同阶段的压力响应和氢气存储效率,采用作为缓冲气,并根据注入和生产压力差及时间计算效率。
- 敏感性分析:以均质储层模型为基础,分析储层尺寸和注入 / 生产压力对氢气存储效率的影响,考虑不同储层面积和厚度以及压力变化情况,为优化储氢操作提供参考。
- 结果与讨论
- Barnett 页岩储层预可行性评估:Barnett 页岩储层在几何和岩石物理筛选标准方面符合 UHS 要求,其内部天然裂缝网络增加了气体产量,热历史和高硅含量使其有利于氢气存储,但存在含水层和压实问题,可能影响注入性,需要进一步研究其对氢气存储的适用性。
- 模拟结果分析
- 均质储层模型:氢气注入阶段储层压力显著上升,开采时下降,第二周期后储层中氢气剩余量增加,存储效率提高,表明枯竭气藏可有效存储氢气。
- 多层储层模型:与均质储层类似,注入时压力上升,开采时下降,但达到最大压力约束时间长,生产阶段未达最小压力限制,氢气损失可能性大,存储效率低于均质储层,且两种模型中储层压力增加迅速,可能导致安全问题。
- 敏感性分析:增加储层面积、保持厚度不变可提高循环效率,降低压力差可适度提高效率,高压力差虽能增加氢气浓度但降低效率,表明优化储层参数对提高 UHS 效率至关重要。
作者单位
德克萨斯理工大学鲍勃・L・赫德石油工程系

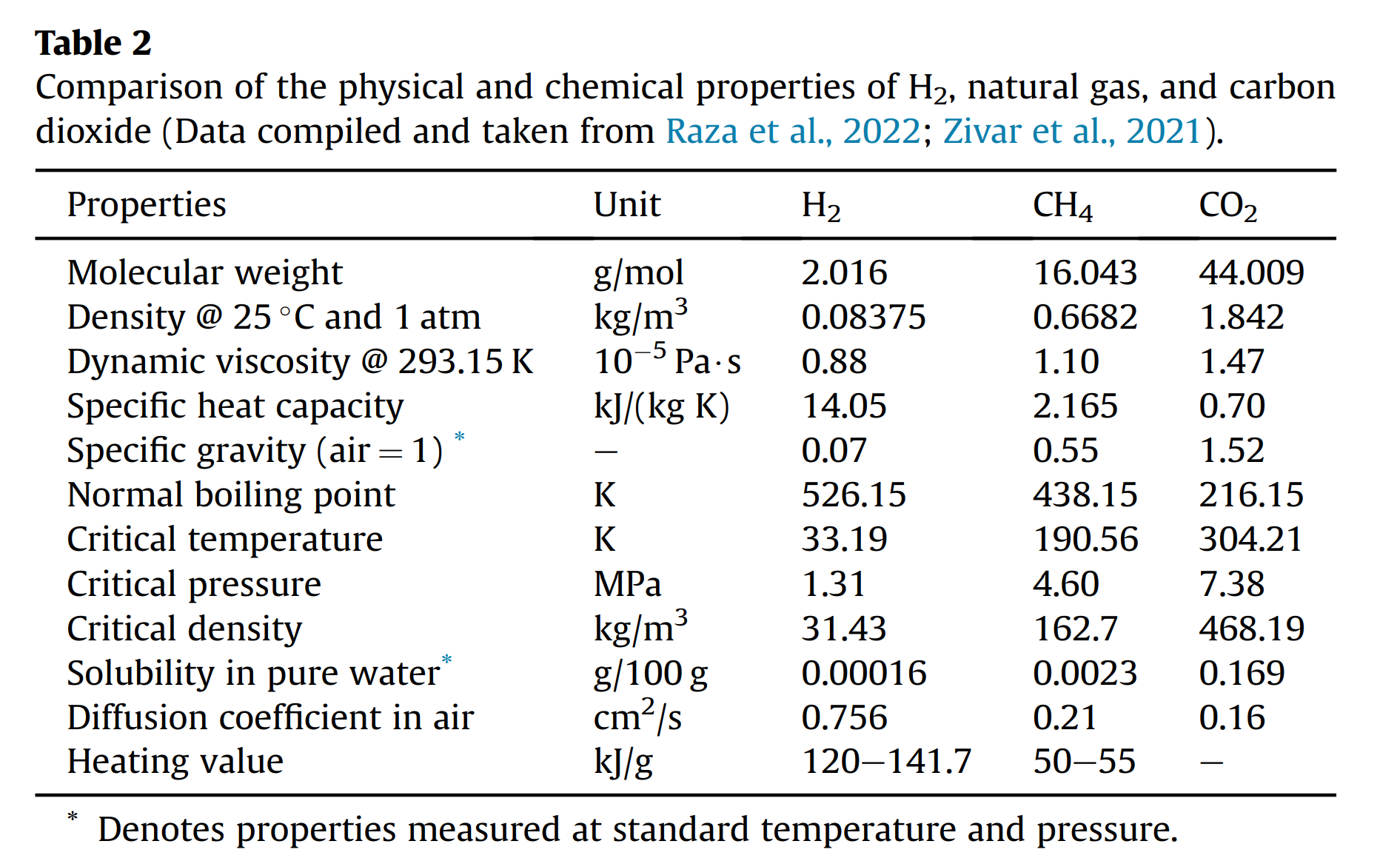
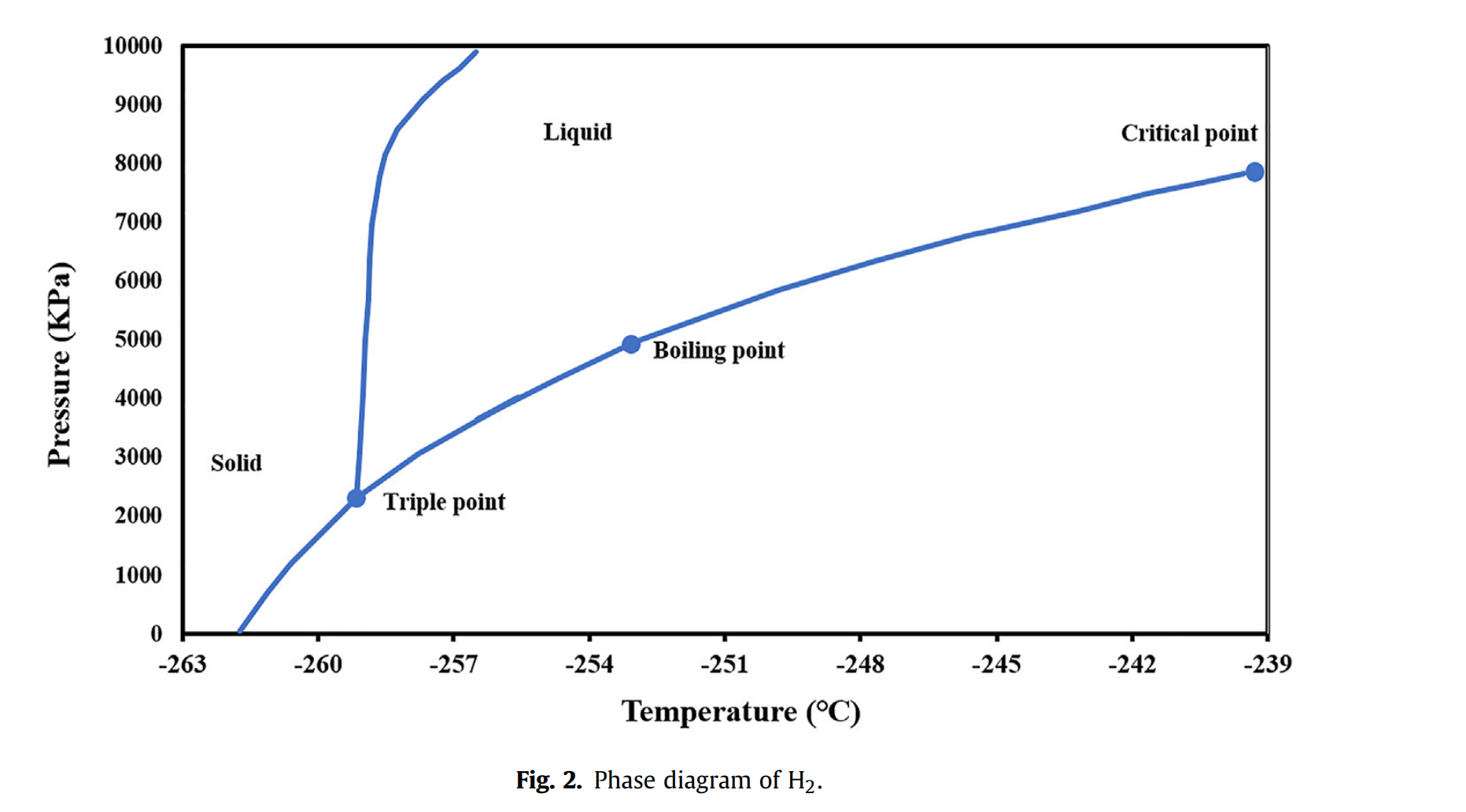
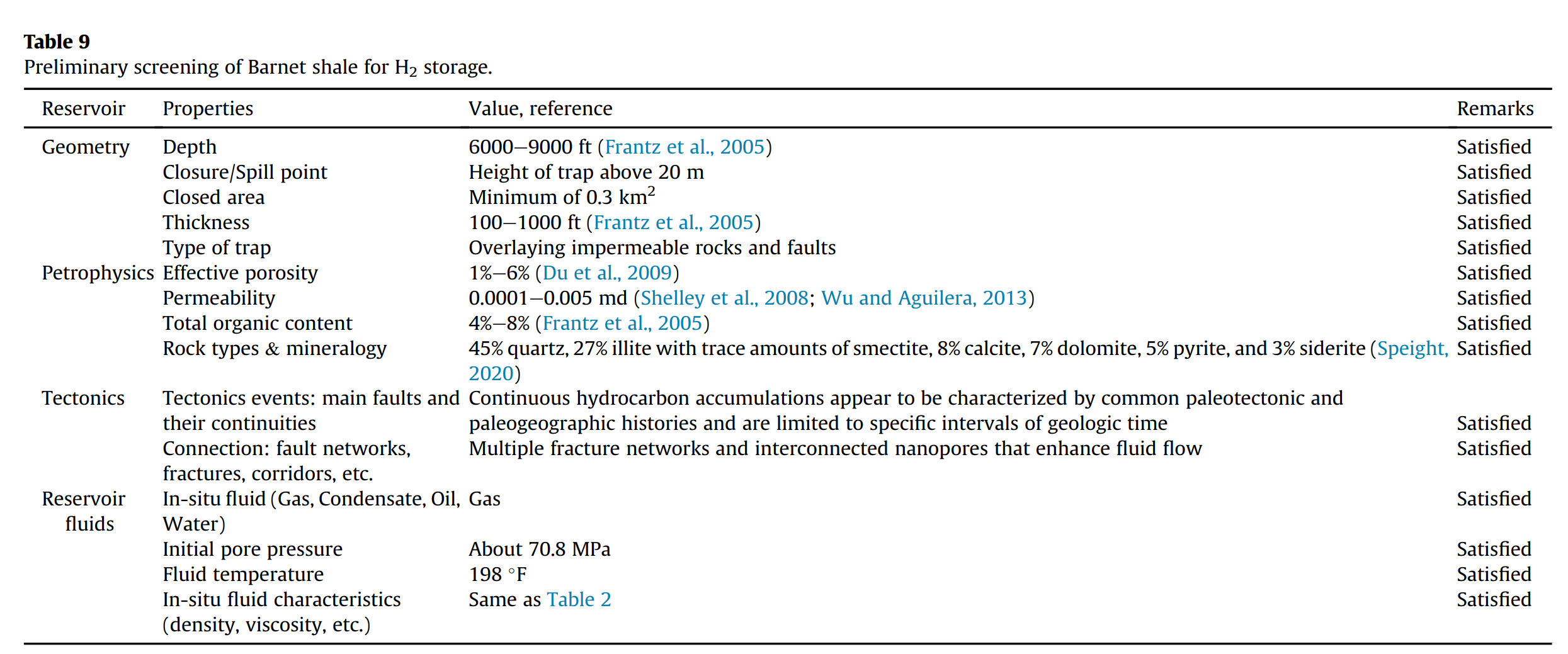
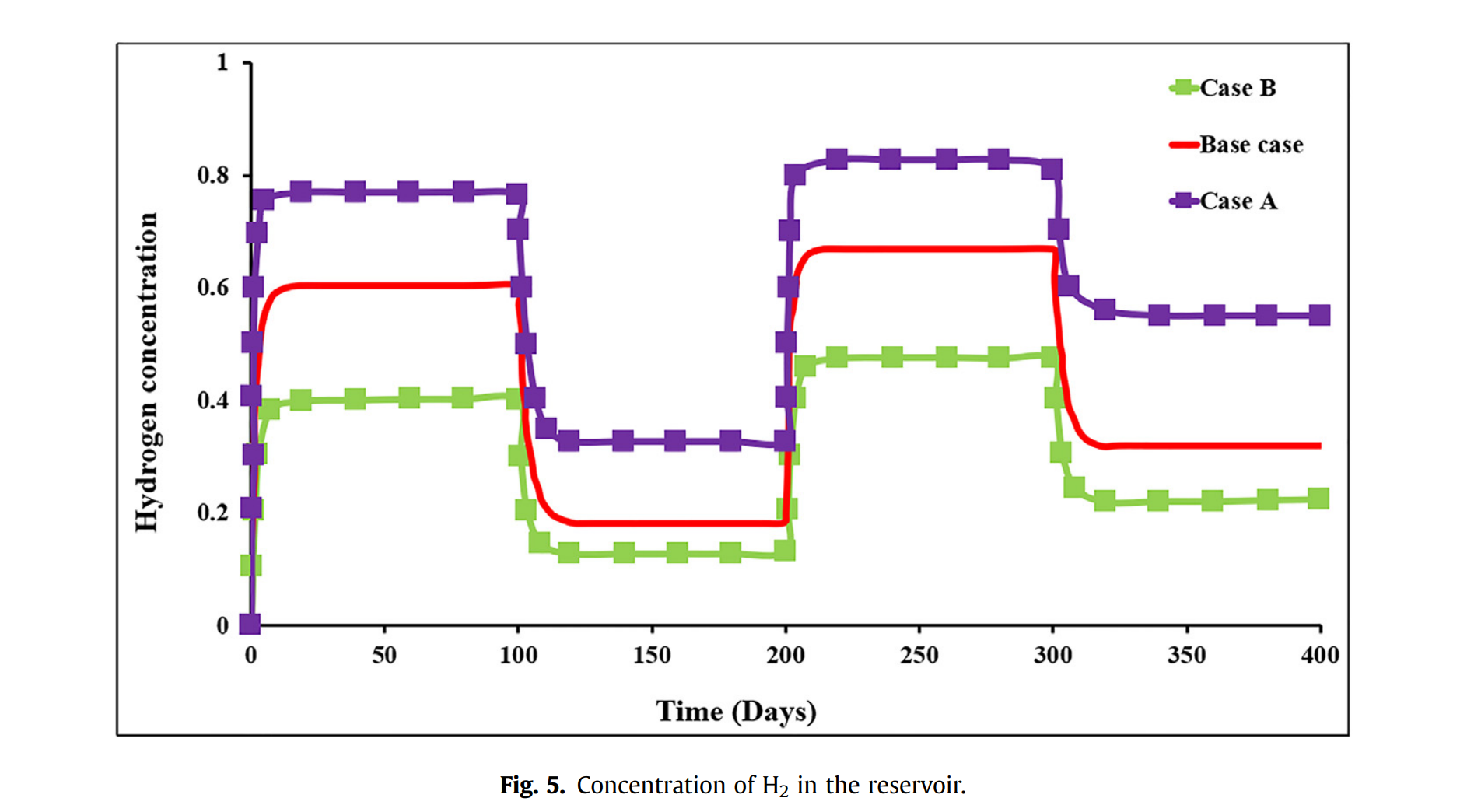
Abstract
With rising demand for clean energy, global focus turns to finding ideal sites for large-scale underground hydrogen storage (UHS) in depleted petroleum reservoirs. A thorough preliminary reservoir evaluation before hydrogen (H2) injection is crucial for UHS success and safety. Recent criteria for UHS often emphasize economics and chemistry, neglecting key reservoir attributes. This study introduces a comprehensive framework for the reservoir-scale preliminary assessment, specifically tailored for long term H2 storage within depleted gas reservoirs. The evaluation criteria encompass critical components, including reservoir geometry, petrophysical properties, tectonics, and formation fluids. To illustrate the practical application of this approach, we assess the Barnett shale play reservoir parameters. The assessment unfolds through three key stages: (1) A systematic evaluation of the reservoir’s properties against our comprehensive screening criteria determines its suitability for H2 storage. (2) Using both homogeneous and multilayered gas reservoir models, we explore the feasibility and efficiency of H2 storage. This phase involves an in-depth examination of reservoir behavior during the injection stage. (3) To enhance understanding of UHS performance, sensitivity analyses investigate the impact of varying reservoir dimensions and injection/production pressures. The findings reveal the following: (a) Despite potential challenges associated with reservoir compaction and aquifer support, the reservoir exhibits substantial promise as an H2 storage site. (b) Notably, a pronounced increase in reservoir pressure manifests during the injection stage, particularly in homogeneous reservoirs. (c) Furthermore, optimizing injection-extraction cycle efficiency can be achieved by augmenting reservoir dimensions while maintaining a consistent thickness. To ensure a smooth transition to implementation, further comprehensive investigations are advised, including experimental and numerical studies to address injectivity concerns and explore storage site development. This evaluation framework is a valuable tool for assessing the potential of depleted gas reservoirs for large-scale hydrogen storage, advancing global eco-friendly energy systems.
