The U.S. Gas Flooding Experience: CO2 Injection Strategies and Impact on Ultimate Recovery
Abstract
The Permian Basin in West Texas and southwestern New Mexico has seen 45 years of oil reserve growth through CO2 enhanced oil recovery (CO2 EOR). More than 60 CO2 EOR projects are currently active in the region’s limestone, sandstone and dolomite reservoirs. Water alternating gas (WAG) has been the development strategy of choice in the Permian for several technical and economic reasons.
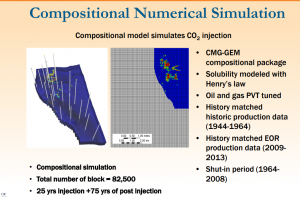
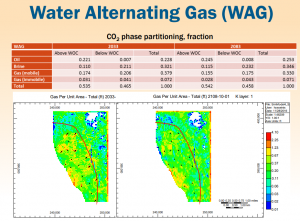
More recently, the technology started to get implemented in the much more porous and permeable clastic depositional systems of the onshore U.S. Gulf Coast. Continued CO2 injection (CGI), as opposed to WAG, was selected as the injection strategy to develop Gulf Coast oil fields, where CO2 injection volumes are significantly larger (up to 6 times larger) than those of the Permian. We conducted a compositional simulation based study with the objective of comparing the CO2 utilization ratios (volume of CO2 injected to produce a barrel of oil) of 4 conventional and novel CO2 injection strategies: (1) continuous gas injection (CGI), (2) water alternating gas (WAG), (3) water curtain injection (WCI), and (4) WAG and WCI combination.
These injection scenarios were simulated using the GEM module from the Computer Modeling Group (CMG). GEM is an advanced general equation-of-state compositional simulator, which includes equation of state, CO2 miscible flood, CO2/brine interactions, and complex phase behavior. The simulator is set up to model three fluid phases including water, oil, and gas. Our study demonstrates how the selected field development strategy has a significant impact on the ultimate recovery of CO2-EOR projects, with GCI injection providing maximum oil recovery in absolute volume terms, but with WAG offering a more balanced technical-economical approach

二氧化碳注入策略及其对最终采收率的影响:美国二叠纪盆地气驱经验
摘要
德克萨斯州西部和新墨西哥州西南部的二叠纪盆地通过CO2强化采油(CO2 EOR)实现了45年的石油储量增长。目前,该地区的石灰岩、砂岩和白云石储层中有60多个二氧化碳提高采收率项目。出于技术和经济原因,水交替气(WAG)一直是二叠纪首选的开发策略。
最近,这项技术开始在美国和沿海岸的陆上的多孔性和渗透性更强的碎屑沉积油藏中得到应用。与WAG相反,持续CO2注入(CGI)被选为开发墨西哥湾沿岸油田的注入策略,在墨西哥湾沿岸油田,CO2注入量明显大于二叠纪油田(高达6倍)。我们进行了一项基于组分模拟的研究,目的是比较4种常规和新型CO2注入策略的CO2换油率(生产一桶油所注入的CO2体积):(1)连续气体注入(CGI),(2)水交替气体注入(WAG),(3)水垫注入(WCI),(4)WAG和WCI组合。
使用计算机模拟软件集团(CMG)的GEM模块模拟了这些注入场景。GEM是一种先进的通用状态方程组分模拟器,包括状态方程、CO2混相驱、CO2/盐水相互作用和复杂的相行为。该模拟器用于模拟三个流体相,包括水、油和气。我们的研究表明,选定的油田开发策略如何对CO2-EOR项目的最终采收率产生重大影响,GCI注入得到最大的采油量,但WAG方案的经济评价最好。
