Evaluation of Miscible Gas Injection Strategies for Enhanced Oil Recovery in High-Salinity Reservoirs
本研究针对高矿化度油藏中混相注气(MGI)提高采收率(EOR)的策略进行了系统评估,重点以美国密西西比州Smith县的Raleigh油田为研究对象。研究采用CMG WinProp软件建立并校准状态方程(EOS)模型,模拟了8种不同注气方案(包括纯CO₂、富气、LPG、N₂、CH₄及其混合物)下的相态、混相能力和膨胀因子。结果表明,CO₂和富集分离气在技术和经济上均为最优选择,其中CO₂具有更低的混相压力和更高的原油膨胀能力。研究强调了CO₂-EOR在压力衰竭型高盐度油藏中的可持续性和有效性。
CMG软件应用情况:
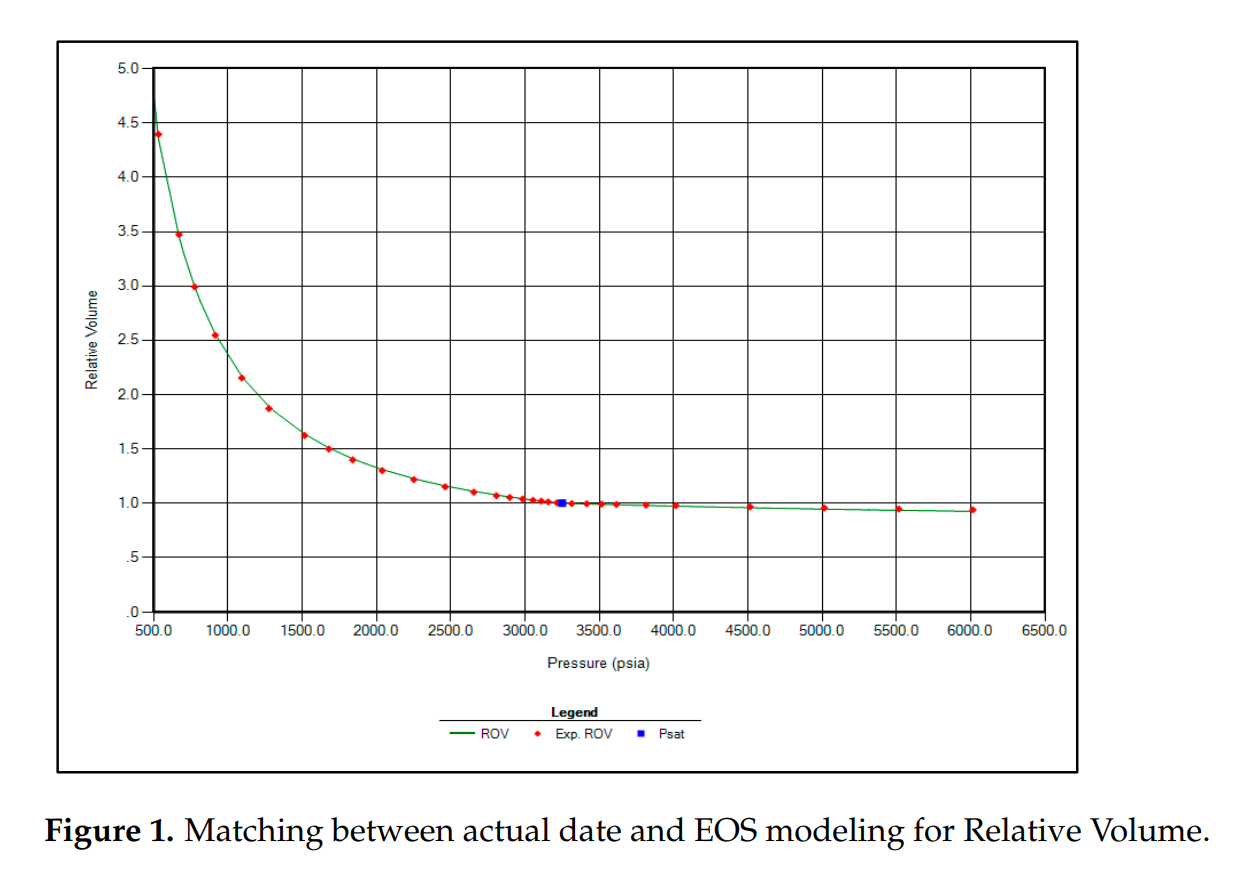
本研究使用CMG WinProp软件进行PVT建模与状态方程(EOS)校准,模拟不同气体注入条件下的相态行为和混相特性。通过回归分析调整关键参数(如临界压力、温度、偏心因子等),使模型预测结果与实验数据高度吻合。随后利用该模型计算了不同注入气体的最小混相压力(MMP)和膨胀因子,为优选注气方案提供依据。
结论:
- 在8种注气方案中,CO₂和富集分离气被确定为Raleigh油田最具可行性的EOR方案。
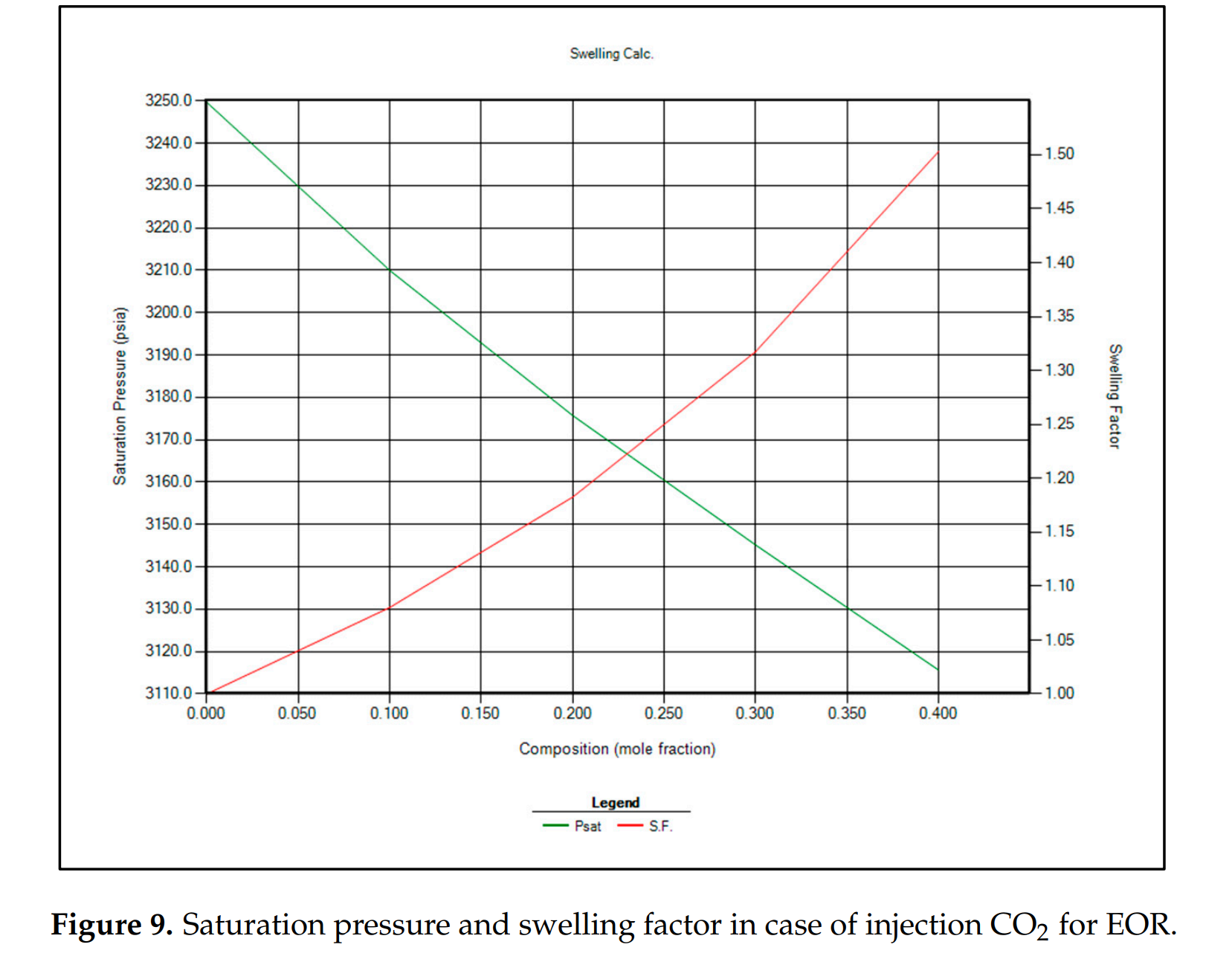
- CO₂的最小混相压力为3250 psi,膨胀因子约为31%,优于其他气体。
- 鉴于油藏压力已从初始的5783 psi快速下降至3500 psi以下,CO₂注入被认为是维持油藏压力、提高采收率的最佳策略。
- 建议在油藏压力降至饱和压力(3250 psi)时启动CO₂-EOR作业,以实现最佳技术效果和经济效益。
- CO₂-EOR不仅具有技术优势,还具备碳封存的环境效益,符合可持续发展目标。
作者单位:
美国新墨西哥矿业与技术学院 石油工程系
Abstract
This study presents a comprehensive evaluation of miscible gas injection (MGI) strategies for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) in high-salinity reservoirs, with a focus on the Raleigh Oil Field. Using a calibrated Equation of State (EOS) model in CMG WinProp™, eight gas injection scenarios were simulated to assess phase behavior, miscibility, and swelling factors. The results indicate that carbon dioxide (CO2) and enriched separator gas offer the most technically and economically viable options, with CO2 demonstrating superior swelling performance and lower miscibility pressure requirements. The findings underscore the potential of CO2-EOR as a sustainable and effective recovery method in pressure-depleted, high-salinity environments.
