ROLE OF CO2 INJECTION ON ENHANCE METHANE ECOVERY – A CASE STUDY FROM TURKISH COAL SEAM, AMASRA COAL FIELD TURKEY
提高煤层气采收率(ECBM)是许多高级科研人员的研究领域。为提高煤层气藏的甲烷气产量,已采用并实施了各种开采技术。一种方法是向煤层中注入CO2,最大限度地将吸附的甲烷从煤基质表面置换出来,并提高甲烷采收率。使用CMG-GEM软件建立了土耳其Amasra煤田Turkish煤层数值模型,模拟煤层气一次开采及注入CO2提高采收率。储层中驱动CO2注入的关键岩石物理参数是割理渗透率、割理孔隙度、甲烷吸附时间、甲烷Langmuir等温线和CO2 Langmuil等温线。Palmer-Mansoori参数(孔隙度、压缩系数和煤层压力)也用于模拟压实和膨胀过程。
建立了3个方案来评估CO2注入对甲烷开采的影响。方案1为没有CO2注入的基本方案;方案2为煤层中的注入CO2的方案;方案3为分析不同注入时间的影响,研究最终甲烷采收率的方案。除此之外,还评估了割理孔隙度、割理渗透率和煤密度等不同参数的影响。结果表明,在一次开采中采出的甲烷量为28.2 Bscf,而在方案2中通过CO2注入采出的甲烷气量为45.4 Bscf。因此,初步模拟研究表明,ECBM采出的煤层气高于常规一次开采过程。
ABSTRACT
The study of Enhanced Coalbed Methane Recovery (ECBM) has become the interest of many researchers in many tertiary research institutes. Various recovery techniques have been identified and implemented to increase the production of methane gas from coal bed reservoirs. One of the methods is CO2 injection into coal seams where it helps to maximize the displacement of the adsorbed methane from the surface of coal matrix and enhance the methane recovery. A numerical model from Turkish Coal Seam Bed from Amasra Coal Field, Turkey was developed using CMG-GEM software by Computer Modelling Group to simulate the primary methane production and enhance recovery using CO2 injection. The key petrophysical reservoir parameters to drive the CO2 injection in coal bed methane reservoir are cleat permeability, cleat porosity, methane adsorption time, methane Langmuir isotherm and CO2 Langmuir isotherm. Palmer and Mansoori parameters (porosity, compressibility and coal seam pressure) were also applied to model the compaction and dilation process as well.
Three (3) cases were constructed to evaluate the impact of CO2 injection on methane recovery. Case 1 acts as the base case where there is no CO2 injection and is used in the first model while Case 2 includes the CO2 injection in the coal beds. On the other hand, Case 3 was constructed to analyse the impact of different injection timing to investigate the final methane recovery. Other than that, the effect of varying parameters such as cleat porosity, cleat permeability and coal density were also assessed. The results show that the amount of methane recovered in the primary production is 28.2 Bscf while 45.4 Bscf of methane gas was recovered by CO2 injection in Case 2. Therefore, it is found that the total recovery of methane from coal seams during enhanced production is more than that of primary recovery during the preliminary simulation model.
Keywords: coal bed methane, carbon dioxide, CO2 injection, CMG, sorption.

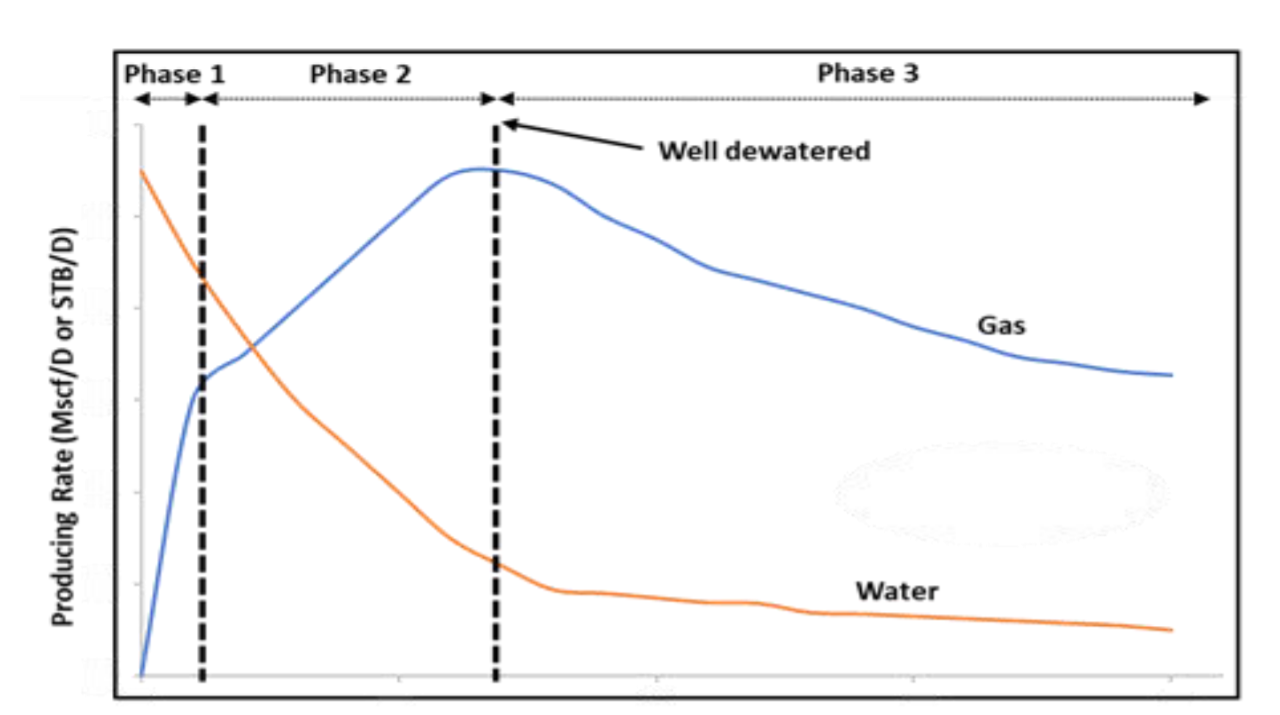
Figure-4. Gas and Water Rates for a typical Coalbed Methane Production Profile (Zuber, 1996).