Large-scale underground hydrogen storage: Integrated modeling of reservoir-wellbore system
地下储氢(UHS)近年来受到了广泛关注,因为氢似乎非常适合用于调节季节性能源缺口。我们为北海的“维京A”枯竭气田提出了一个集成的储气库-井模型,作为潜在的UHS场地。
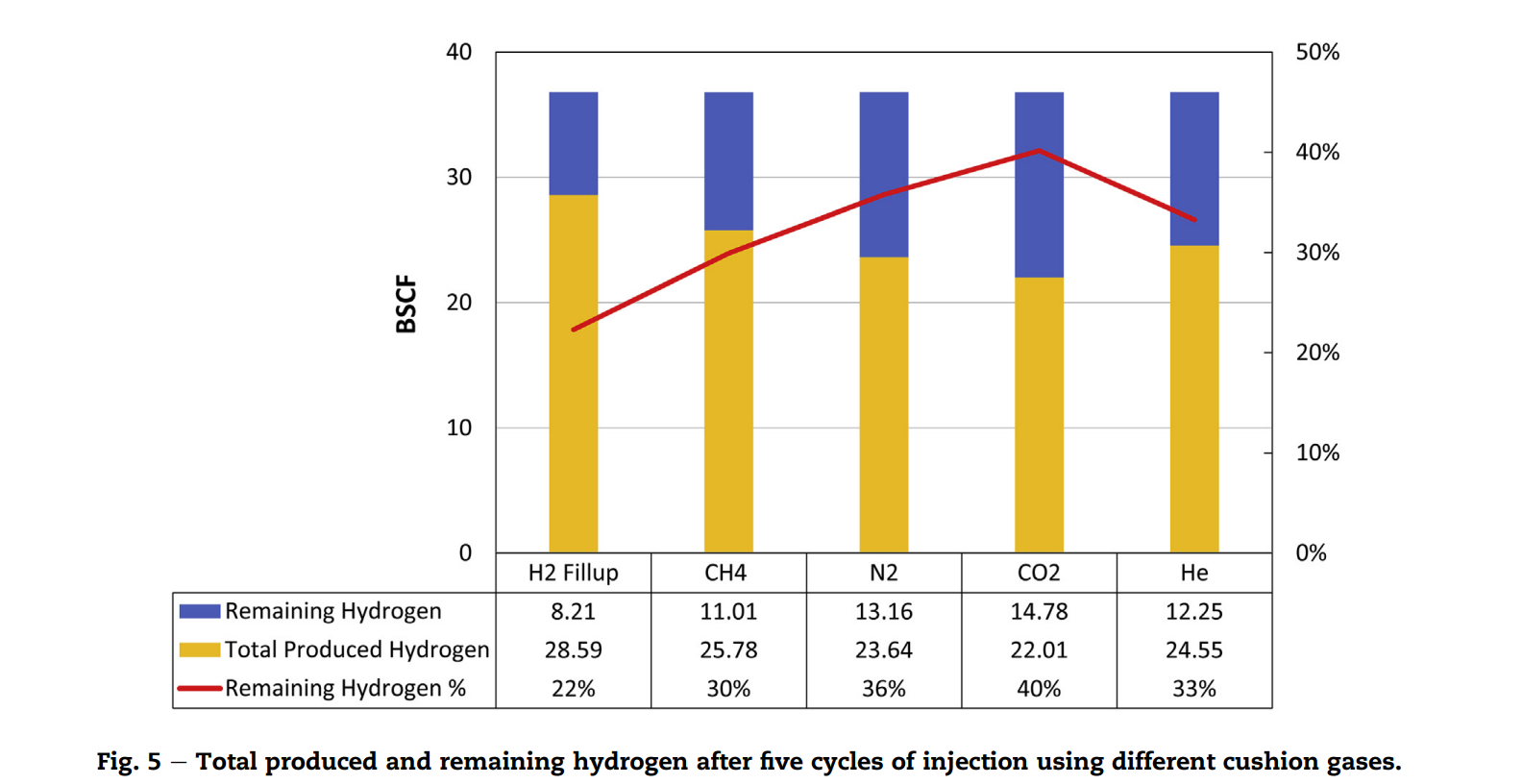
研究结果表明,利用一体化模型可以得出更合理的预测,因为气体组分随时间而变化。敏感性分析表明,垫层气体越轻,可以获得的产量就越多。然而,所产生的氢纯度会在一定程度上受到影响,可以通过增加灌注期和注入速率来改善。研究结果还显示,尽管氢扩散到储层中并与天然流体(主要是甲烷)混合,但氢扩散的影响微乎其微。所有这些因素都将可能影响该项目的经济效益。
Highlights
•Integrated modeling will enhance the predictions.
•The type of cushion gas is crucial for production targets.
•Hydrogen diffusion has a minor impact on a field scale seasonal storage.
•The injection-production strategy will influence production efficiency.
Abstract
Underground Hydrogen Storage (UHS) has received significant attention over the past few years as hydrogen seems well-suited for adjusting seasonal energy gaps.
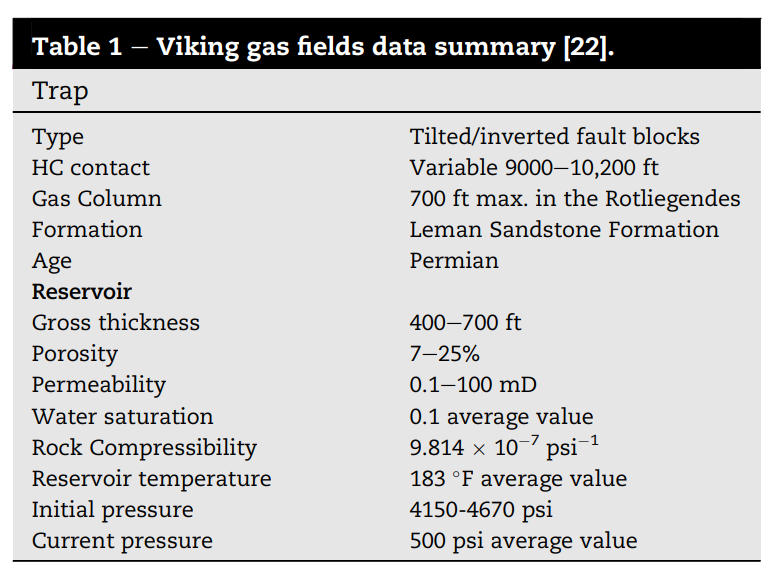
We present an integrated reservoir-well model for “Viking A″ the depleted gas field in the North Sea, as a potential site for UHS. Our findings show that utilizing the integrated model results in more reasonable predictions as the gas composition changes over time. Sensitivity analyses show that the lighter the cushion gas, the more production can be obtained. However, the purity of the produced hydrogen will be affected to some extent, which can be enhanced by increasing the fill-up period and the injection rate. The results also show that even though hydrogen diffuses into the reservoir and mixes up with the native fluids (mainly methane), the impact of hydrogen diffusion is marginal. All these factors will potentially influence the project’s economics.
Keywords
Underground hydrogen storage Depleted gas reservoir Integrated modeling Cushion gas Hydrogen diffusion Injection-production strategy