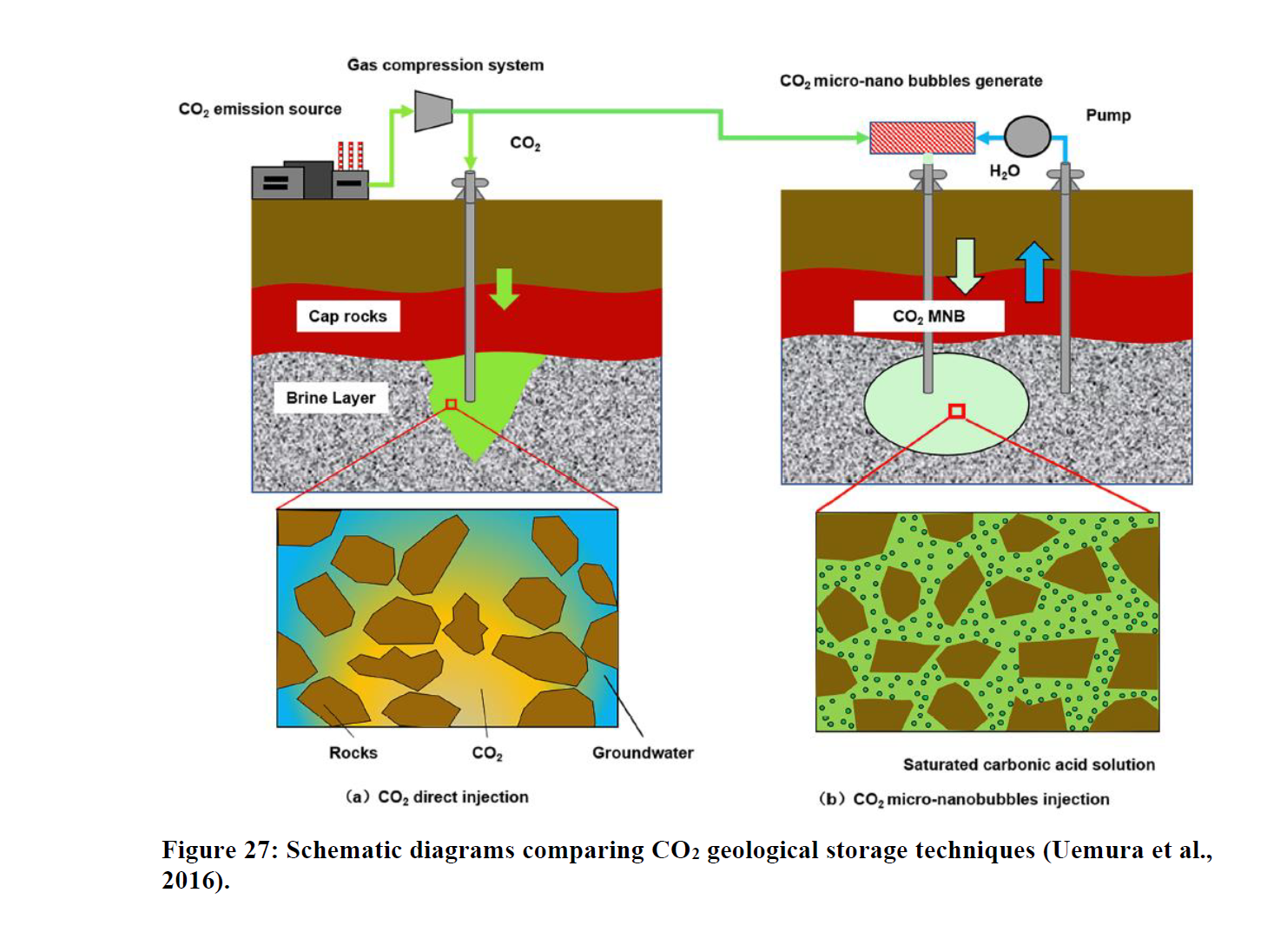
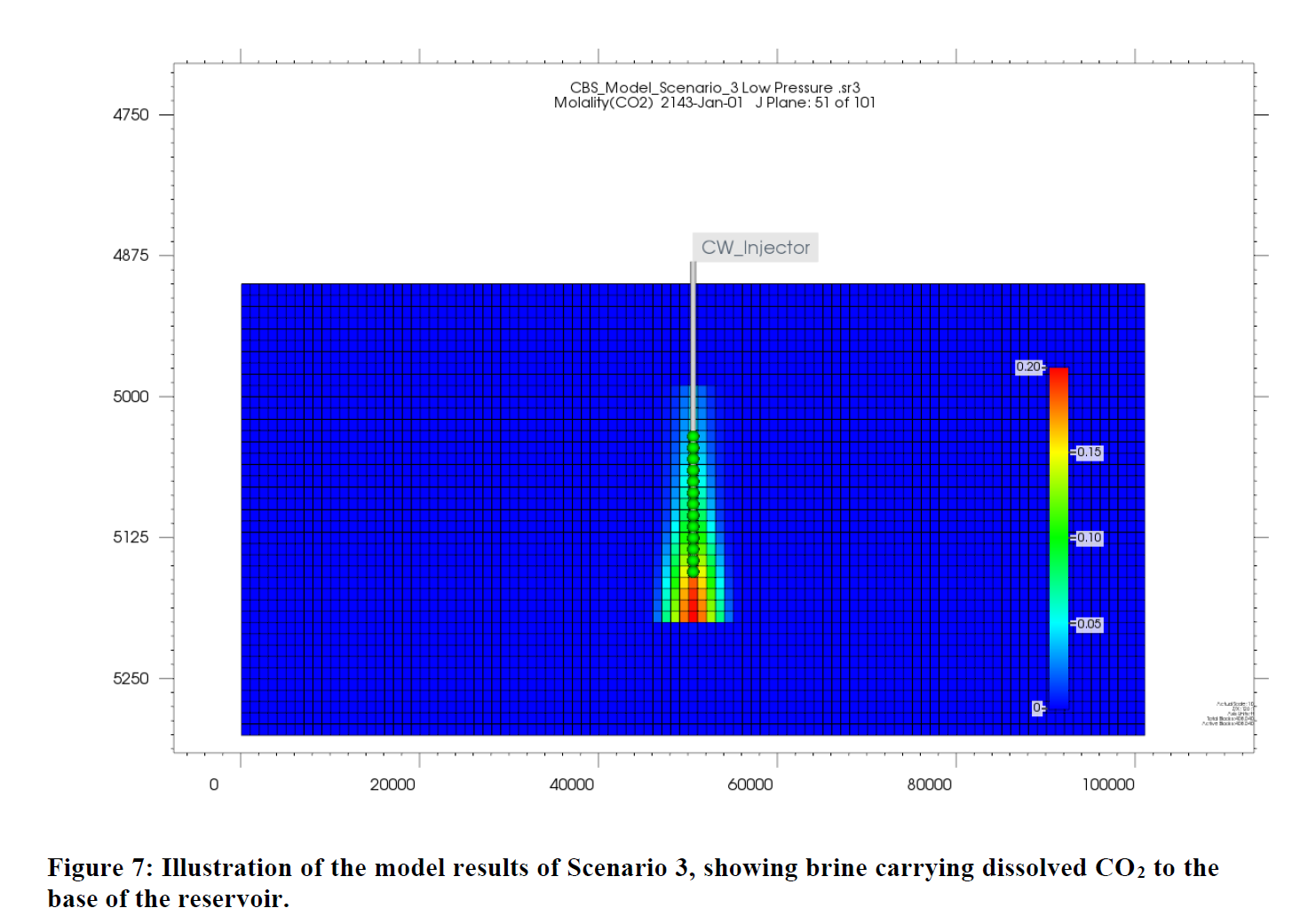
Assessment of Carbonated Brine Injection as Low-risk Strategy for Geologic Carbon Storage
CMG(Computer Modeling Group)软件在地质碳储存领域的应用主要集中在模拟和评估碳酸盐水注入(CBI)作为一种低风险的地质碳储存策略。以下是对CMG软件应用的一个总结:
1. 研究背景与目标
文件中提到的研究主要关注于评估碳酸盐水注入(CBI)作为地质碳储存的可行性和风险。CBI策略涉及将二氧化碳(CO2)预先溶解到将要注入的盐水中,以减少或消除地下储存过程中的泄漏风险。研究的主要目标是评估结合盐水和CO2储存在盐水处置井中的技术经济可行性和相关风险。
2. CMG软件的应用
- 模型建立:使用CMG软件的Builder组件来创建油藏模型,包括网格创建、网格属性定义、生产数据整合、流体属性、岩石-流体相互作用、流体模型和初始条件的设定。
- 注入模拟:通过CMG的GEM组件进行注入模拟,模拟了不同的CO2浓度、温度和压力条件下的CO2溶解度和相行为。
- 结果分析:利用CMG软件的结果图组件来展示和分析模拟结果,包括压力变化、CO2溶解度、井筒腐蚀预测等。
3. 模拟结果
- CO2溶解度:模拟结果表明,在较低的CO2摩尔浓度下,可以成功地将CO2溶解到盐水中,而不会对油藏产生显著的压力变化或流动性影响。
- 井筒腐蚀:研究了注入含CO2的盐水对井筒材料的腐蚀影响,发现在适当的CO2浓度下,腐蚀率可以接受,并且可以通过增加CO2浓度来降低井筒腐蚀的风险。
- 长期储存安全性:通过反应传输模型,研究了注入期间和关闭期间的岩石-流体相互作用,发现溶解的CO2在长期储存中是安全的,并且可以通过矿物沉淀进一步稳定。
4. 技术与经济可行性
文件中还讨论了CBI技术的潜在经济效益,包括通过美国国内税收法案45Q条款获得的税收抵免,以及利用现有的盐水处置基础设施来减少资本投入和风险。
5. 监管考虑
研究还提出了CBI技术的监管考虑,包括盐水地上储存的规定和在Class II注入井下获得批准的路径。
6. 结论
CMG软件在模拟CBI过程中发挥了关键作用,证明了CBI是一种低风险的地质碳储存策略。通过精确模拟CO2的溶解和储存过程,CMG软件帮助研究人员评估了CBI技术的可行性,为未来的地质碳储存项目提供了宝贵的数据和见解。
Abstract
The main objective of this early-phase research was to evaluate the techno-economic feasibility and risk associated with combined brine and CO2 storage in SWD wells using brine dissolution in the North Dakota portion of the Williston Basin. Three simulation studies were conducted to investigate: (1) CO2 phases at different conditions, (2) wellbore compatibility, and (3) long-term storage fate in reservoir. (1) A simple reservoir model and injection simulations were created using data to represent the BEST (brine extraction and storage test) site, an operational SWD facility located near Watford City, North Dakota. The pressure evolution caused by CO2 comingled in produced water injectate in a layer cake reservoir was then modeled while tracking aqueous CO2 throughout the project. The salinity of the injection water, the salinity of the reservoir brine, and the amount of dissolved CO2 comingled in the injection water were varied. (2) A wellbore corrosion model was performed using the CO2 concentrations selected based on the reservoir modeling to examine the carbonated produced water impact on wellbore. (3) Reactive transport modeling was conducted with the optimal CO2 concentration for this injection site to study the rock-fluid interactions and CO2 fate in the reservoir. Results suggest that CO2 dissolved in produced water can be injected without appreciably increasing subsurface pressure or leakage risks. Pressure buildup was found to vary with salinity but not with CO2 mass fraction. Simulation results show that lower CO2 percent mass fraction leads to a higher amount of CO2 that can be dissolved at a higher injection salinity. Furthermore, the long-term goal of dissolution trapping in a traditional carbon storage project is accomplished from the start, mitigating risks associated with potential migration of buoyant CO2, so long as the reservoir pressure and temperature are used to determine the maximum mass fraction of the dissolved CO2.
摘要:早期阶段研究目标在于评估在北达科他州威利斯顿盆地的北部区域使用卤水溶解结合二氧化碳存储技术的经济可行性和风险。进行了三项模拟研究:(1)不同条件下的CO2相,(2)井眼兼容性,以及(3)储层中的长期存储命运。首先,通过创建简单的储层模型和注入模拟,模拟了位于北达科他州沃特福德城附近的卤水注入和存储测试站点的情况,探讨了CO2对产水压力的影响及CO2的水溶性。其次,进行了井眼腐蚀模型,研究了不同CO2浓度对井眼的影响。最后,利用最佳CO2浓度进行了反应传输模拟,研究了岩石-流体相互作用和CO2在储层中的命运。研究结果表明,CO2溶解在产水中能够进行注入,不会显著增加地下压力或泄漏风险。压力增加与盐度变化相关,而与CO2质量分数无关。较低的CO2质量分数在高盐度下会导致更多CO2溶解。此外,通过实施溶解捕集来减轻与浮力CO2迁移相关的风险,只要确定最大溶解CO2质量分数即可。