CO2 Injection to Mitigate Reservoir Damage in Edge/Bottom-Water Condensate Gas Reservoirs
凝析气藏因同时富含天然气和高价值凝析油而备受关注,但在开发过程中面临“反凝析+水侵”双重伤害,导致采收率普遍低于30%。本文以新疆油田P区块边/底水凝析气藏为对象,通过长岩心驱替实验+CMG-GEM/WinProp数值模拟,系统评价CO₂驱替对解除反凝析液锁、抑制底水锥进及实现地质封存的多重效益。
CMG软件应用情况
- WinProp™:完成PVT拟合,建立7组分伪组分模型,精确再现露点38.93 MPa、反凝析液量及最小混相压力21.5 MPa。
- CMG-GEM™2022:
– 构建长岩心一维组分模型,历史拟合采收率、压力梯度、突破时间,R²>0.93;
– 建立31×31×20 三维全油田机理模型,模拟不同渗透率、韵律性、注采压力/速率对采收率与含水的影响;
– 通过RSM-ANOVA 多目标优化,输出“地质-工程”耦合参数窗口,并生成可视化3D优化图版。
主要结论
- 边/底水凝析气藏应先衰竭至13.5 MPa 临界压力,再实施CO₂混相驱,可最大限度发挥“膨胀-降黏-蒸发”协同效应。
- 复合韵律储层(高-低-高渗透交替)最有利于CO₂横向扩展与垂向封隔,采收率比正/反韵律分别高6.3 和8.5 个百分点。
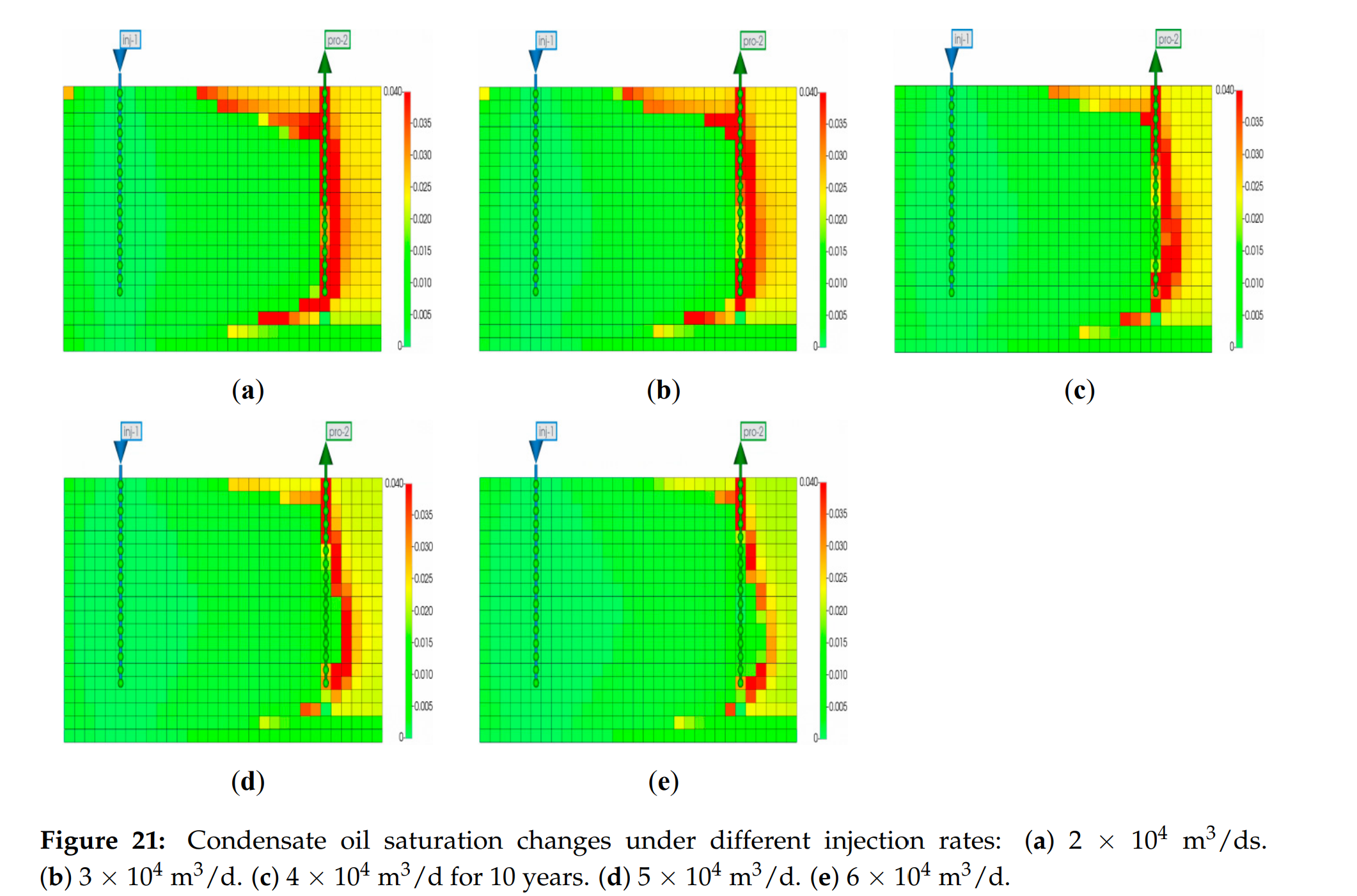
- 最优工程参数:注入压力22.5 MPa(略高于MMP)、注入速率5×10⁴ m³/d,可在10 年内实现60.9% 凝析油采收率,并将含水上升速率降低34%。
- 提出的“四维耦合”优化框架(渗透率-韵律-压力-速率)可直接推广至其他边/底水凝析气藏的CO₂-EGR/CCUS 方案设计。
作者单位
- 西南石油大学
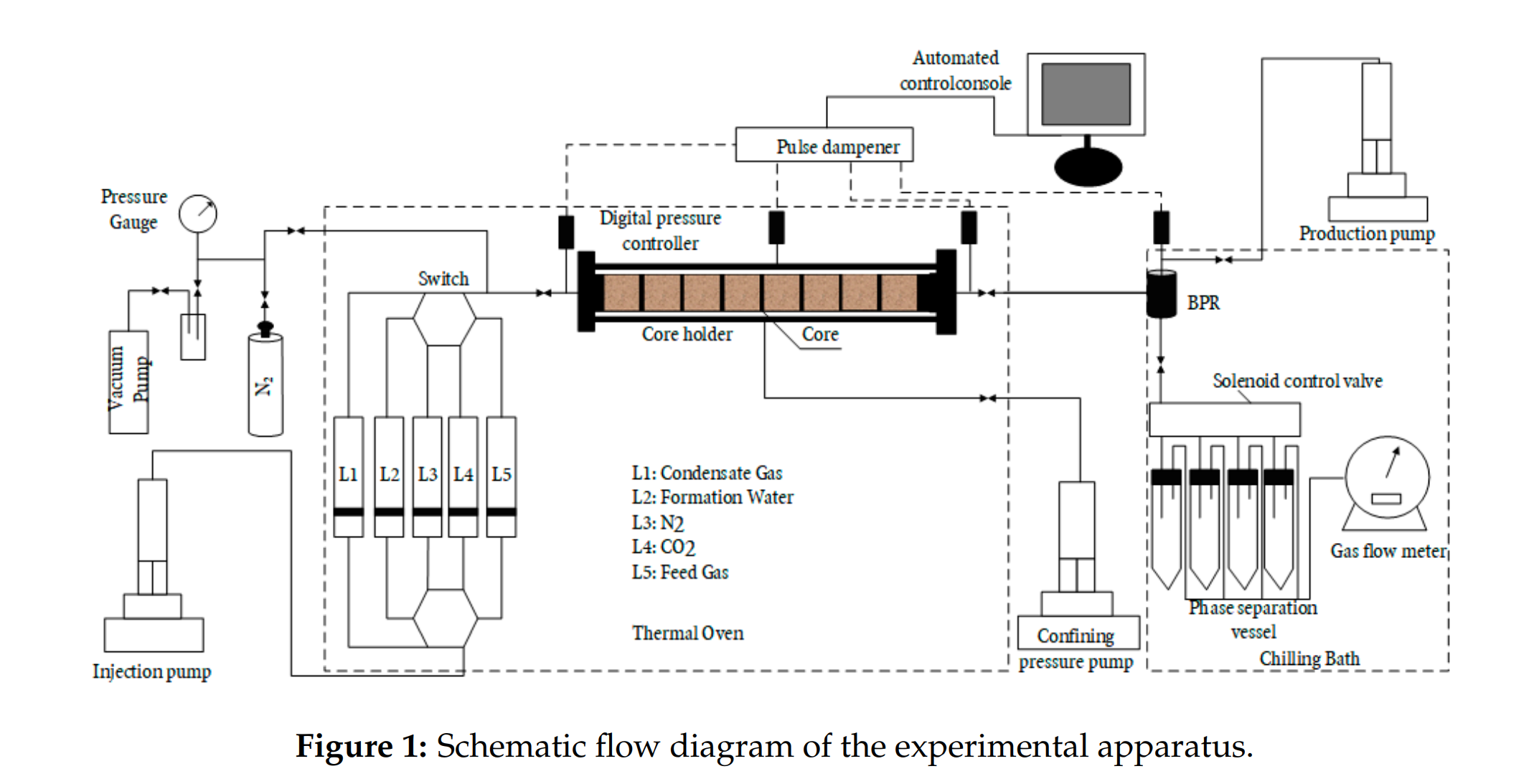
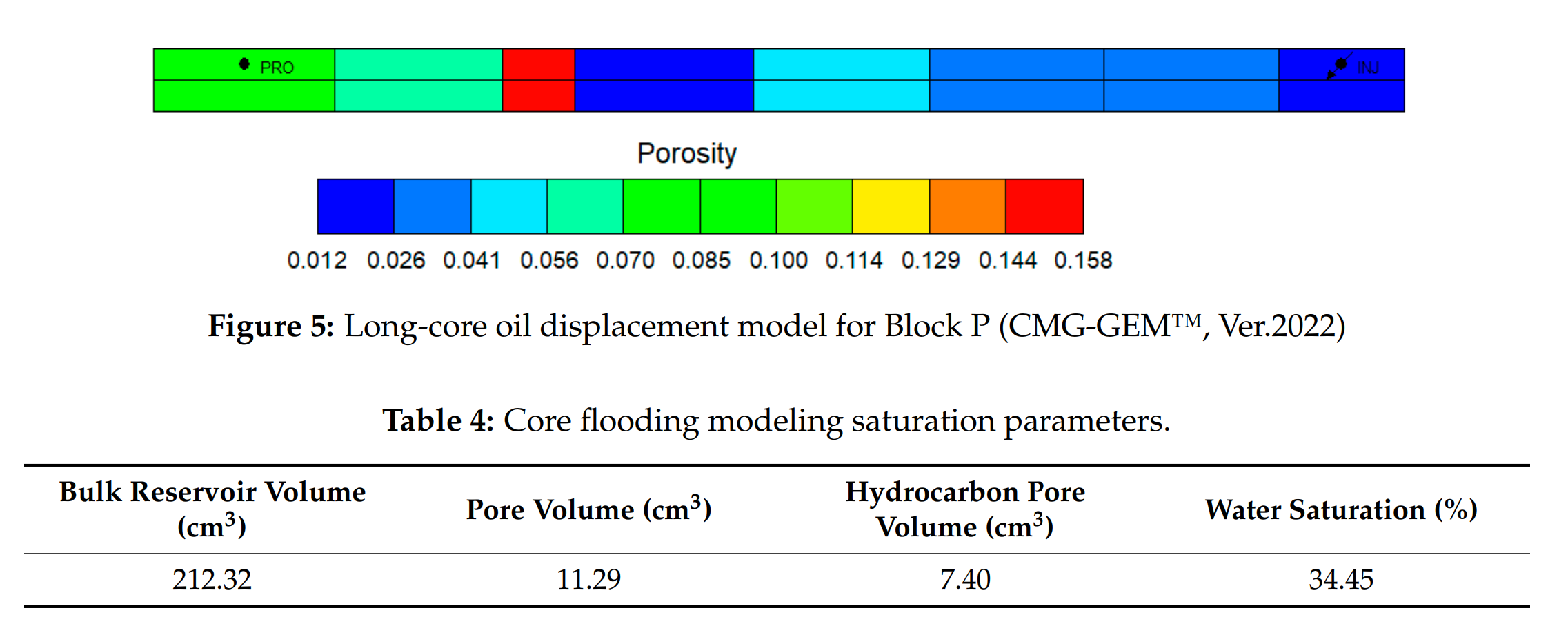
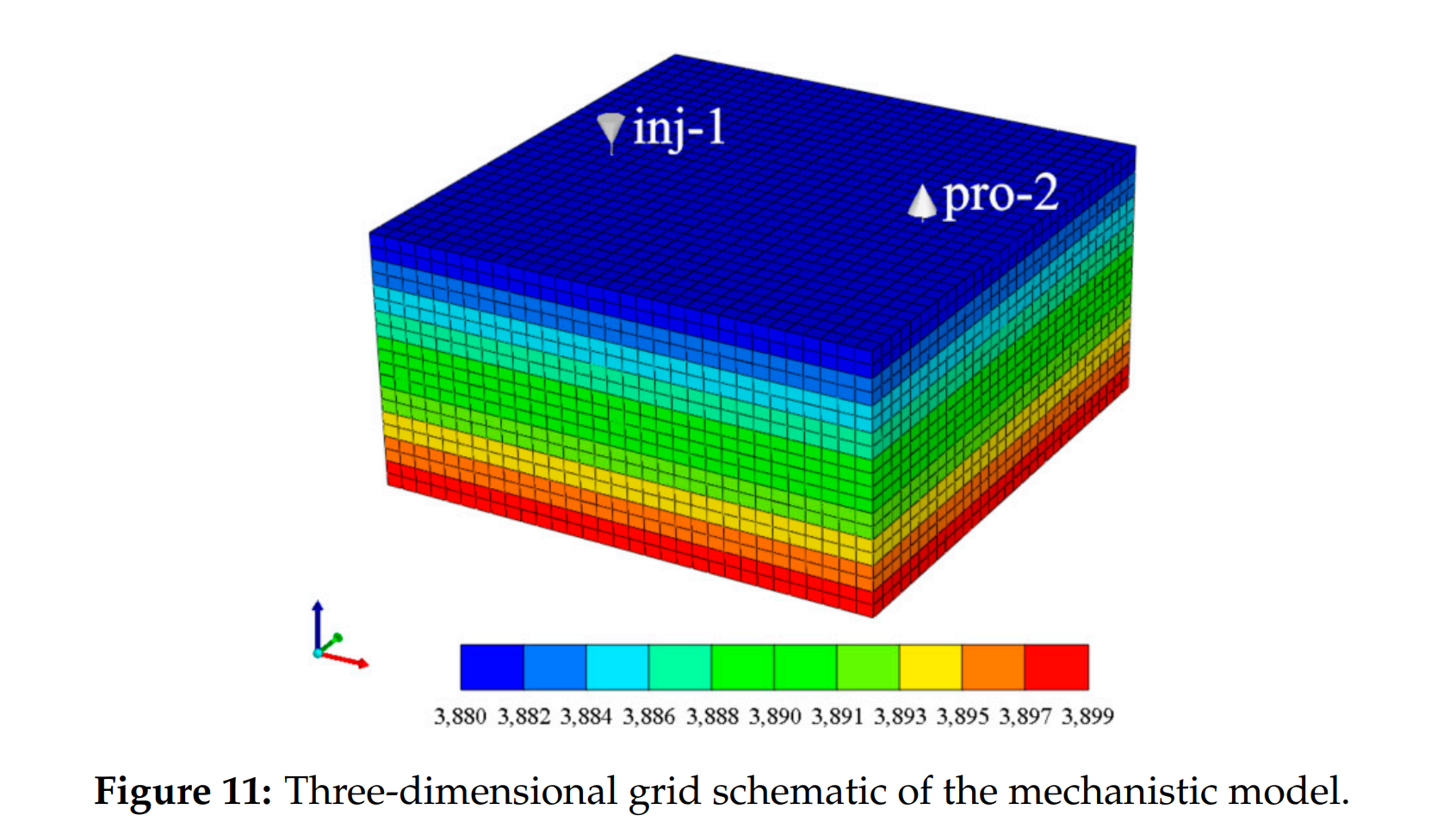
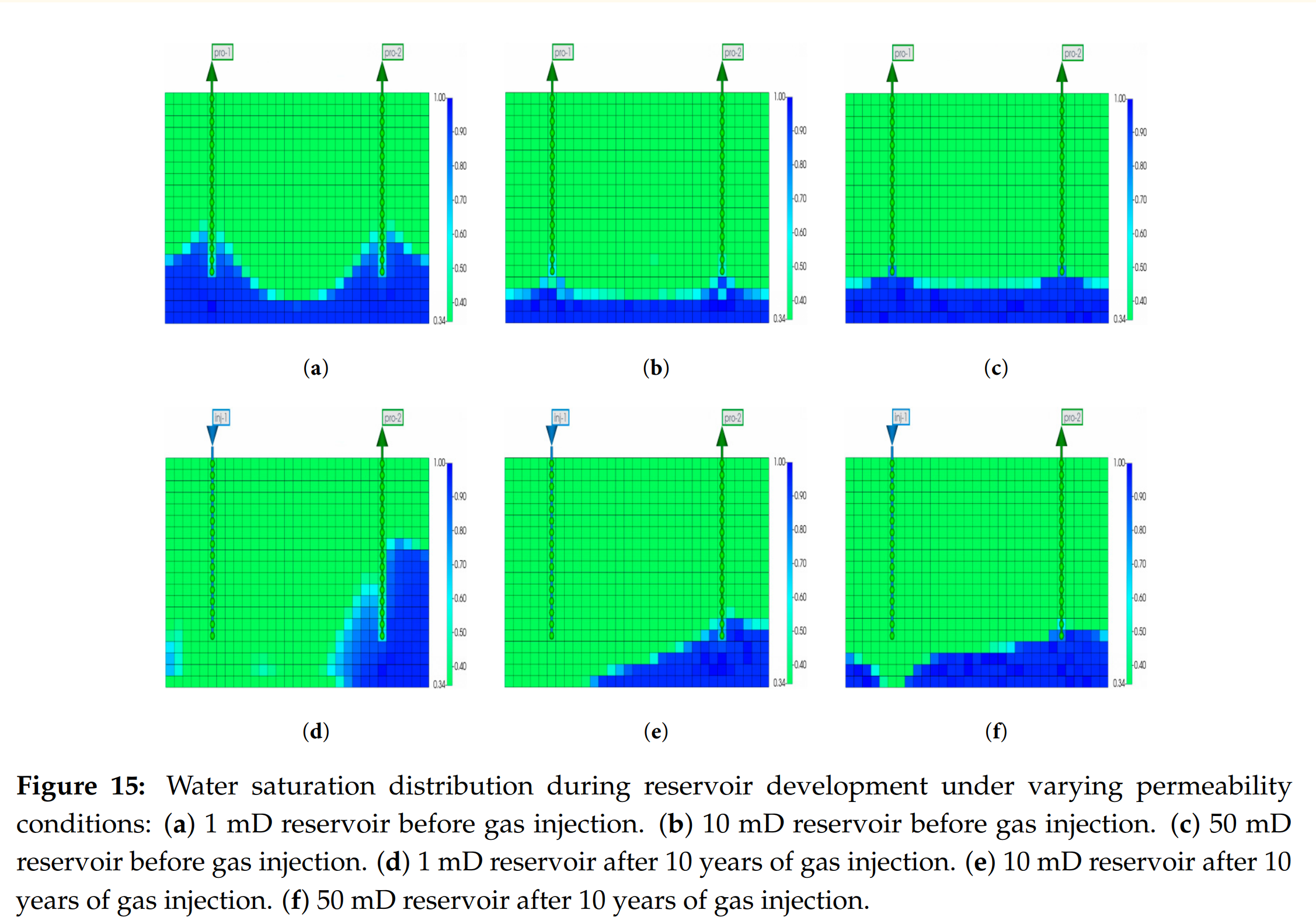
Abstract
Condensate gas reservoirs have attracted increasing attention in recent years due to their significant development potential and dual value from both natural gas and condensate oil. However, their exploitation is often hindered by the dual challenges of retrograde condensation and water invasion, which can markedly reduce recovery factors. CO2 injection offers a promising solution by alleviating condensate blockage, suppressing water influx, and simultaneously enabling geological CO2 storage. Accordingly, research on optimizing CO2 injection to mitigate formation damage is critical for the efficient development and management of edge- and bottom-water condensate gas reservoirs. In this study, a long-core displacement mechanism model was constructed using CMG-GEMTM and WinPropTM. The model simulates reservoir depletion from initial conditions (41.2 MPa, 102.5°C) to the current reservoir pressure (13.5 MPa), followed by gas injection. It was then upscaled to the edge- and bottom-water reservoir scale to capture complex fluid phase behavior, enabling a multi-factor coupled optimization of CO2 injection strategies. Model reliability was verified through comparison with core experimental results. Subsequently, the effects of geological parameters (e.g., reservoir permeability and rhythmic heterogeneity) and engineering parameters (e.g., injection pressure and rate) on reservoir performance were systematically evaluated. The results indicate that appropriate target zone selection and optimization of injection pressure and rate—avoiding formation fracturing and preventing gas channeling—can substantially improve reservoir development outcomes. Applying this approach to the K Gas Reservoir, the optimal strategy involved injecting CO2 at a rate of 5 × 104 m3/d, restoring pressure to 22.5 MPa in a composite rhythmic reservoir with an average permeability of 10 mD. This scheme increased the condensate oil recovery factor by 18.7 percentage points (from 43.9% to 60.9%) while reducing the water-cut rise rate by approximately 34%.
