Integration between experimental investigation and numerical simulation of alkaline surfactant foam flooding in carbonate reservoirs
本文旨在评估巴西盐下碳酸盐岩储层中化学增强采油(cEOR)的潜力,特别关注碱、表面活性剂泡沫(ASF)驱油技术。通过实验表征和油藏模拟预测,本研究提出了一种创新方法,以评估碳酸盐岩储层中ASF的采油潜力。实验部分包括相行为和吸附分析,为模拟提供了关键参数,如最佳矿化度、表面活性剂吸附和泡沫流动阻力因子。
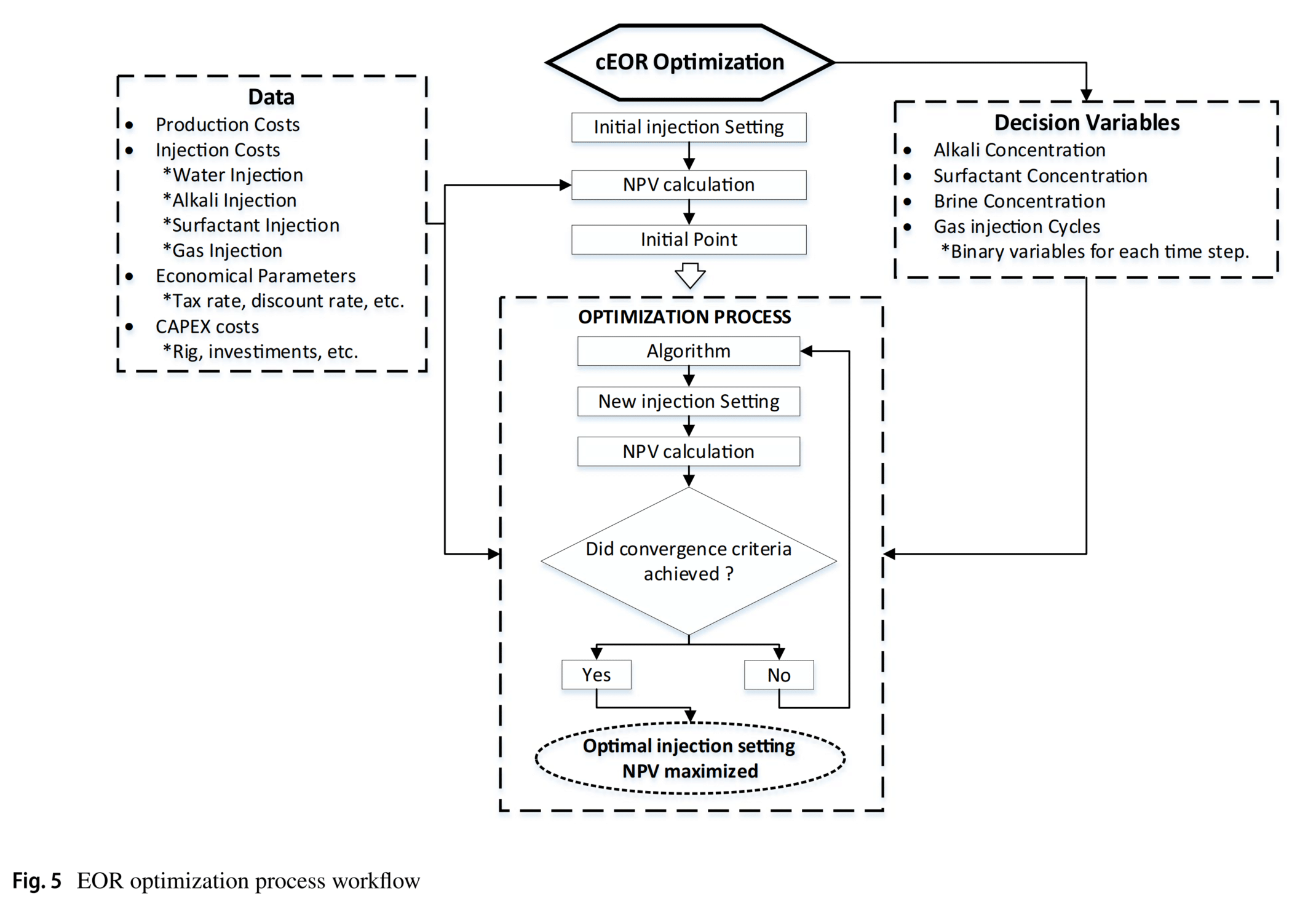
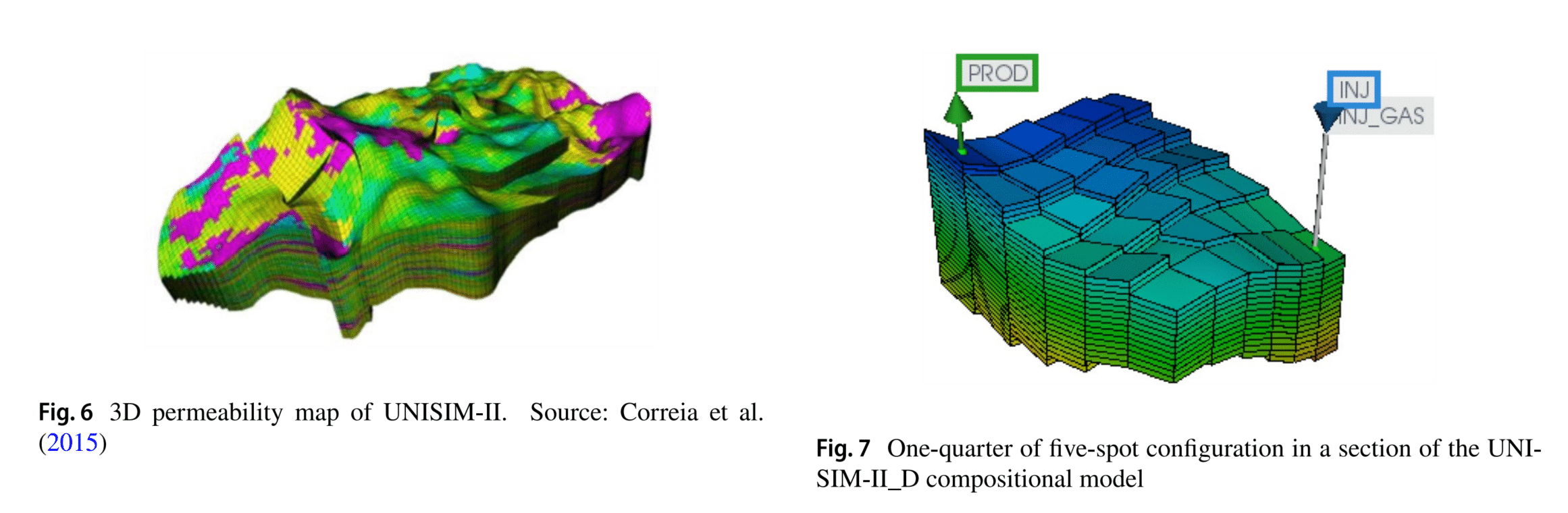
通过两个案例研究,使用UNISISM-II基准模型的一部分,采用五点模型的四分之一,对碱、表面活性剂(AS)和ASF驱油进行了模拟。通过快速遗传算法优化过程,与注水基础案例相比,ASF注入案例的净现值(NPV)提高了1443万美元,累积原油产量增加了4.5%。通过生产曲线和油饱和度图的分析,观察到油产量的显著提前,这是NPV提高的主要原因,证明了ASF方法在碳酸盐岩储层中应用的高潜力。
CMG软件应用情况:
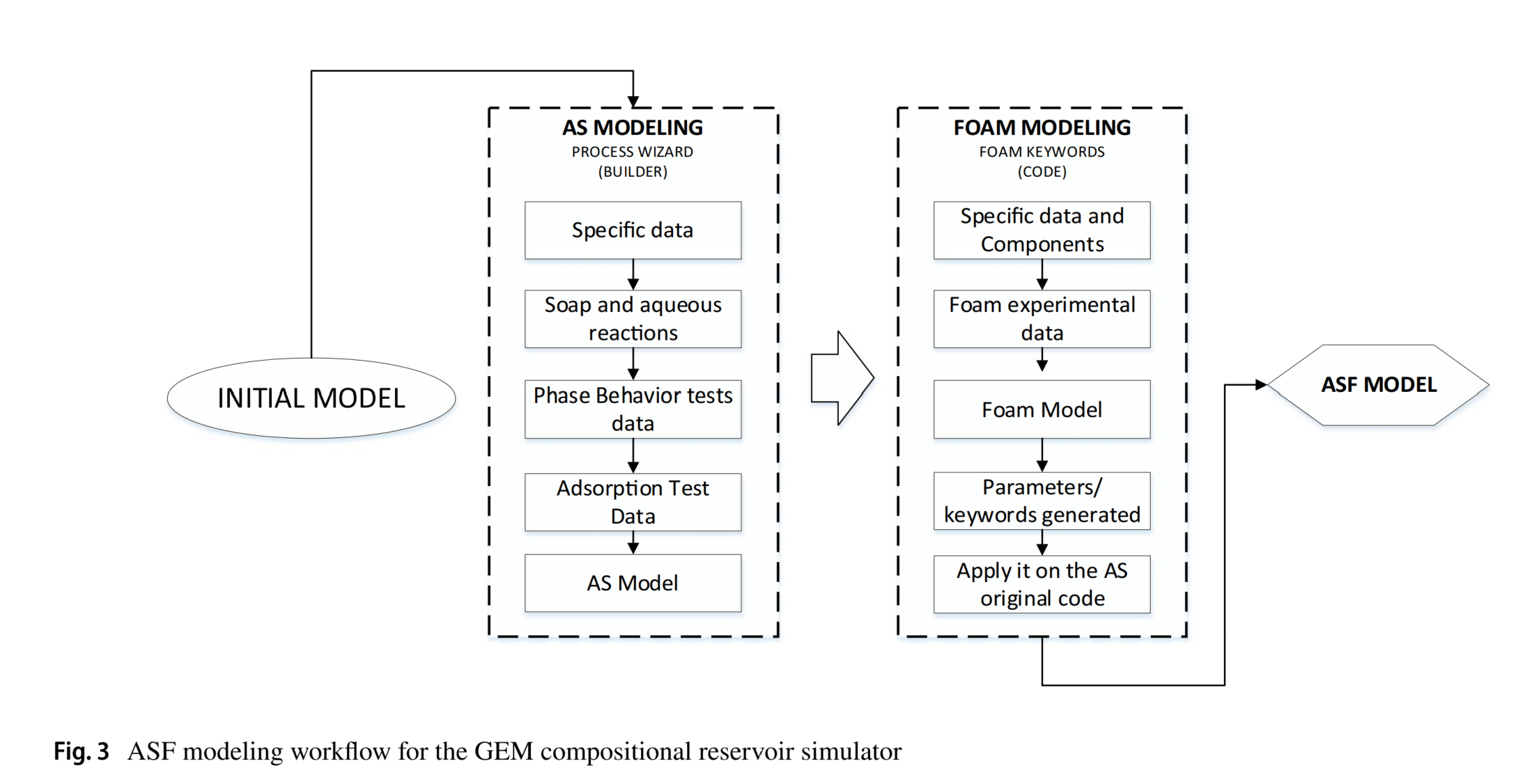
在数值模拟部分,研究者使用了CMG软件(Computer Modelling Group Ltd.)的GEM组成模拟器,将实验得到的ASF实验表征数据整合到具有严格条件的碳酸盐岩储层模型中,以实现最大油田采收率。通过模拟,研究者能够验证和估计AS和ASF注入对油产量的影响,并使用快速遗传算法方法优化NPV。

作者单位:
巴西圣保罗大学矿山与石油工程系
Abstract
In Brazil, pre-salt carbonate reservoirs are largely responsible for the current increase in oil production. However, due to its peculiar characteristics, increasing oil recovery by water injection is not enough. Therefore, we seek to evaluate the recovery potential using chemical methods (cEOR). Among these, the Alkali Surfactant Foam (ASF) method appears with high potential, a variant of Alkali Surfactant Polymers (ASP) without the problems presented by it. Therefore, this work presents an innovative methodology, which seeks to evaluate the potential for recovery with ASF in carbonate reservoirs by integrating experimental characterization and recovery prediction using reservoir simulation. For this, phase behavior and adsorption analyses were carried out. The experimental results provided key parameters for the simulation, such as optimal salinity, surfactant adsorption, foam mobility reduction factors. The results are from two case studies of AS and ASF flooding, using a section of UNISIM-II benchmark, using a one-quarter of five-spot model. Having the modelling for these cEOR methods defined, an optimization process for each method was applied, allowing a reliable comparison among the methods and over a base case of water injection, seeking the maximization of the net present value (NPV). As a result, in the experimental part, a low interfacial tension (IFT) value of 0.003 mN/m was achieved with a surfactant adsorption reduction of 17.9% for an optimal setting among brine (NaCl), alkali (NaBO2.4H2O), and surfactant (BIO-TERGE AS 40). In the reservoir simulation part, using a fast genetic algorithm in the optimization process, a NPV of US$ 14.43 million higher than the base case (water injection) and a 4.5% increase in cumulative oil production for the ASF injection case were obtained. Considering the analyses of production curves (cumulative oil production and oil rate) and oil saturation maps, a considerable oil production anticipation was observed, which was the main reason for NPV improvement, proving the high potential for application of the ASF method in carbonate reservoirs.
