Comprehensive Investigation for CO2 Flooding Methodology in a Reservoir with High Water Content
本文针对中国某高含水、低孔低渗、强非均质性致密砂岩C油藏,系统开展了CO₂驱油适应性评价与开发优化研究。通过模糊综合评价、岩心驱替实验与CMG数值模拟相结合的方法,评估了CO₂驱、表面活性剂驱与水驱的开发效果。
实验结果表明,在束缚水饱和度约30%条件下,CO₂驱采收率高达68.38%,明显优于其他驱替方式。但高含水会显著抑制CO₂驱效果。数值模拟进一步表明,在保持注入压力高于最小混相压力(16.44 MPa)的前提下,注入速度受地层破裂压力限制,区块A和B的10年采收率分别为27.39%和0.48%,换油率较低,开发经济性差。研究为类似高含水致密油藏的开发提供了重要参考。
CMG软件应用情况
- 软件平台:CMG GEM模块
- 模拟内容:
- 建立三维地质模型(由Petrel导入),模拟CO₂驱油过程;
- 采用五点井网(1口生产井+4口注入井)进行开发模拟;
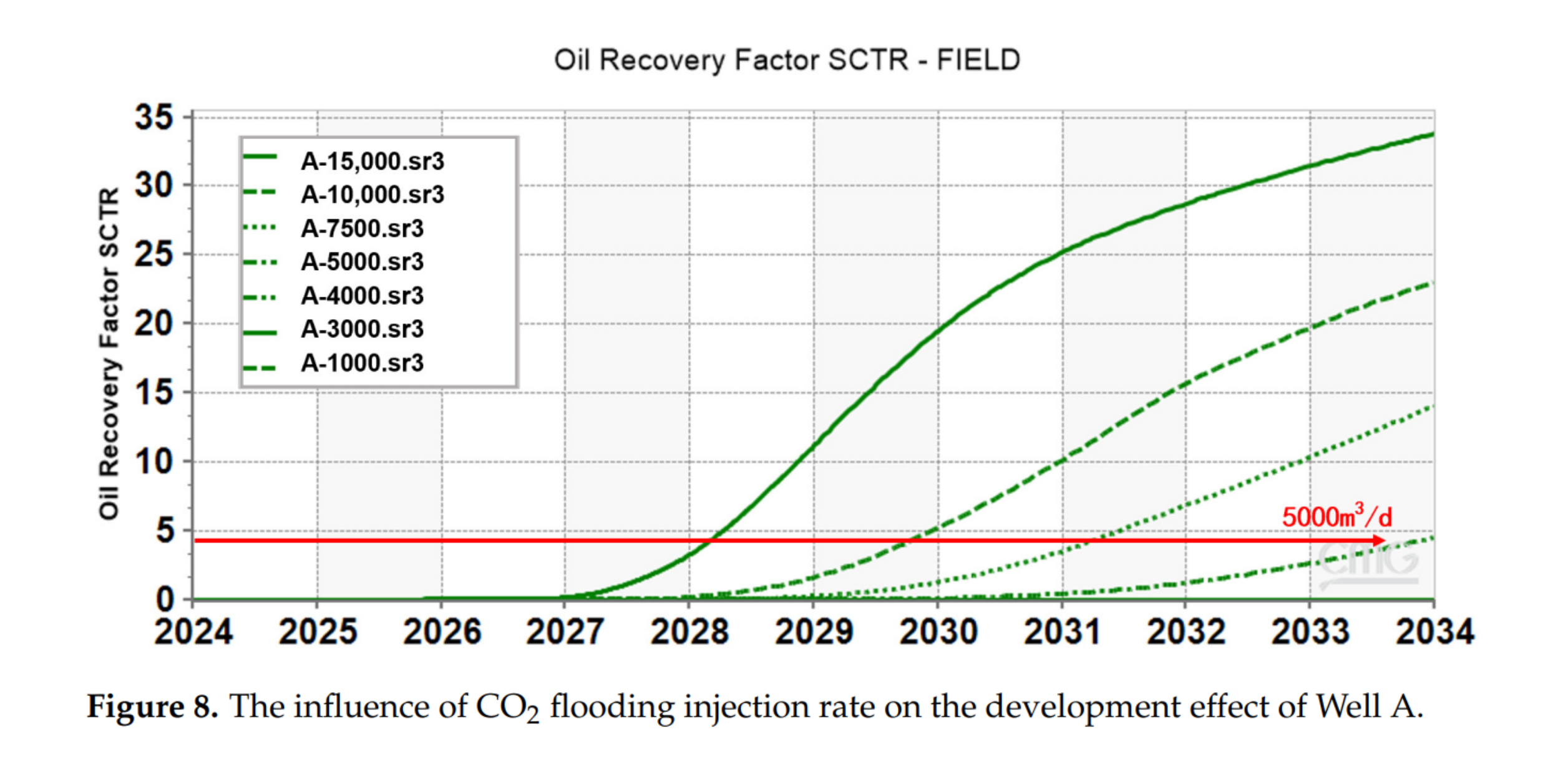
- 优化注入速度(1000~15000 m³/d),分析其对采收率与注入压力的影响;
- 模拟不同压差下的换油率(t/t)与开发效果;
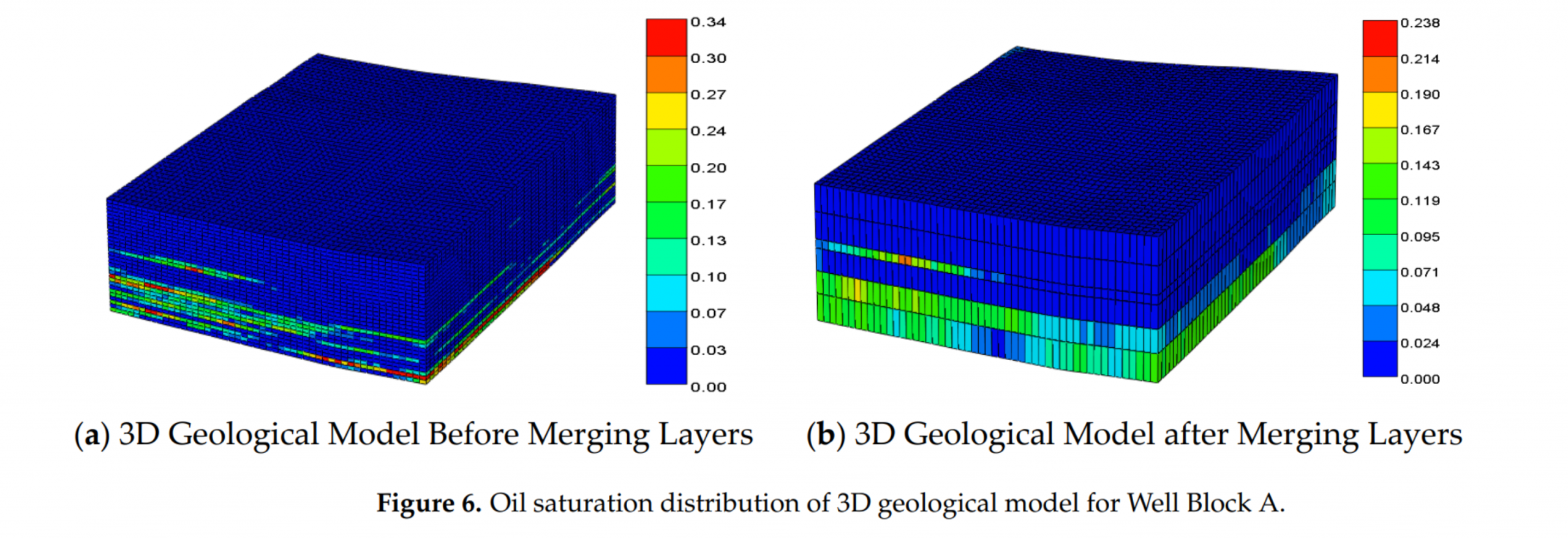
- 模拟层合并前后产量一致性,验证模型简化合理性;
- 模拟时间跨度为10年,考虑混相驱与地层破裂压力限制。
结论
- 适应性评价:采用模糊层次综合评价法,C油藏CO₂驱适应性指数为0.8711,表明其适合CO₂驱开发。
- 实验结果:CO₂驱采收率最高达68.38%,远高于水驱(51.61%)和表面活性剂驱(62.55%),但高含水(>50%)会显著降低驱油效果。
- 吞吐实验:CO₂吞吐采收率为35.29%,低于连续驱替;添加表面活性剂可略微提高至36.14%,但经济性不佳。
- 数值模拟优化:
- 区块A:注入速度≤7500 m³/d,10年采收率为27.39%,换油率为0.2 t/t;
- 区块B:注入速度≤3000 m³/d,10年采收率仅0.48%,换油率为0.07 t/t;
- 提高注入速率有利于提高采收率,但受限于地层破裂压力。
- 经济性评价:尽管CO₂驱技术可行,但由于油藏含水高、油换率低、需新增注采井,整体开发经济性较差,需谨慎推进。
作者单位
中国石油冀东油田分公司


Abstract
In response to the development challenges caused by the high initial water saturation, low porosity, low permeability, and strong heterogeneity in C tight sandstone reservoirs, a comprehensive study was conducted on the optimization of development methods using a AcademicEditor: QingbangMeng Received: 29September2025 Revised: 4November2025 Accepted: 7November2025 Published: 11 November2025 Citation: Chen,S.;Wang,B.;Wu,Q.; Miao,J.; Kang, H.; Wang,X. ComprehensiveInvestigationfor CO2 Flooding MethodologyinaReservoir withHighWaterContent. Processes 2025, 13, 3657. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/pr13113657 Copyright: ©2025bytheauthors. Licensee MDPI,Basel,Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the termsand conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY)license (https://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by/4.0/). fuzzy model, core flooding experiments, and reservoir numerical simulations. The initial evaluation indicates the good adaptability of CO2 flooding for improving oil recovery in a Creservoir; the experimental result of the CO2 displacement method also performs the best, with a recovery rate of 68.38% at a connate water saturation of about 30%, compared with surfactant flooding and water flooding. However, higher water saturation inhibits the CO2 development effect. The oil recovery factor of pure CO2 huff-n-puff is 32.24% lower than the CO2 displacement method, while surfactant-assisted CO2 huff-n-puff can increase the recovery rate by 0.85% compared to pure CO2. Based on actual geological models, numerical simulations were conducted on Well Block A and B. The results showed that the optimized production pressure is above the Minimum Miscibility Pressure (16.44 MPa); with consideration of the fracture pressure limitation, the CO2 injection rate in Block A should be less than 3000 m3/d, andtherecovery rate after 10 years is only 0.48% (oil change ratio is 0.07 t/t), while the CO2 displacement rate of Block B should not exceed 7500 m3/d, and the recovery rate after 10 years can reach 27.39% (oil change ratio is 0.2 t/t). CO2 displacement is an effective development method for a C reservoir, but due to a high water content the oil change ratio is very low, indicating a low potential for further development. The research provides important references for the development of similar oil reservoirs.
