New Insight of Nanosheet Enhanced Oil Recovery Modeling: Structural Disjoining Pressure and Profile Control Technique Simulation
本研究提出了一种使用智能黑纳米卡(SLNs)的新型提高采收率(EOR)方法,以减轻传统热采对环境的影响,特别是在全球变暖的背景下。与以往通过吸附改变润湿性的研究不同,本研究创新性地在储层模拟器中模拟“油膜脱离”以实现润湿性改变。
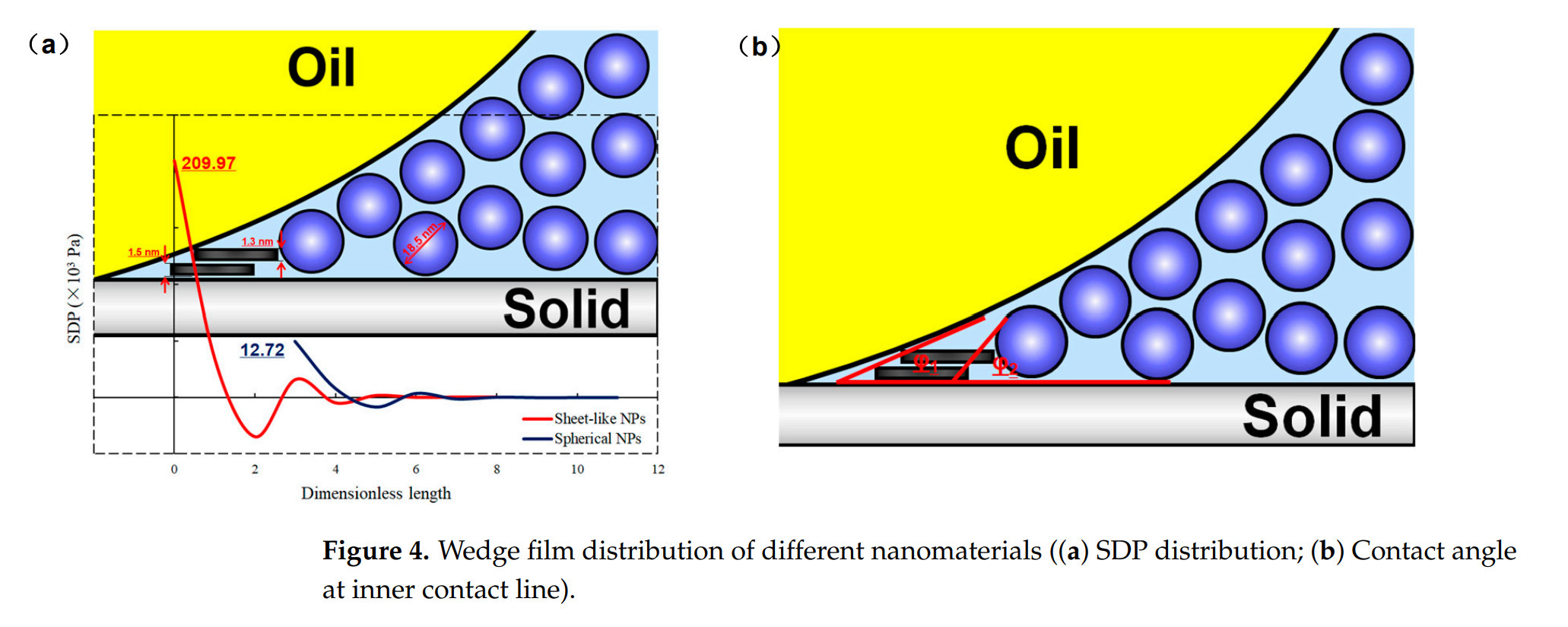
使用CMG-STARS(2020)模拟器,本研究强调SLNs在降低残余油饱和度和将润湿性转向水湿条件方面的优越性能,超越了传统的化学EOR和球形纳米颗粒。SLNs的结构分离压力(SDP)达到20.99×10³ Pa,比直径为18.5 nm的球形颗粒高出16.5倍。基于Percus–Yevick(PY)理论,数值模型在生产历史拟合中实现了高精度,采收率和含水率的拟合精度误差范围分别为0.02和0.05。这项研究推进了化学EOR技术,并为低渗透率和重油储层提供了一种环境可持续、高效的开采策略,及作为热采的有前景的替代方案。
CMG软件应用情况
本研究使用CMG-STARS评估SLNs在原油开采中的效果。CMG软件用于模拟油膜脱离过程,并通过调整结构分离压力(SDP)和薄膜相互作用能量(FIE)来优化采收率。模拟过程中计算插值因子,以精确表示相对渗透率和毛管压力曲线的变化。
Abstract:
This study presents a novel Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) method using Smart Black Nanocards (SLNs) to mitigate the environmental impact of conventional thermal recovery, especially under global warming. Unlike prior studies focusing on wettability alteration via adsorption, this research innovatively models ‘oil film detachment’ in a reservoir simulator to achieve wettability alteration. Using the CMG-STARS (2020) simulator, this study highlights SLNs’ superior performance over traditional chemical EOR and spherical nanoparticles by reducing residual oil saturation and shifting wettability toward water-wet conditions. The structural disjoining pressure (SDP) of SLNs reaches 20.99 × 103 Pa, 16.5 times higher than spherical particles with an 18.5 nm diameter. Supported by the Percus–Yevick (PY) theory, the numerical model achieves high accuracy in production history matching, with oil recovery and water cut fitting within precision error ranges of 0.02 and 0.05, respectively. This research advances chemical EOR technologies and offers an environmentally sustainable, efficient recovery strategy for low-permeability and heavy oil reservoirs, serving as a promising alternative to thermal methods.
Keywords: nanofluid; modeling; structural disjoining pressure; self-profile control and flooding
作者单位
- 中国石油勘探开发研究院(RIPED)
