The Effects of Reservoir Temperature on Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Nitrogen (N2) Gas Sorption in Enhanced Coal Bed Methane (ECBM)
近年来,增强型煤层气(ECBM)生产已成为众多研究者的兴趣所在,尤其是那些与能源产业相关的研究者。多年来,这种方法的实施已经能够刺激煤层的气体生产,并能够挖掘从煤体中获取更多烃类气体的潜力。许多研究已经进行,以调查可能影响CO2和N2气体注入煤层效率的几个因素,以便更好地理解这种方法。本报告的核心趋势之一是了解温度如何影响CO2和N2与甲烷(CH4)气体在不同油藏温度下的吸附行为,因为吸附是一个物理过程,可以很容易地被系统的物理变化所改变。为了回答这个问题,本报告将展示在不同油藏温度下,CO2和N2置换煤层中CH4的效率的油藏模拟研究。为了完成研究的目标,研究将涉及使用CMG的GEM油藏模拟器对不同煤层油藏温度下ECBM生产的模拟。报告结果将比较在不同油藏温度下,不同气体的ECBM的最大吸附容量、吸附速率和注入前沿形状。
CMG软件的应用情况:
在本研究中,主要使用CMG的GEM模拟软件来完成ECBM生产在不同油藏温度下的模拟研究。GEM软件能够模拟三次采油过程,广泛应用于煤层气(CBM & E-CBM)和CO2处理过程。该软件将用于模拟在不同油藏温度下,通过CO2和N2注入辅助的煤层气生产行为。此外,如果时间允许,还将使用Schlumberger的ECLIPSE-E300模拟软件作为GEM的备份软件,该软件也能够模拟在不同温度下,通过CO2和N2注入辅助的生产行为。
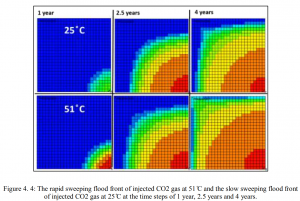
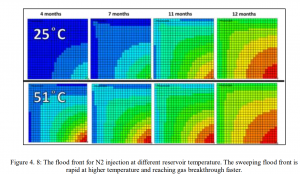

ABSTRACT:
Recently, the enhanced coal bed methane (ECBM) production has become the interest of many researchers especially for those who are related to the industry of energy. Over the years, the implementation of this method has been able to stimulate the production of coal seams and able to unlock the potential of gaining the more hydrocarbon gas from the coal bed body. Many studies been done in relation to investigate on few factors that may affect the efficiency of the carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen (N2) gases injection into the coal seams for better understanding on the method. One of the trends of study which is becoming the backbone this report is to understand on how does the temperature effects on the sorption behavior of CO2 and N2 with methane (CH4) gas at different reservoir temperatures, as sorption is a physical process which can be easily altered by the physical
changes of the system. To answer this question, this report will present on the reservoir simulation study on the efficiency of CO2 and N2 to displace CH4 in the coal seam at different reservoir temperatures. In order to accomplish the objectives of the study, the study will be involving reservoir simulation on the production of ECBM at different coal bed reservoir temperature by using CMG’s GEM reservoir simulator. The report resulted in the comparison of the maximum adsorption capacity, rate of adsorption and the flood front shape of the ECBM of different gases at different reservoir temperature.
作者单位:
Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS(马来西亚国油科技大学),位于Bandar Seri Iskandar, 31750 Tronoh, Perak Darul Ridzuan, Malaysia。
