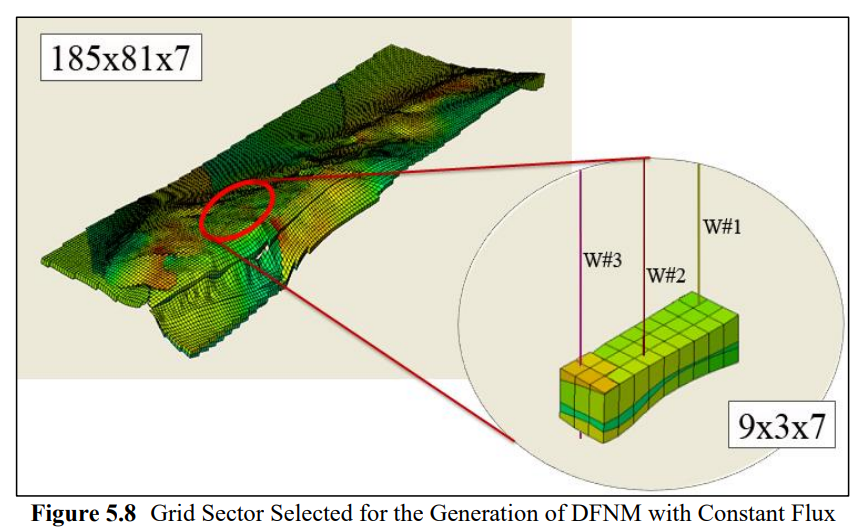
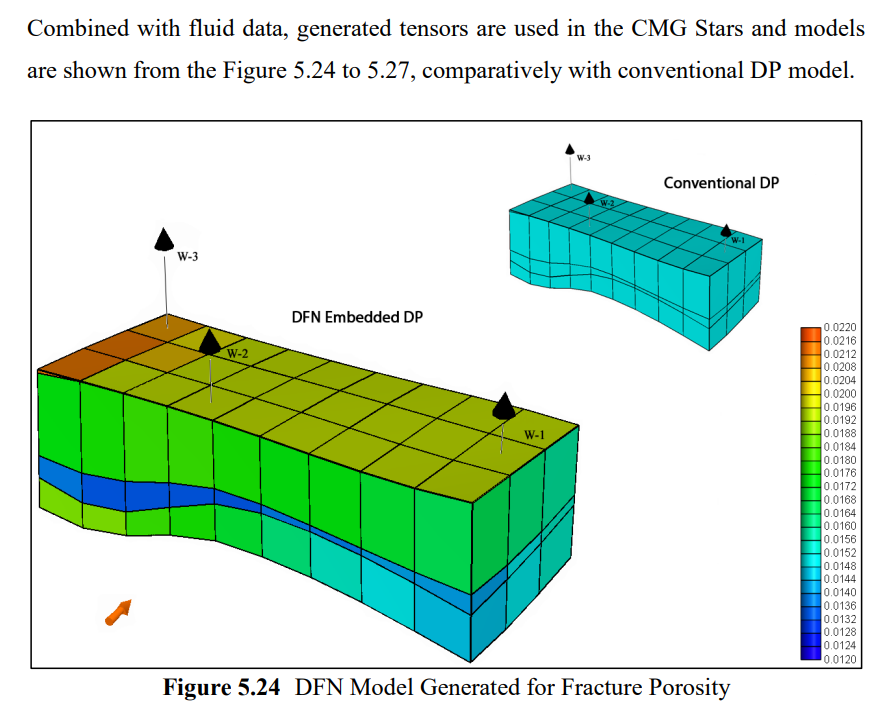
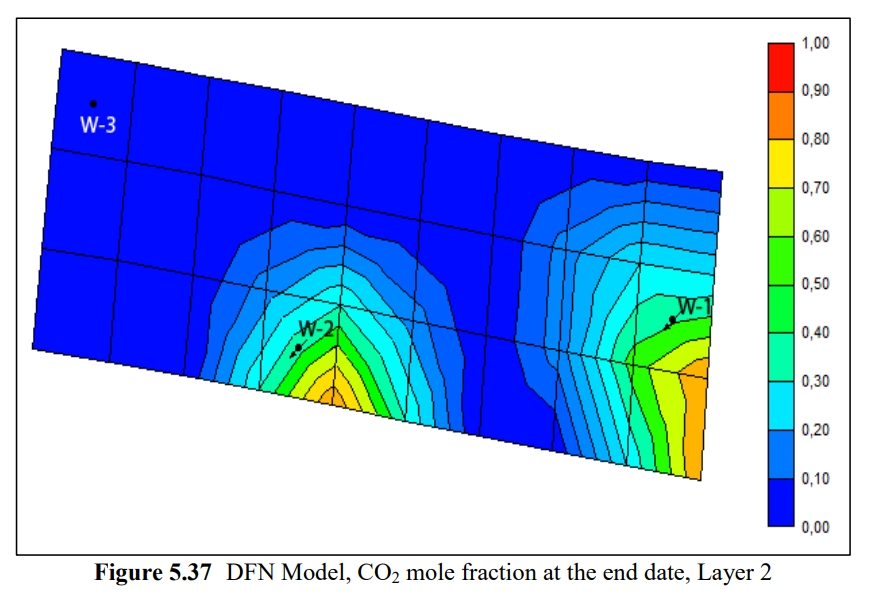
油气储层常见裂缝发育,裂缝分析至关重要,其可能对流体流动模式产生重要影响。离散裂缝网络(DFN)模型是裂缝性储层模拟的有效手段,可以通过连接的裂缝表征来考虑裂缝岩石中的流体流动和传输过程。与采用连续介质方法的双孔模型不同,DFN数据用来自裂缝测井和压力瞬态数据等数据源,模拟裂缝连通性。在本研究中,采用DFN方法模拟稠油油藏CO2注入过程。并被用作将有关裂缝的地质信息粗化到双重孔隙流体流动模拟的工具。通过调节岩心扫描中观察到的裂缝参数,创建DFN分区模型,并通过现场试井分析数据进行验证。结果表明,使用DFN模型的历史拟合优于未使用粗化裂缝信息的拟合。
DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELING IN A CARBON DIOXIDE FLOODED HEAVY OIL RESERVOIR
Abstract
Fracture analysis is crucial because of their abundance in reservoirs and can have a strong effect on fluid flow patterns. Accordingly, Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) model is an efficient alternative approach to modeling fractured reservoirs and it is a special tool that considers fluid flow and transport processes in fractured rock masses through a system of connected fractures. Unlike Dual Porosity Model, where a continuum approach is applied, DFN uses detailed information about fracture and fracture connectivity from data sources like fracture logs and pressure transient data to create distinct fracture sets. In this study, a heavy oil reservoir going through CO2 injection is modeled using DFN approach. It was used as a tool for upscaling geologic information about fractures to the dual-porosity fluid flow simulation. A DFN sector model was created by conditioning to fractures observed in a core scanner and are validated by well test analysis from the field. It has been observed that history matches obtained using a DFN sector model was better than those obtained without upscaled fracture information.
Keywords: Discrete Fracture Network Modeling, Natural Fractures, Carbonates