Performance of the Horizontal Wells in a Naturally Fractured Carbonate Reservoir
世界上约60%的探明石油储量和40%的天然气储量被困在碳酸盐岩储层中。碳酸盐岩储层的采收率相对较低,由于这些储层的非均质性,预测难度极大。大多数碳酸盐岩储层含有裂缝,其大小可能从毫米到千米不等。这类油藏的典型例子是伊拉克北部的油气田,几乎全部采用直井开发。本文将研究使用水平井提高其中一个储层的产能。
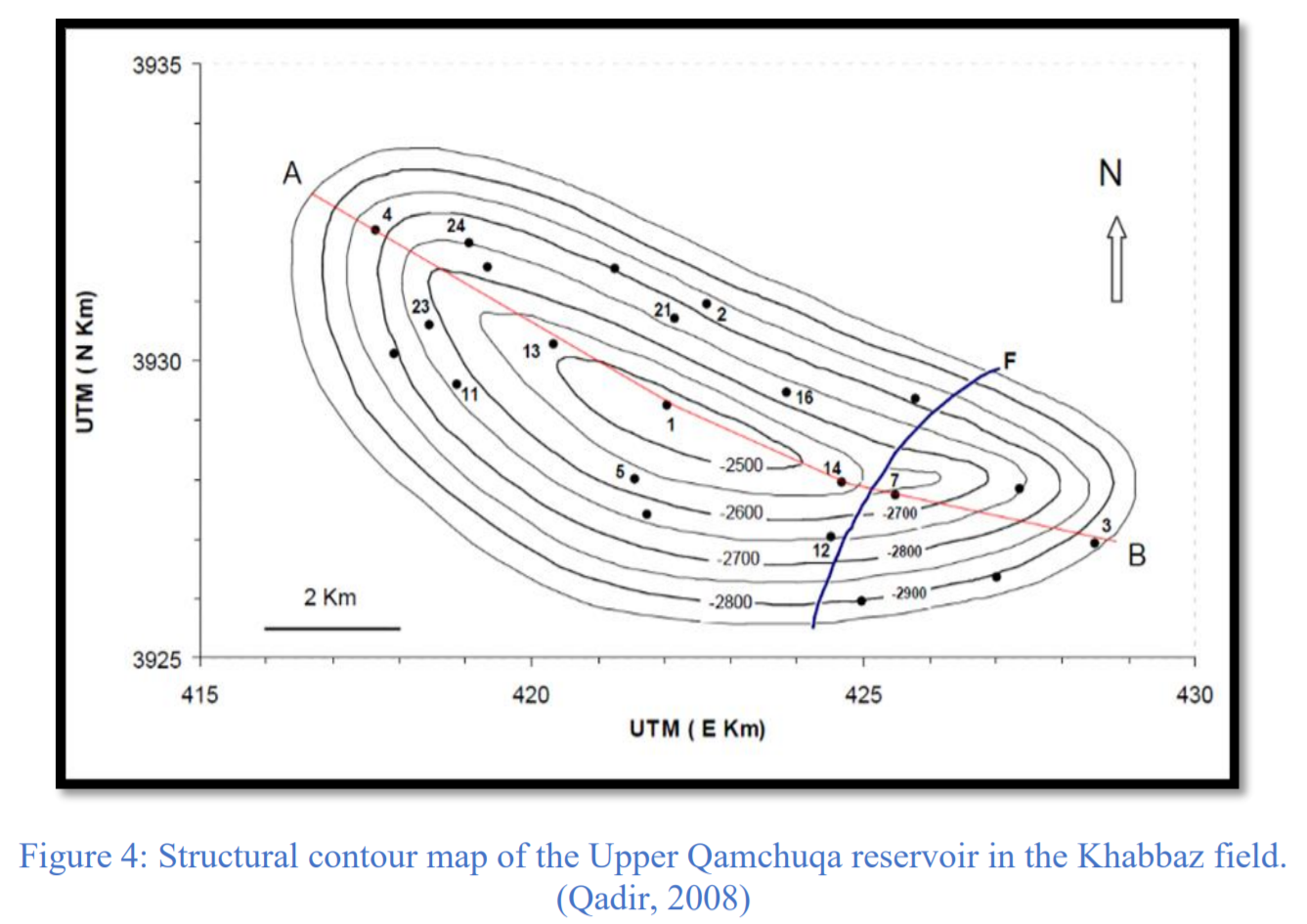
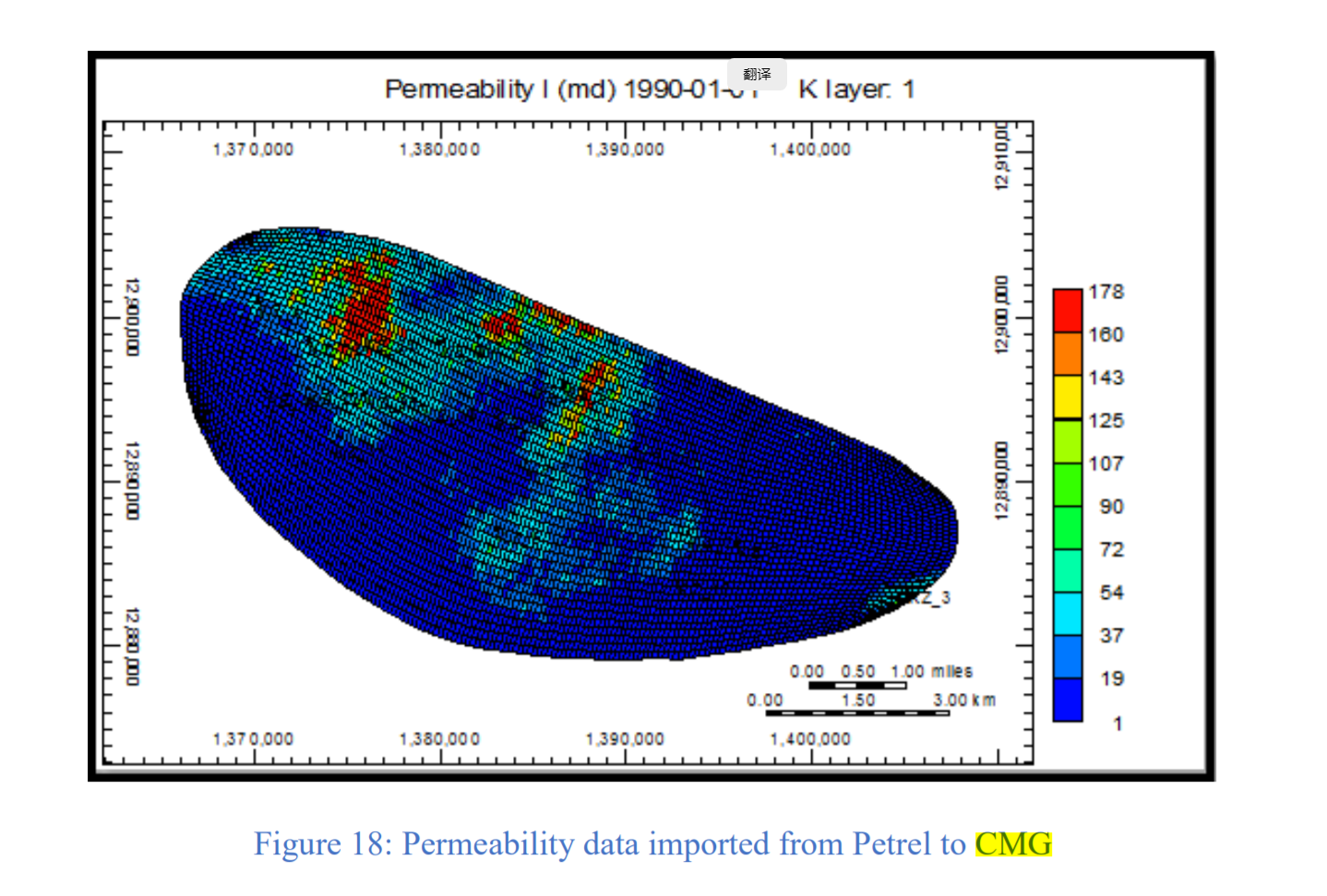
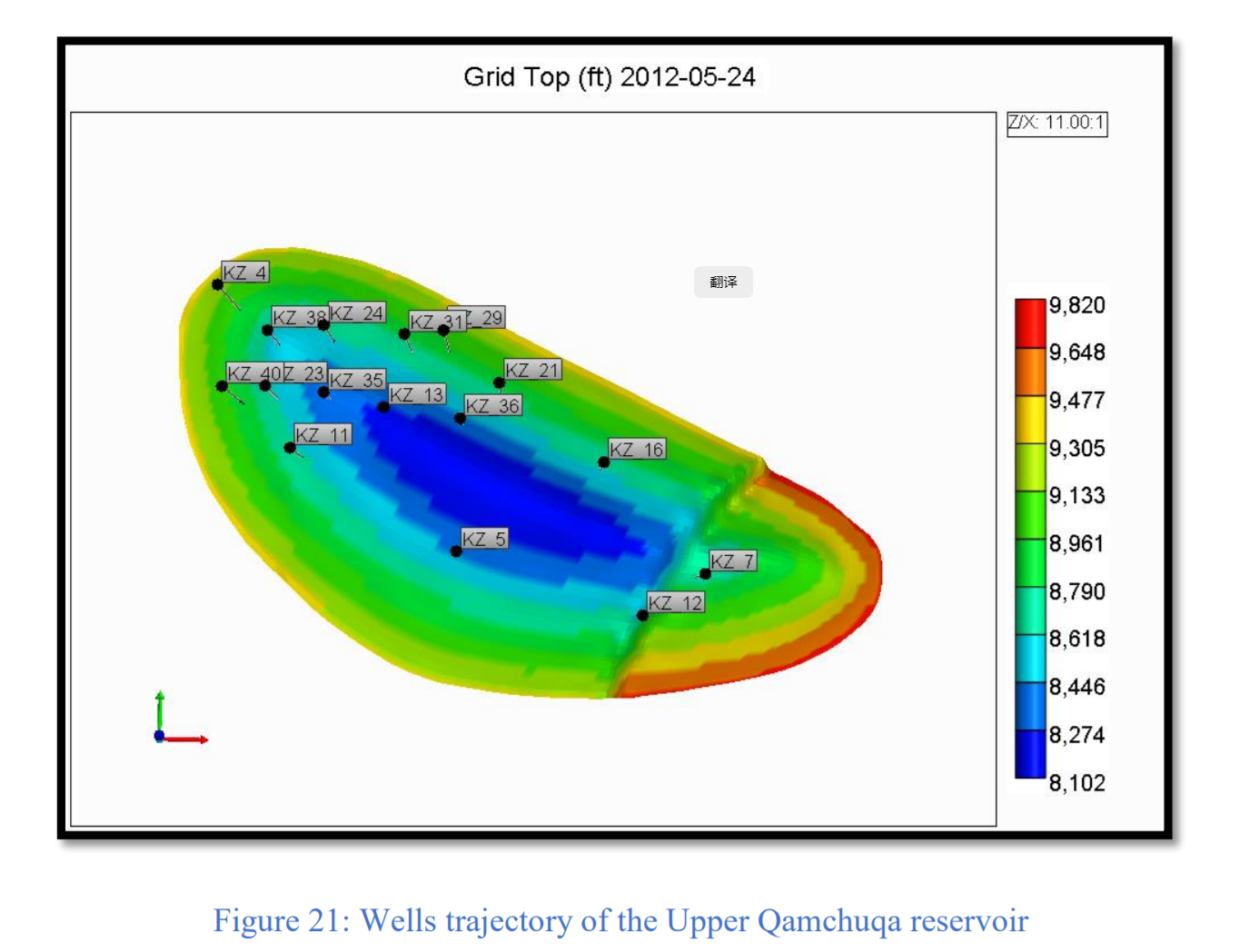
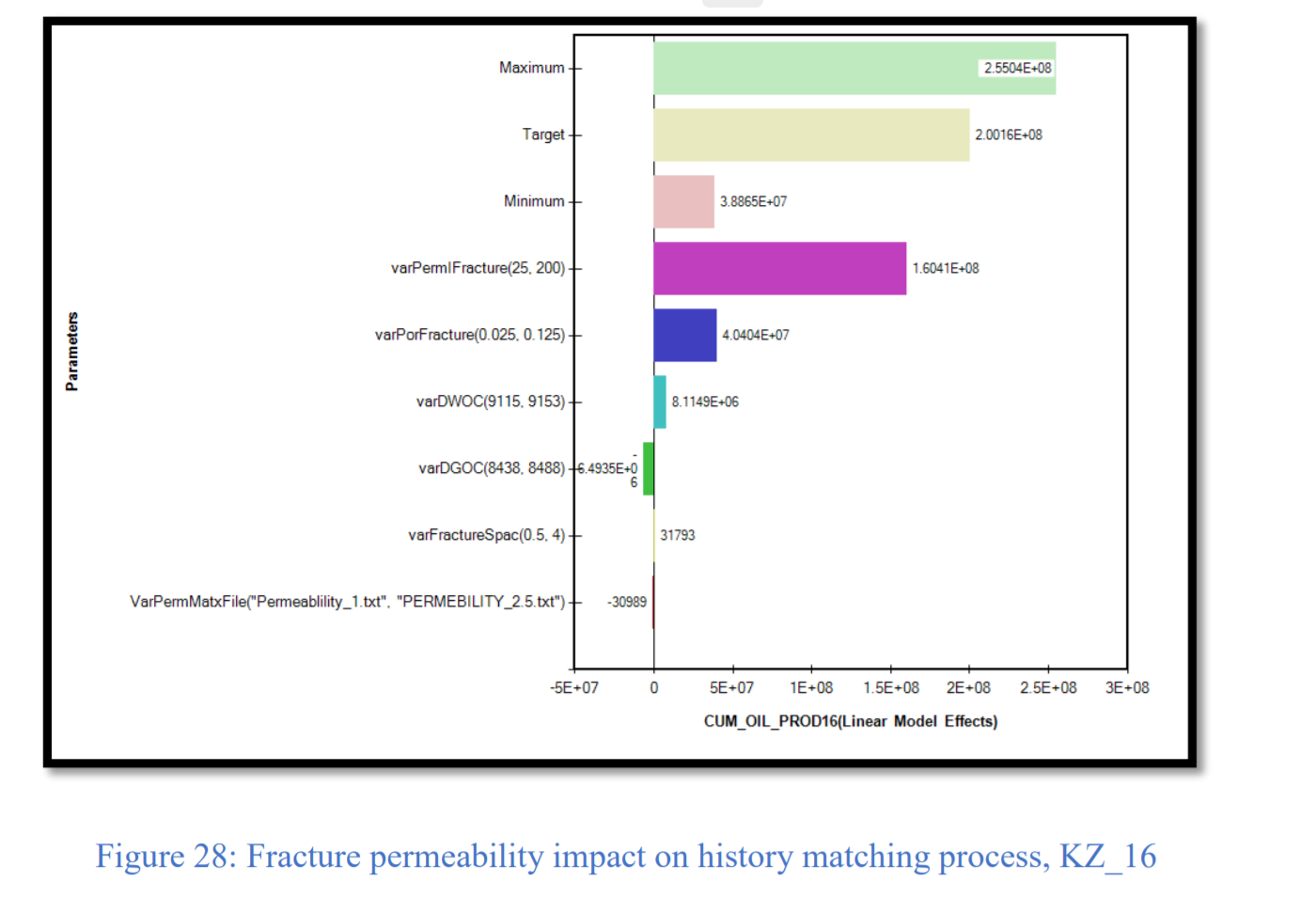
CMG软件用于模拟伊拉克东北部Khabbaz油田的Upper Qamchuqa油藏。上Qamchuqa油层是一个背斜构造,东翼有一条主要的正断层。此外,地层矿物主要由白云石、白云石灰岩、石灰岩和泥灰岩组成。通过拟合历史产量验证了模拟模型。然后将水平井添加到模型中,并研究了最佳井位和井长度。此外,确定了对历史拟合和预测水平井产能有重大影响的储层参数,以供油田未来开发使用。本研究的结果可为降低该地区类似天然裂缝性油藏的运营成本和提高产能提供指导。
About 60 percent of the world’s proven oil reserves and 40 percent of gas reserves are trapped in carbonate reservoirs. Recovery rates are relatively low in carbonate reservoirs, and it is extremely challenging to predict due to the heterogeneous nature of these reservoirs. The majority of carbonate reservoirs contain fractures which may vary in size from millimeters to kilometers. A typical example of this type of reservoirs is oil and gas fields in the northern Iraq. These fields are almost all developed by vertical wells. This study will investigate the use of horizontal wells to enhance the productivity in one of these reservoirs.
CMG software is used to simulate the Upper Qamchuqa reservoir of the Khabbaz oil field northeastern of Iraq. The Upper Qamchuqa reservoir is a subsurface anticline with a major normal fault on the eastern flank. Moreover, it mainly consists of dolomite, dolomitic limestone, limestone and marly limestone. The simulation model was validated by the history matching the production rates. Subsequently, horizontal wells were added to the model, and the optimum placement and lateral length investigated. Furthermore, the reservoir parameters that have a significant influence on the history matching and the predicted horizontal wells’ performance were identified for future development of the field. The results of this study can provide a guideline for reducing the operating costs and increasing the productivity of similar naturally fractured reservoirs in the area.