研究通过PVT实验(包括油藏流体重组、闪蒸分离、恒组成膨胀、定容衰竭实验)和组分油藏模拟,分析了前哨(QS)凝析气藏在开发过程中的反凝析现象。
- 关键发现:
- 通过实验数据拟合EOS模型,预测凝析油饱和度在井区最大约3%。
- 数值模拟显示,垂直井井周5-6米处凝析油饱和度最高(30%),而水平井最大饱和度仅1.5%。
- 水平井因裂缝导流能力高,反凝析污染较轻,垂直井需提前制定解堵措施。
CMG软件应用情况
- 模型构建:使用CMG GEM 2020.10建立单井组分油藏模拟模型,涵盖垂直井和水平井。
- 参数设置:
- 垂直井网格系统:101×101×5,水平井网格系统:105×105×20。
- 结合实际生产数据(气/液产量)进行历史拟合,验证模型可靠性。
- 模拟结果:
- 垂直井井周高饱和度区域随时间扩展,水平井因多裂缝导流未形成高饱和度区。
结论
- 方法论:建立了一套结合实验、EOS调参和数值模拟的工作流程,定量描述凝析油时空分布。
- PVT实验:储层压力与露点压差仅2.9 MPa,开发中必然发生反凝析,但全区域平均饱和度<3%。
- 井型差异:
- 垂直井井周凝析油饱和度峰值30%,年增长率0.22%;
- 水平井饱和度峰值1.5%,年增长率0.54%,但污染范围更广。
- 开发建议:垂直井需提前规划解堵措施,水平井当前无需处理凝析油流动问题。
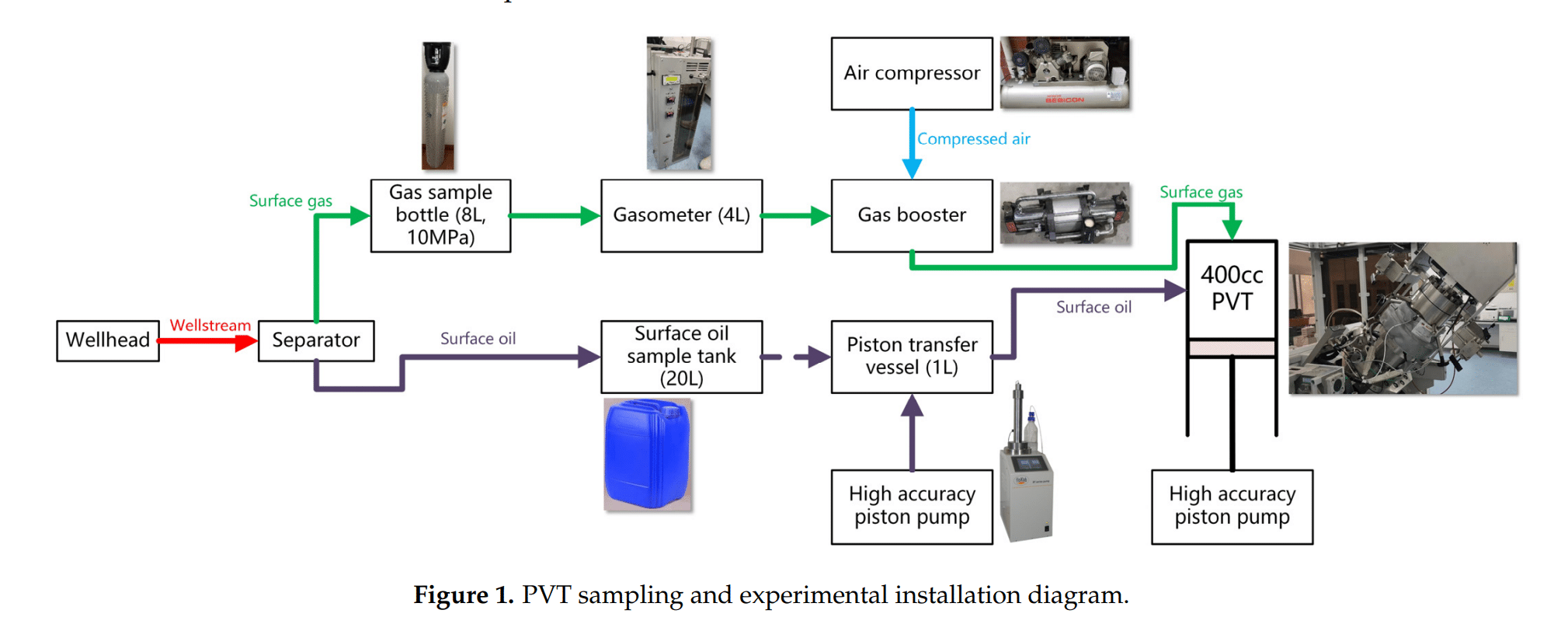
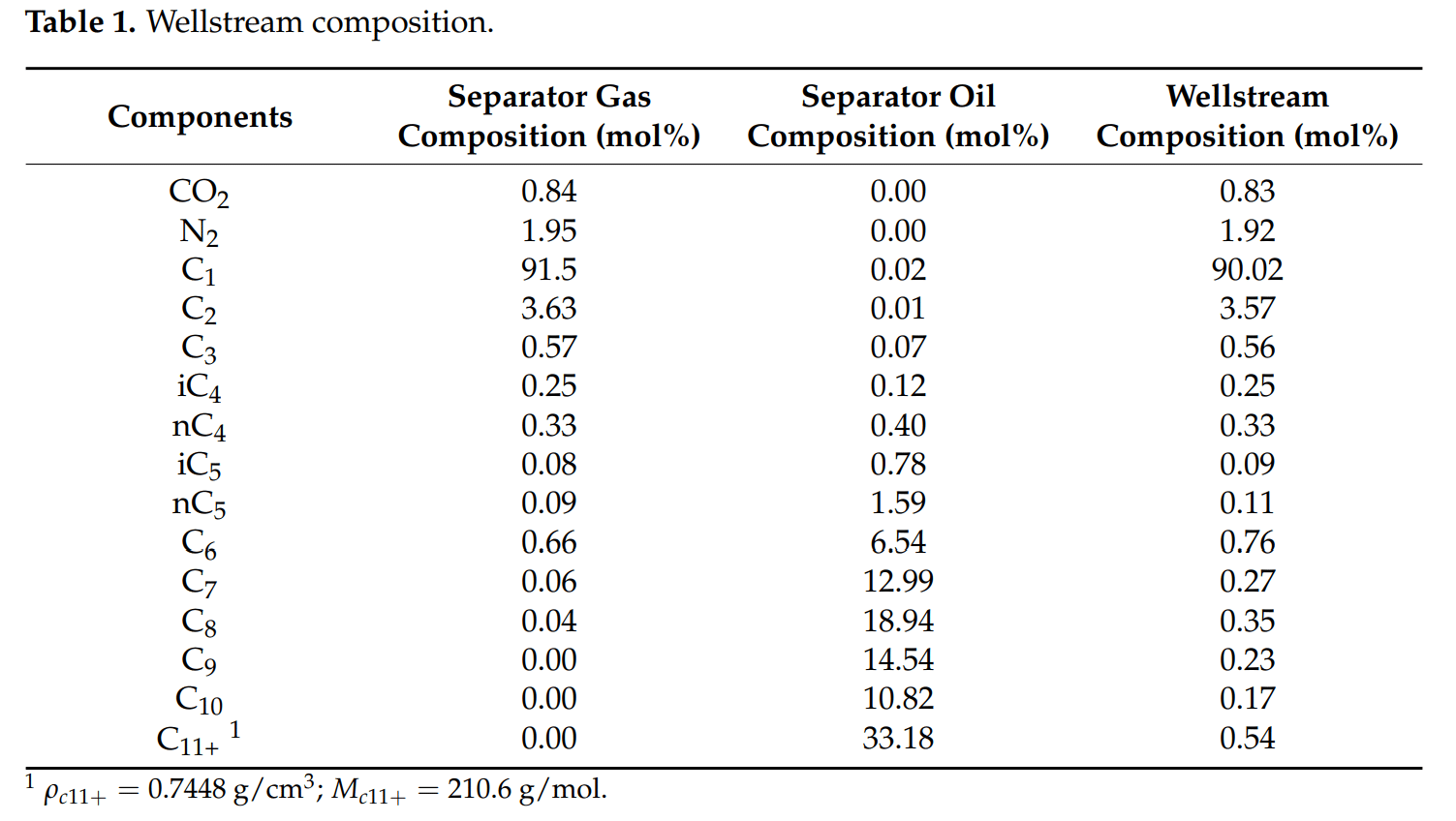
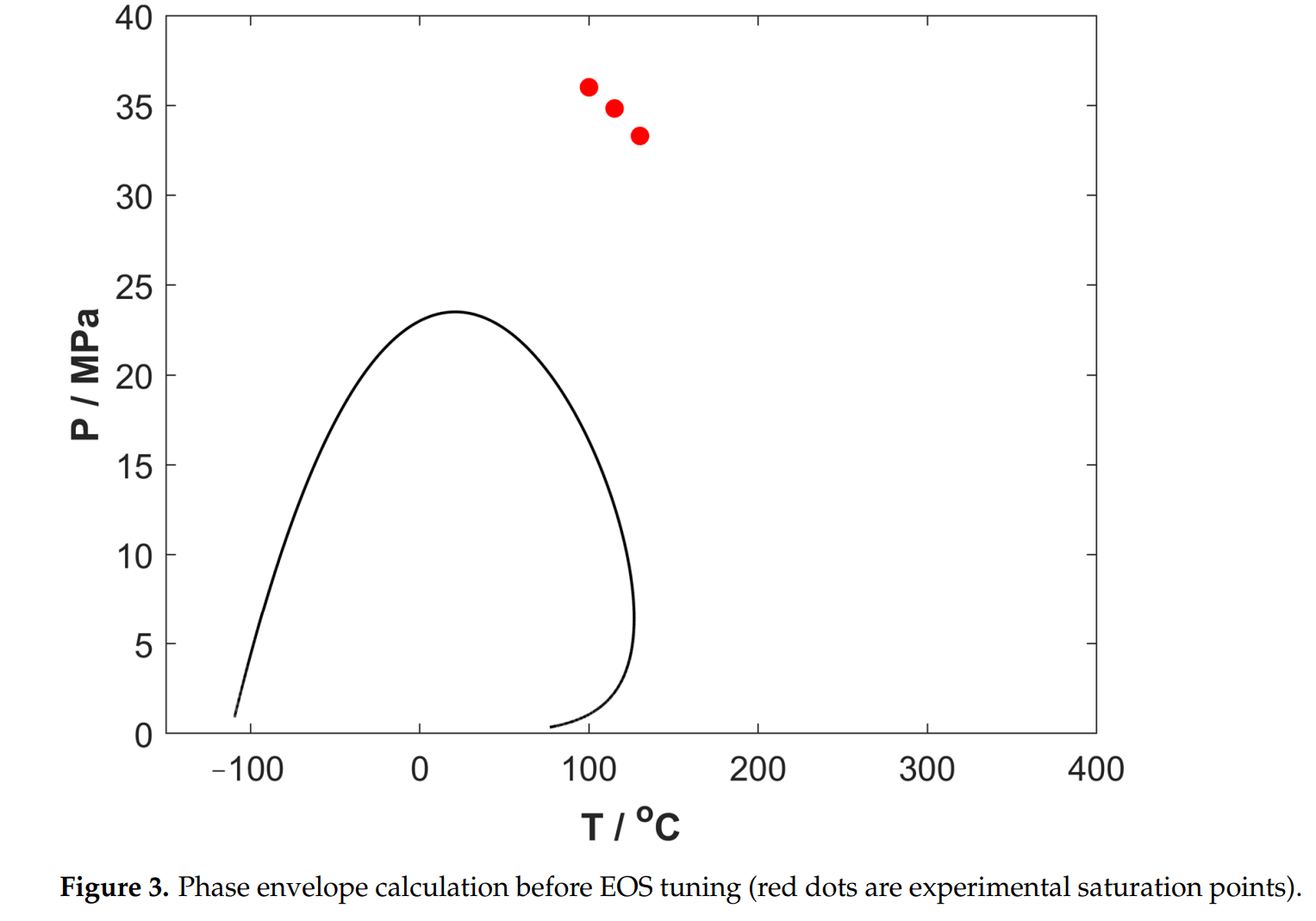
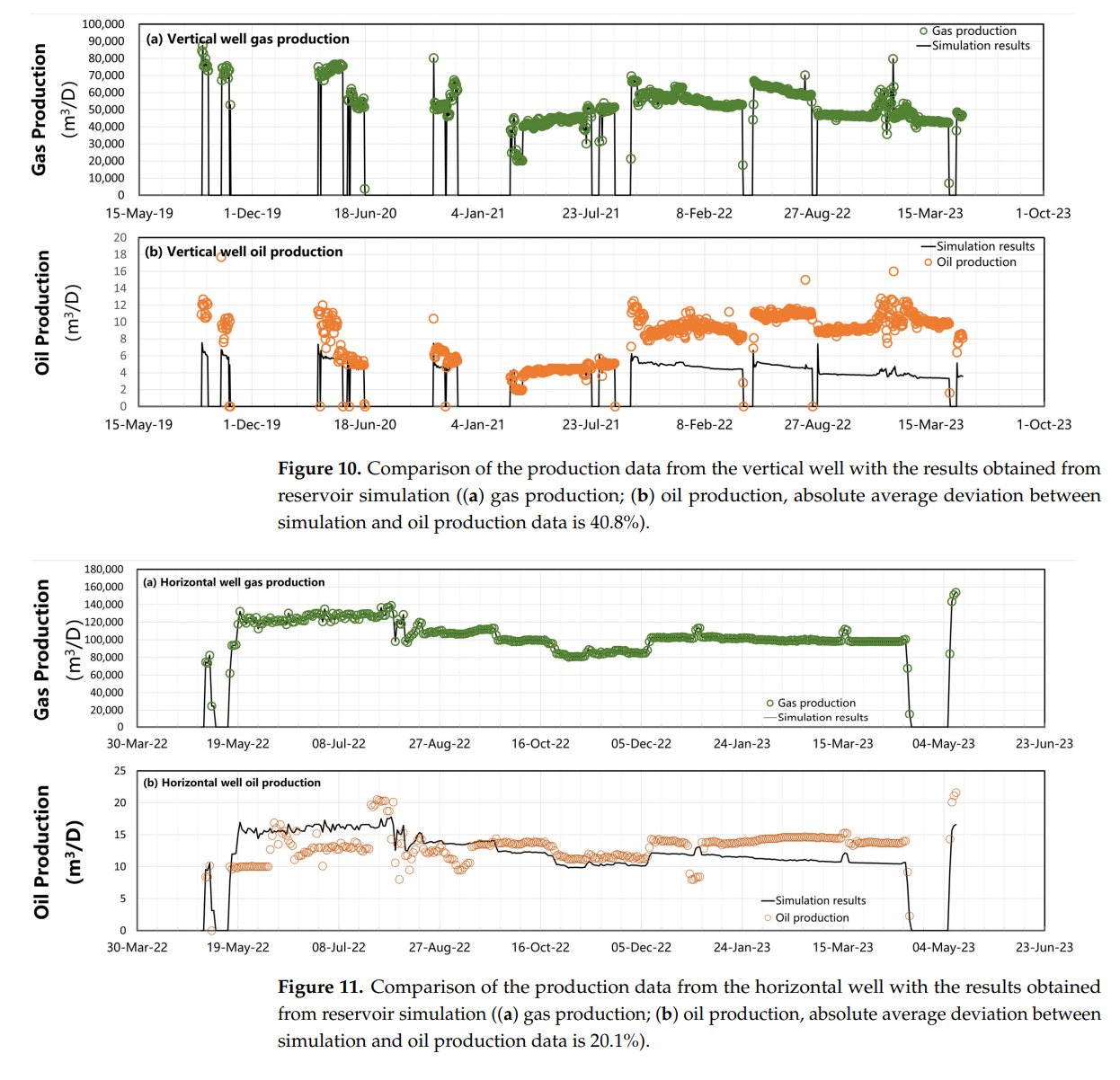
Abstract
In the development of the Qianshao (QS) gas condensate reservoir, it is crucial to consider the phenomenon of retrograde condensation. Understanding the condensate saturation distribution with respect to time and space within the reservoir is essential for planning and implementing effective strategies for the future development of the QS gas condensate reservoir. In this paper, various PVT experiments (including reservoir oil recombination, flash separation, constant composition expansion, and constant volume depletion) were conducted to study the PVT properties and phase behavior of QS gas condensate fluid. Based on experimental data, our in-house PVT computation package was used to determine the appropriate EOS model parameters for the QS gas condensate. A four-step reservoir fluid characterization procedure and workflow for gas condensate reservoirs was developed. Furthermore, by analyzing the pressure-temperature phase envelope, the maximum possible condensate saturation in the QS well area was estimated to be around 3%. Numerical reservoir simulation models were developed using both the EOS model and actual reservoir engineering data. These simulation models were specifically designed to replicate the retrograde condensation process that occurs during production, taking into account both vertical and horizontal wells. By simulating the production process, these single-well reservoir simulation models enable us to quantitatively evaluate the condensate saturation and its distribution over space and time within a specific control area around a single well. Reservoir simulation results show that the condensate build-up around vertical and horizontal wells is quite different. For a vertical well, the maximum condensate oil saturation (30%) around the wellbore is located approximately 5 to 6 m from the well’s center. In contrast, the horizontal well model demonstrates a maximum condensate saturation of no more than 1.5%. This information is crucial for making informed decisions regarding the effective development and management of the QS gas condensate reservoir.
作者单位
新疆油田公司工程技术研究院
