Mechanism and Parameter Optimization of Surfactant-Assisted CO2 Huff-n-Puff for Enhanced Oil Recovery in Tight Conglomerate Reservoirs
中国致密砾岩油藏储量丰富(28.3×10⁸ t),但普遍具有“低孔低渗、黏土含量高、孔喉结构复杂”等特点,常规注水开发效果差。本文以新疆油田某致密砾岩区块为例,建立“多相-多组分-双重孔隙介质”数值模型,并将高压压汞获得的纳米孔喉分布与自研 MATLAB PVT 包耦合,把纳米限域效应引起的相图偏移嵌入 CMG 模拟框架。通过系统敏感性分析,定量评价储层物性、完井与操作参数对 SA-CO₂-HnP(表面活性剂辅助 CO₂ 吞吐)开发效果的影响。
CMG 软件应用情况
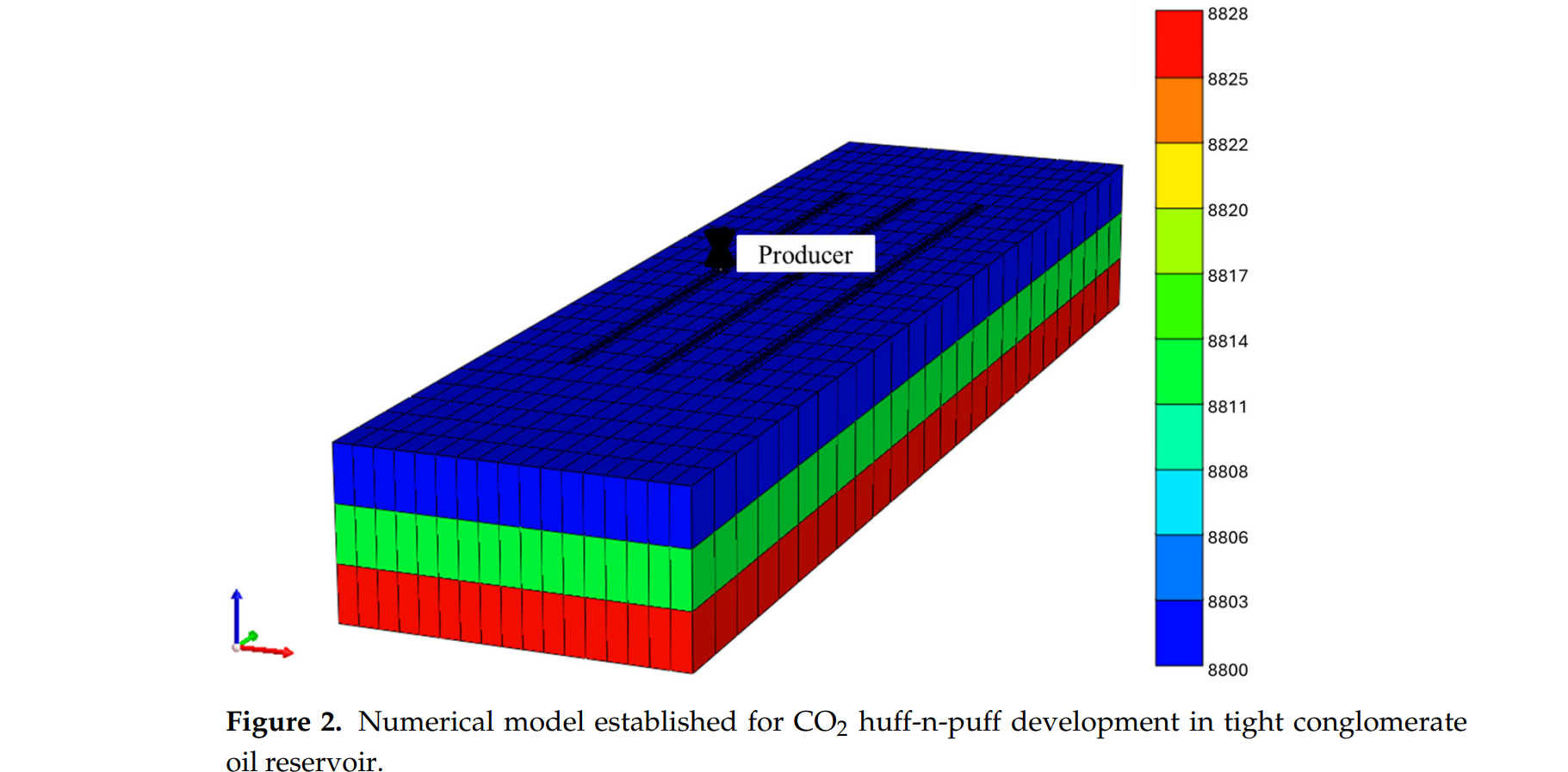
- 主模拟器:采用 CMG(2022 版)GEM 组分模块建立三维双重孔隙介质模型(17×26×3 网格,340 ft×1300 ft×42 ft)。
- 相态耦合:
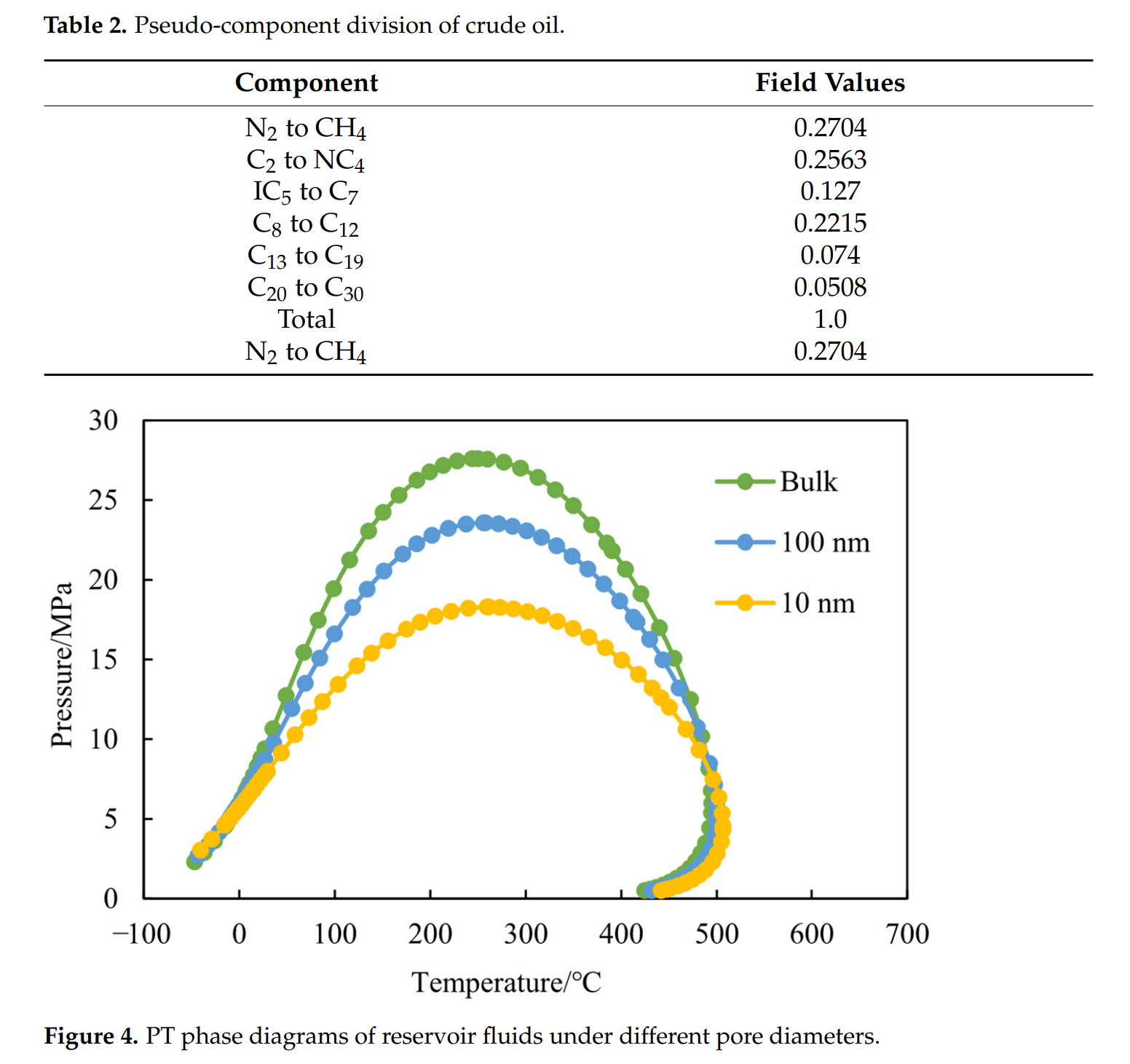
– 利用自研 MATLAB(R2024a)程序计算纳米限域(平均孔径 140 nm)下的临界性质偏移与相图;
– 通过 CMG WinProp 模块对 100 nm 孔径下的 PT 相图进行拟合,将修正后的 6 个拟组分参数返回 GEM 模型,实现“纳米限域-相行为-流动”一体化模拟。 - 模型验证:建立一维岩心尺度模型,与室内岩心驱替实验对比,累积采收率与压差吻合度高,验证了模型可靠性。
- 方案对比与优化:在 GEM 中完成常规 CO₂ 吞吐与 SA-CO₂-HnP 的多周期注入/焖井/回采模拟,并开展 6 组敏感性方案(焖井时间、注入时间、浓度、压力、排量等)的评价。全部数值实验均在 CMG 平台完成。
主要结论
- 注入时间对最终采收率的影响远大于焖井时间——延长焖井 1→5 个月仅提高 <2%,而延长注入时间 4→9 个月可提升 7.7%。
- 表面活性剂浓度与采收率呈负相关:0.0003 摩尔分数效果最佳(37.5%),0.3 摩尔分数降至 35.1%,高浓度易形成泡沫堵塞并产生竞争吸附。
- 注入压力越高越好:10 000→16 000 psi 采收率由 32.3% 增至 47.3%,高压下 CO₂ 密度增大、混相程度提高,可克服纳米孔毛细管阻力。
- 存在最优注液排量:100 bbl/d 时采收率 37.4%,继续提高至 1000 bbl/d 仅增至 37.8%,过高排量导致黏性指进与气窜,体积扫掠效率下降。
- SA-CO₂-HnP 技术在现场推荐参数组合下经济可行,为新疆及类似致密砾岩油藏提供了可复制的参数优化模板。
作者单位
中国石油新疆油田分公司勘探开发研究院

Abstract
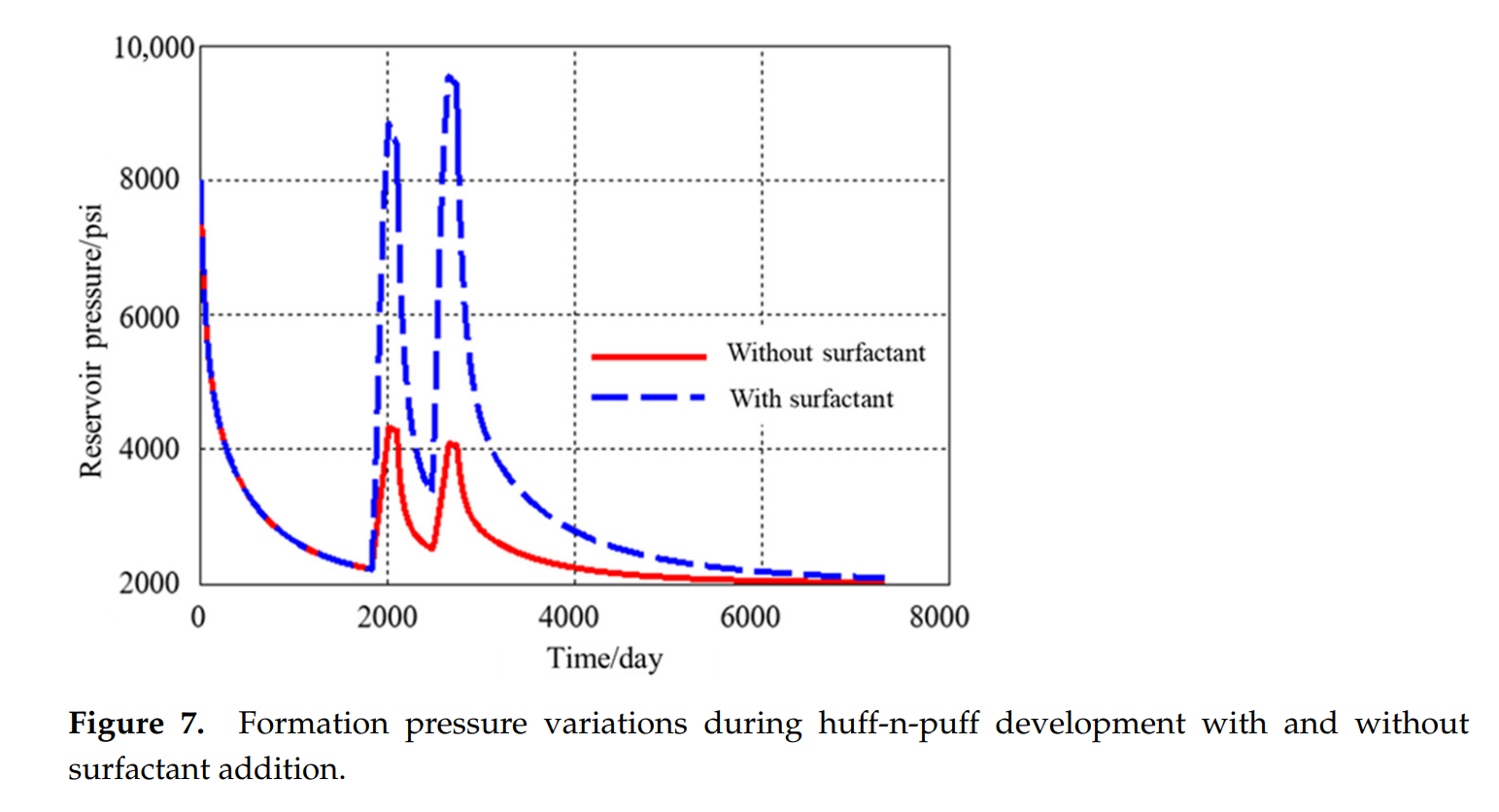
China possesses abundant tight conglomerate oil resources. However, these reservoirs are typically characterized by low porosity and permeability, high clay mineral content, and complex pore structures, resulting in poor performance of conventional waterflooding development. Challenges including insufficient energy replenishment and high flow resistance ultimately lead to low oil recovery factors. This study systematically investigates surfactant-assisted CO2 huff-n-puff (SA-CO2-HnP) for enhanced oil recovery in tight conglomerate reservoirs. For a tight conglomerate reservoir in a Xinjiang block, a fully implicit, multiphase, multicomponent dual-porosity numerical model was established. By integrating pore–throat distributions acquired through high-pressure mercury intrusion with a self-developed MATLAB PVT package, nanoconfinement-induced shifts in the phase envelope were rigorously embedded into the simulation framework. The calibrated model was subsequently employed to conduct a comprehensive sensitivity analysis, quantitatively delineating the influence of petrophysical, completion, and operational variables on production performance. Simulation results demonstrate that compared to conventional CO2 huff-n-puff, the addition of surfactants increases the cumulative recovery factor by 3.5 percentage points over a 20-year production period. The enhancement mechanisms primarily include reducing CO2–oil interfacial tension (IFT) and minimum miscibility pressure (MMP), improving reservoir wettability, and promoting CO2 dissolution and diffusion in crude oil. Sensitivity analysis reveals that injection duration, injection pressure, and injection rate significantly influence recovery efficiency, while soaking time exhibits relatively limited impact. Moreover, an optimal surfactant concentration (0.0003 mole fraction) exists; excessive concentrations lead to diminished enhancement effects due to competitive adsorption and pore blockage. This study demonstrates that SA-CO2-HnP technology offers favorable economic viability and operational feasibility, providing theoretical foundation and parameter optimization guidance for efficient tight conglomerate oil reservoir development.
