Assessing the production potential of Niger Deltareservoirs under uncertainty using numerical simulationtools
尼日尔三角洲是全球重要的含油气盆地,但已有研究多聚焦勘探与静态描述,对开发阶段动态生产行为及不确定性缺乏系统评价。本文以位于滨海沼泽凹陷带的一典型中—深水新区砂泥岩互层油藏为例,建立“确定性基准模型 + 不确定性分析”的工作流程,研究为尼日尔三角洲及类似碎屑岩油田的风险管控和开发方案制定提供了可复制的方法模板。
CMG 软件应用情况
- IMEX(CMG 黑油模块):建立单孔隙度三维网格模型(118 300 个网格,91×130×10),完成 30 年确定性生产预测;
- CMOST(CMG 不确定性/优化平台):
– 对 7 个不确定参数进行蒙特卡罗随机采样,自动生成 59 个实现;
– 嵌入多项式回归代理模型,替代 IMEX 进行 65 000 次概率模拟,满足 R²>0.85、误差<10% 的阈值;
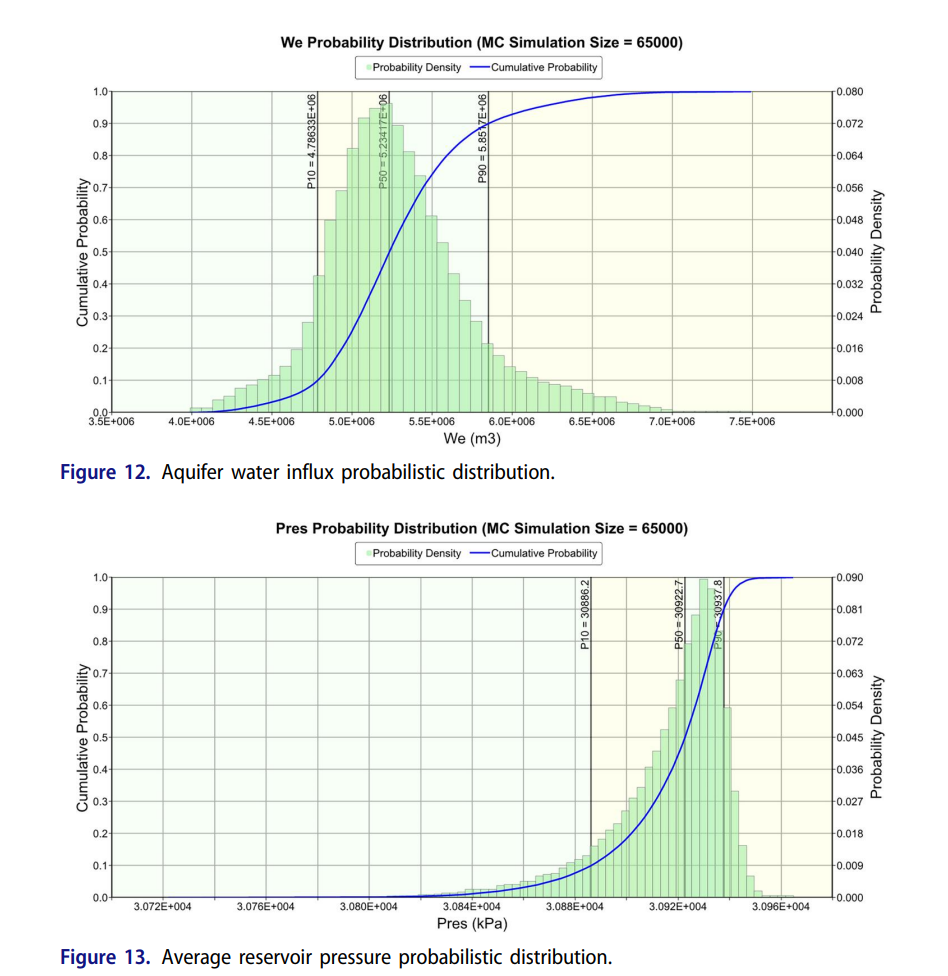
– 输出累积产油、产水、水体侵入、平均压力的概率分布曲线,实现快速不确定性量化。 - 未使用其他第三方软件,全部数值与概率计算均在 CMG 产品体系内完成。
主要结论
- 确定性基准方案 30 年累积产油 1.86×10⁶ m³,底水驱提供约 5×10⁶ m³ 水体侵入,平均压力仅下降 100 kPa,显示极强的天然能量可持续性;
- 代理模型验证精度高(R²>0.92,相对误差<3%),可替代全物理模拟进行大规模不确定性分析;
- 概率模拟揭示累积产油与产水分布范围宽(P90-P10 差异显著),而水体侵入与平均压力分布窄,表明“宏观能量供给风险低、局部可采量风险高”;
- 不确定性主要来自渗透率、孔隙度倍数及水体参数,建议通过井试、示踪剂或早期生产数据同化降低关键参数不确定度;
- 宽范围产出预测需配套灵活的地面水处理能力,并采用分段开发、适时将高含水井转为注水井等策略,以提升经济性与采收率。
作者单位
喀麦隆圣杰罗姆理工学院


Abstract
The Niger Delta region is known as a major hub of oil reserves in the world. However, most studies emphasize exploration and static characterization, with limited attention to the dynamic production behavior and uncertainty management of its reservoirs. Using static models as a foundation, reservoir engineering tools offer an opportunity to address this gap by simulating fluid flow and production under defined production setups, and uncertainty. This study employs numerical reservoir simulation to evaluate the production potential of a representative model of Niger Delta reservoir during its development phase, accounting for geological uncertainties. Polynomial regression, as a proxy model, enabled efficient Monte Carlo-based probabilistic simulations with verified accuracy (R2 > 0.92 and <3% relative error). The findings revealed substantial oil production with excellent production sustainability, primarily driven by aquifer support through water influx, with minimal pressure decline. However, significant risks associated with wide variations in oil production under uncertainties were identified, highlighting the importance of incorporating uncertainty reduction techniques such as data assimilation. The systematic integration of aquifer support within a probabilistic framework provides a novel and replicable approach for evaluating reservoir performance and guiding risk-informed development planning in the Niger Delta and analogous siliciclastic systems.
