Investigation of hydraulic fracture complexity and the benefits of maximizing or minimizing complexity in unconventional resources
本论文讨论了两个独立但相互关联的研究。第一项研究是历史工作的延伸,比较了多相流环境中横向裂缝与纵向裂缝水平井的差异。第二项研究调查了非常规资源和致密储层中水力压裂的复杂性及最大化或最小化复杂性的好处。
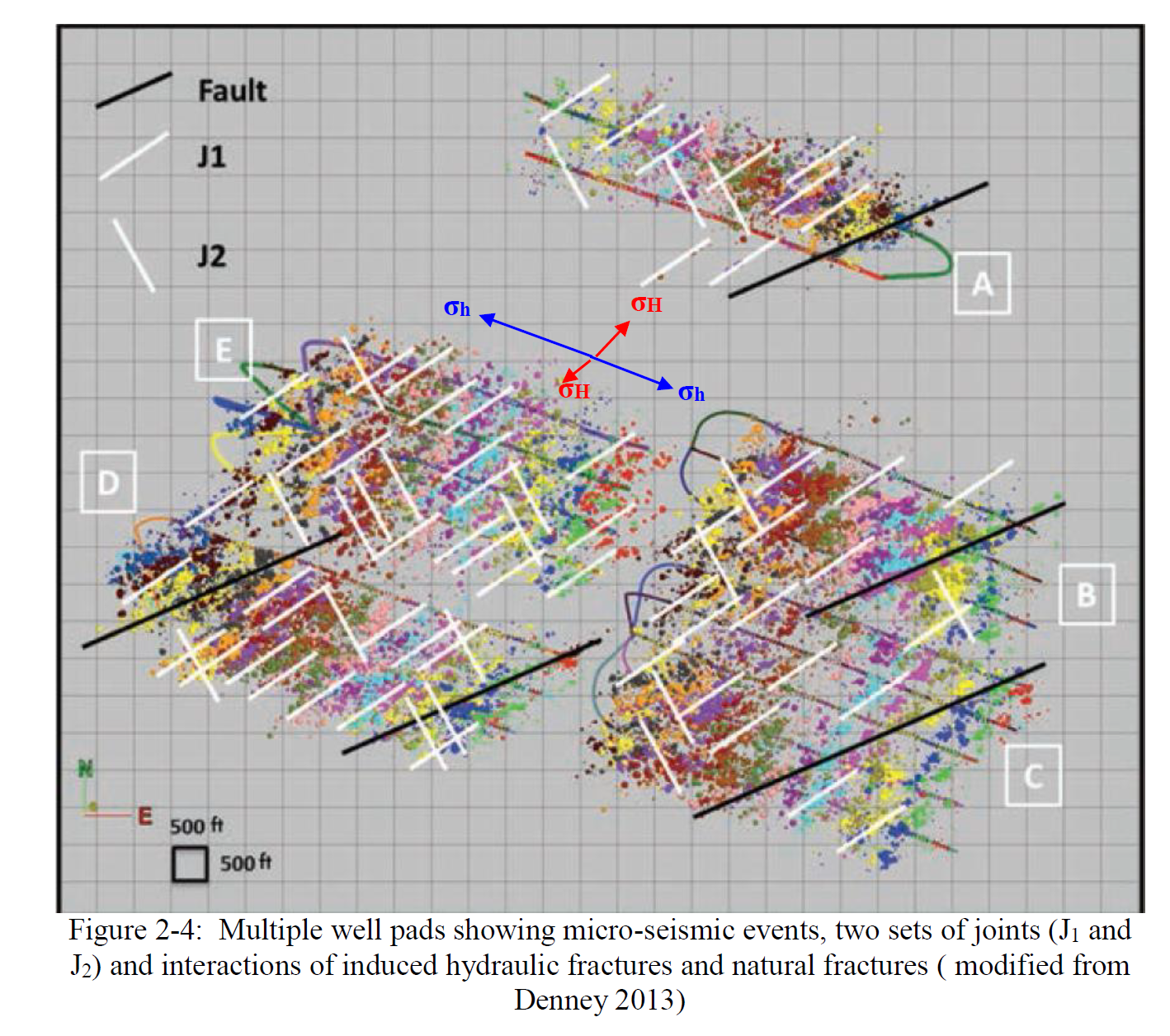
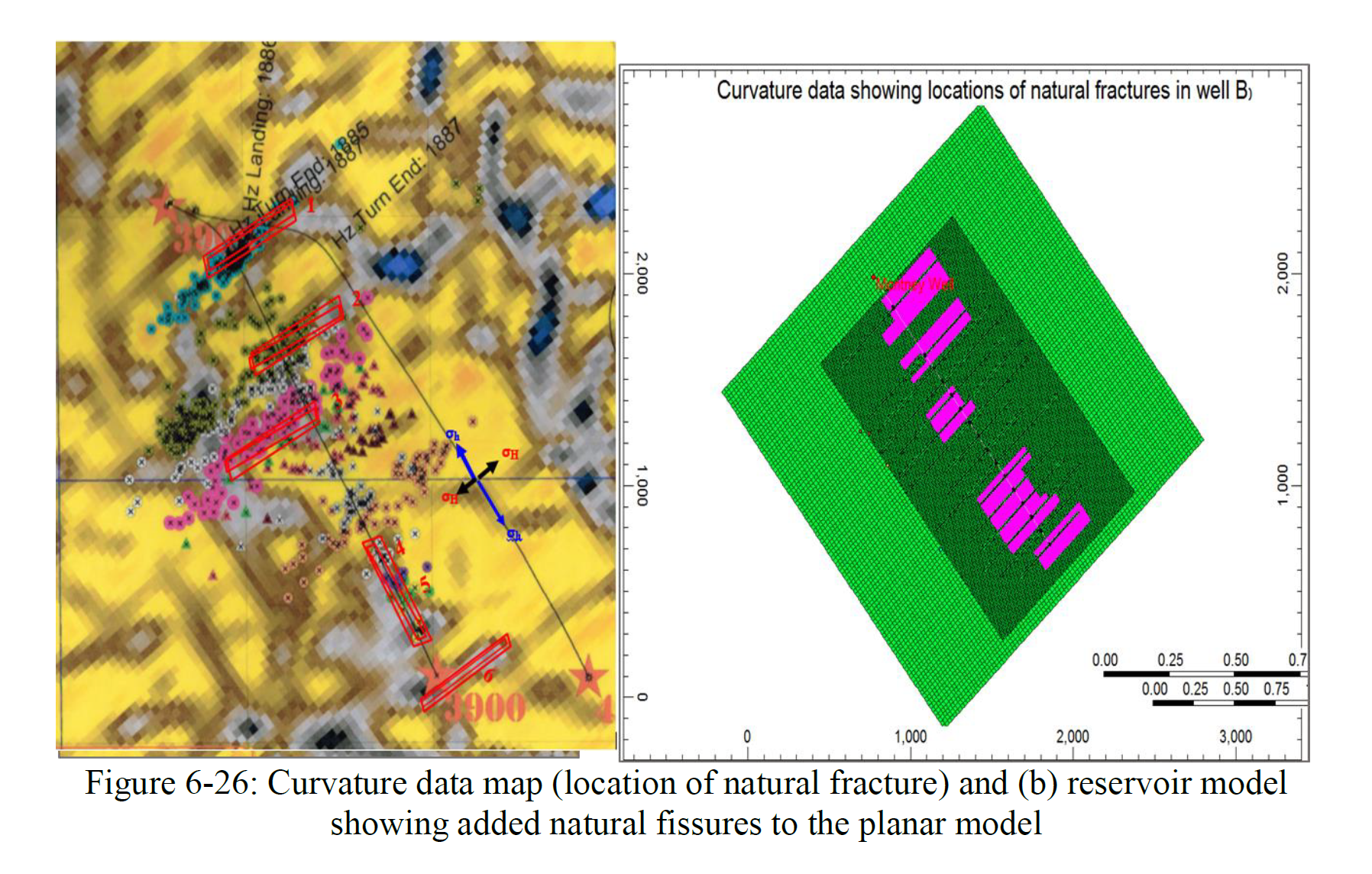
这项研究的主要目标是调查裂缝复杂性及其对井筒性能和经济的影响。为了实现这一目标,建立了三种不同的集成完井和储层模型。其中两个模型是混合储层模型和基于微地震的改造储层体积(SRV)模型,用于表征离散裂缝网络(DFN)的存在。DFN模型的结果与具有有限或无裂缝复杂性的集成面裂缝模型进行了比较。
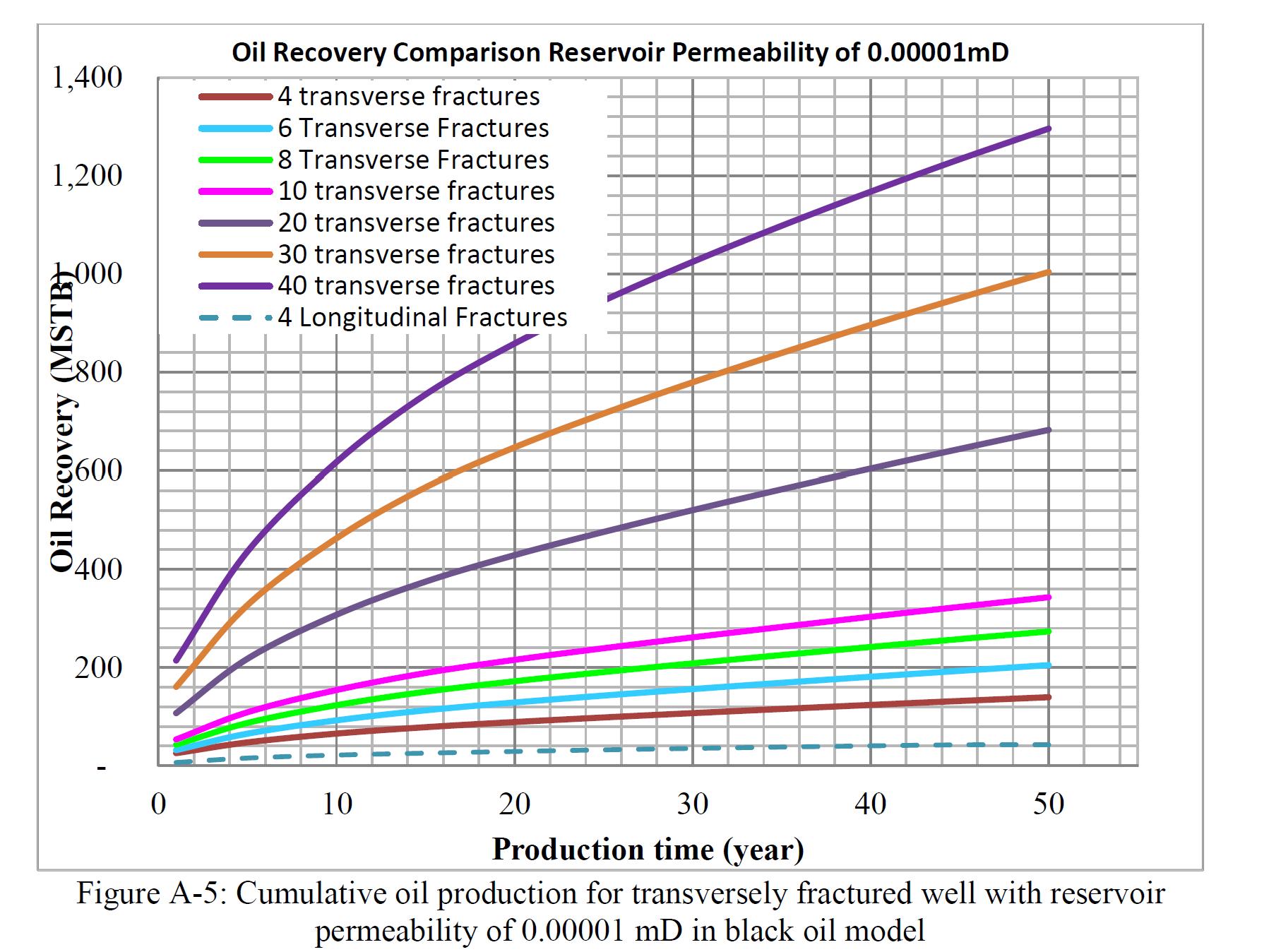
这项研究的第二个目标是确定储层渗透率的截断准则,可作为在多相流环境中选择是钻探横向裂缝还是纵向裂缝水平井时的指南。用于多相流的储层模型还将研究应力依赖性渗透率、吸附气体和非达西流动效应的影响。
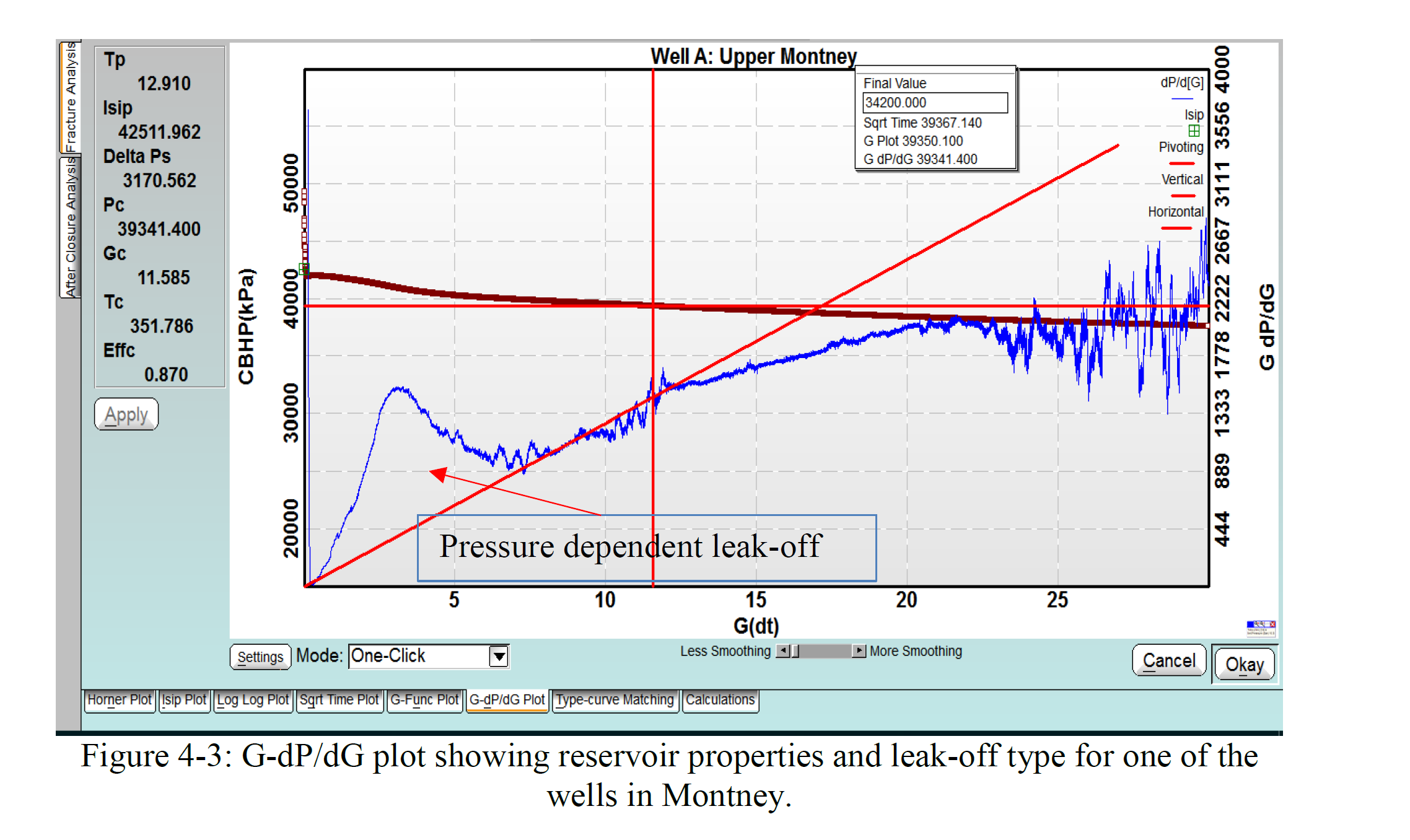
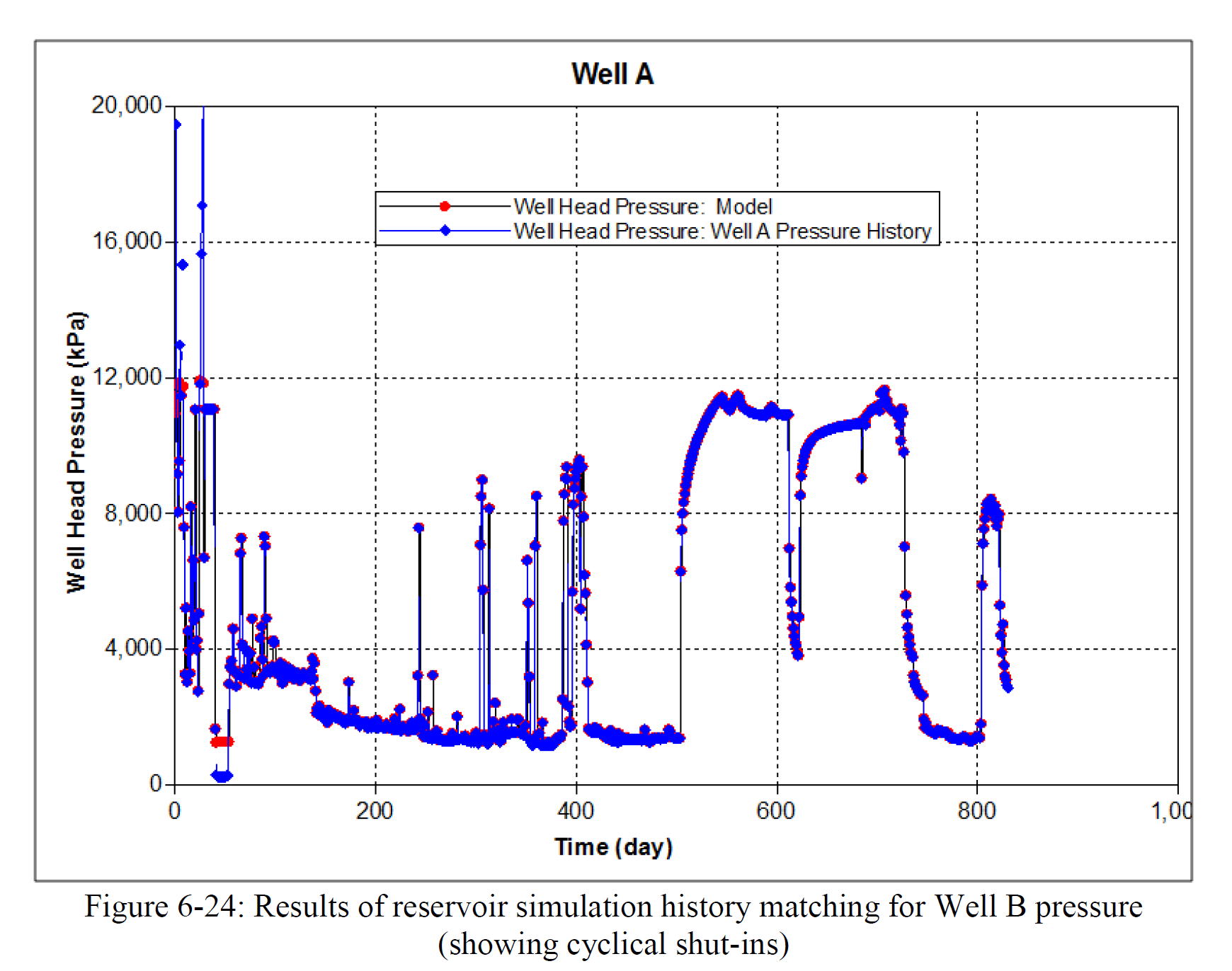
该研究的第三个目标是为蒙特尼页岩(尤其是上蒙特尼组)开发一个校准的水力压裂和储层模型。该模型将帮助公司选择上蒙特尼的最佳横向位置选项,确定阶段性钻井目标,并进行基于模型的裂缝段间距设定。
Abstract
“This dissertation discusses two separate, yet inter-related studies. The first study was an extension of historical work comparing transversely fractured versus longitudinally fractured horizontal wells in multiphase flow environment. The second study investigated hydraulic fracture complexities and the benefits of maximizing or minimizing complexities in unconventional resources and tight reservoirs.
The main objective of this research was to investigate fracture complexity and its impact on well performance and economics. To achieve that objective, three different integrated completions and reservoir models were built. Two of the three models, a hybrid reservoir model and micro-seismic based SRV (stimulated reservoir volume) model, were built to capture presences of discrete fracture networks (DFN). The results of the DFN-based models were compared to an integrated planar fracture model, which had bi-wing fractures with limited or no fracture complexity. The second objective of this research was to determine reservoir permeability based cut-off criterion that can be used as guide when selecting whether to drill transversely fractured versus longitudinally fractured horizontal wells in multiphase flow environment. The reservoir models built for the multiphase flow would also investigate the effects of stress dependent permeability, adsorption gas and non-Darcy flow effect.
The third objective of this research was to develop a calibrated hydraulic fracture and reservoir model for the Montney shale, particularly for the Upper Montney Formation. This model would help companies select best lateral placement options in the Upper Montney, stage perforation targets and model-based stage spacing”
Keywords and Phrases
Hydraulic fracture complexity; Petroleum economic analysis; PVT analysis; Reservoir simulations; Unconventional resources; Well stimulations