Developing machine learning models to predict CO2 trapping performance in deep saline aquifers
深层盐水层被视为地质储存二氧化碳(GCS)的潜在地点。为了更深入地了解盐水层中CO₂捕集的机制,有必要开发可靠的工具来评估CO₂固定效率。本文介绍了高斯过程回归(GPR)、支持向量机(SVM)和随机森林(RF)在盐水层中预测CO₂捕集效率的应用。
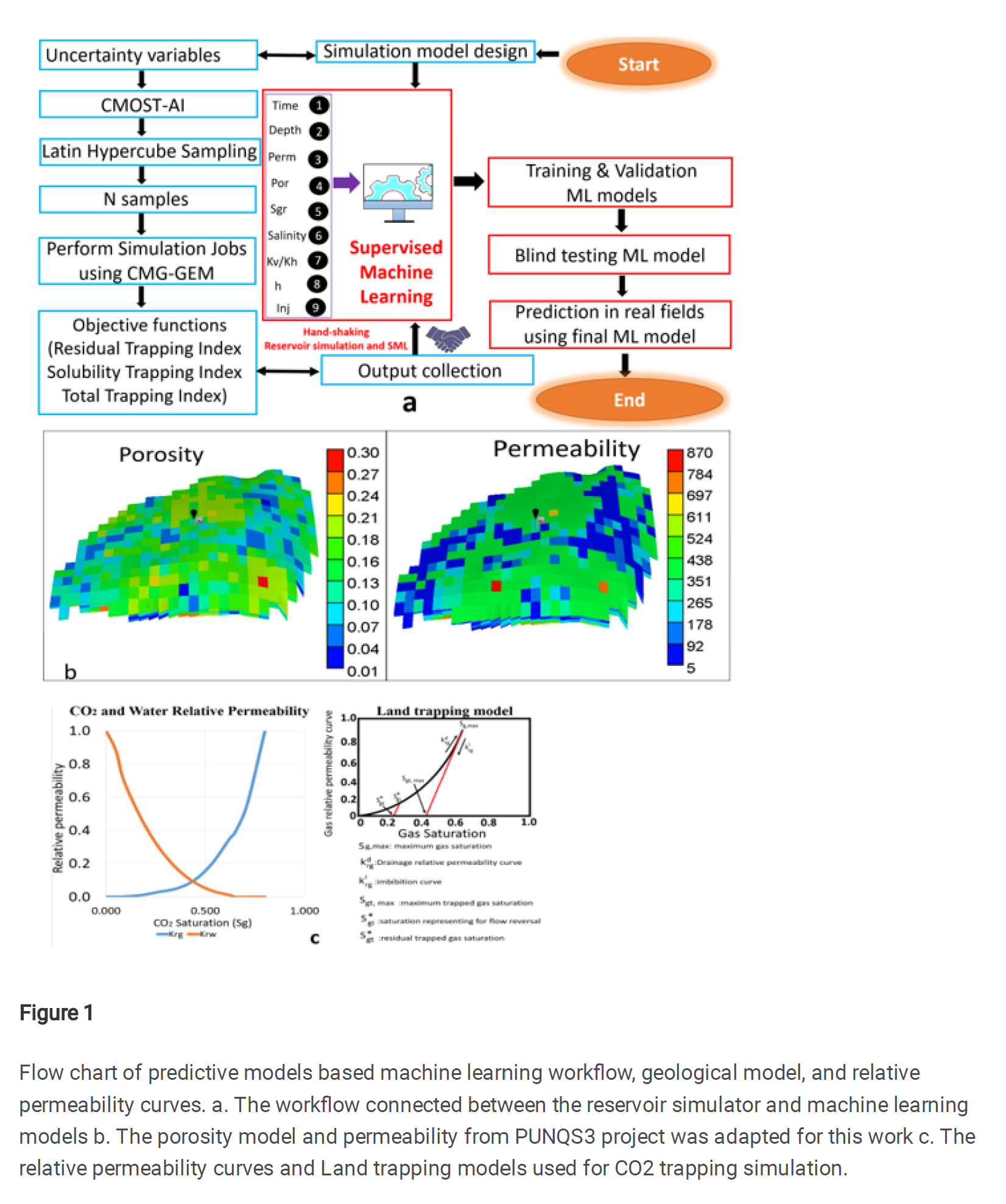
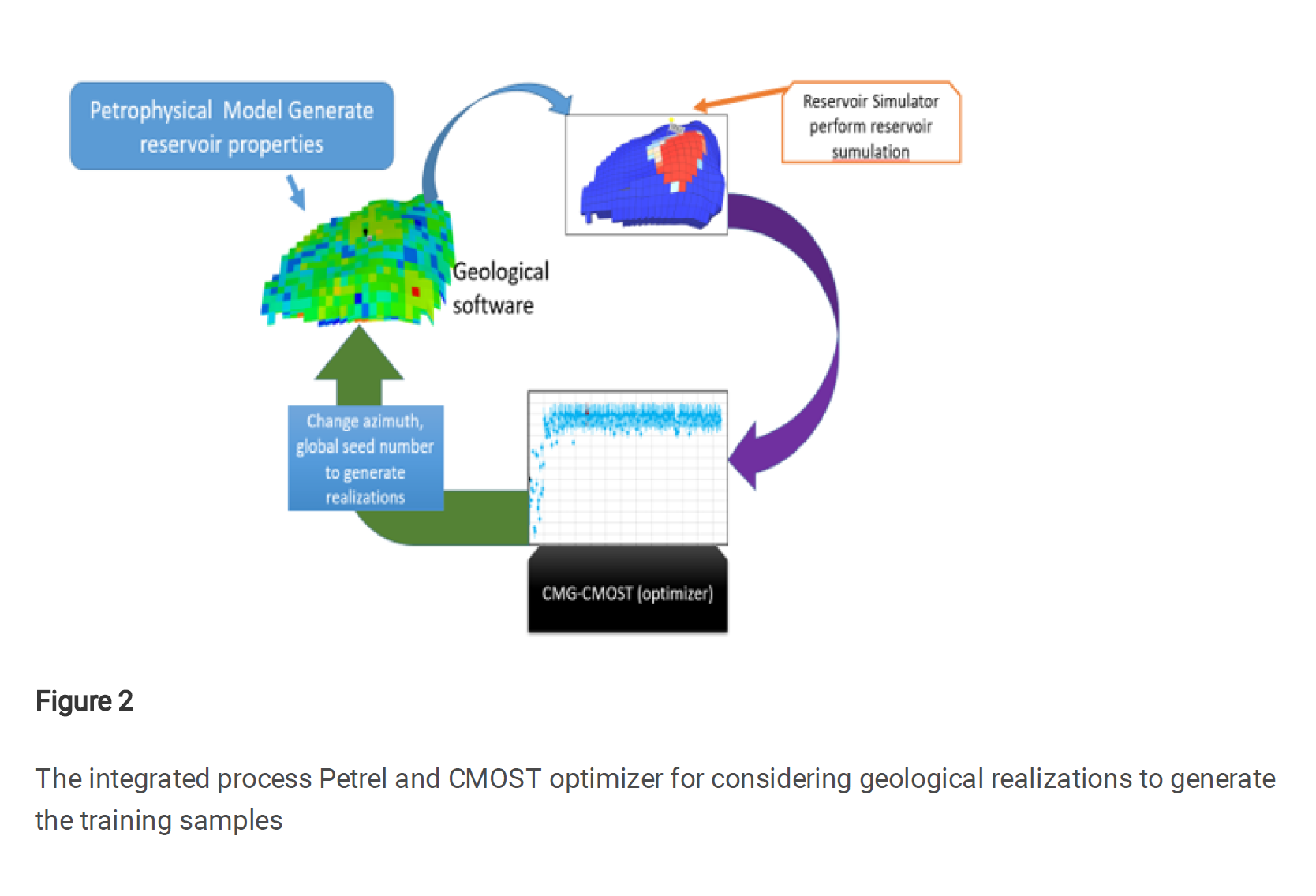
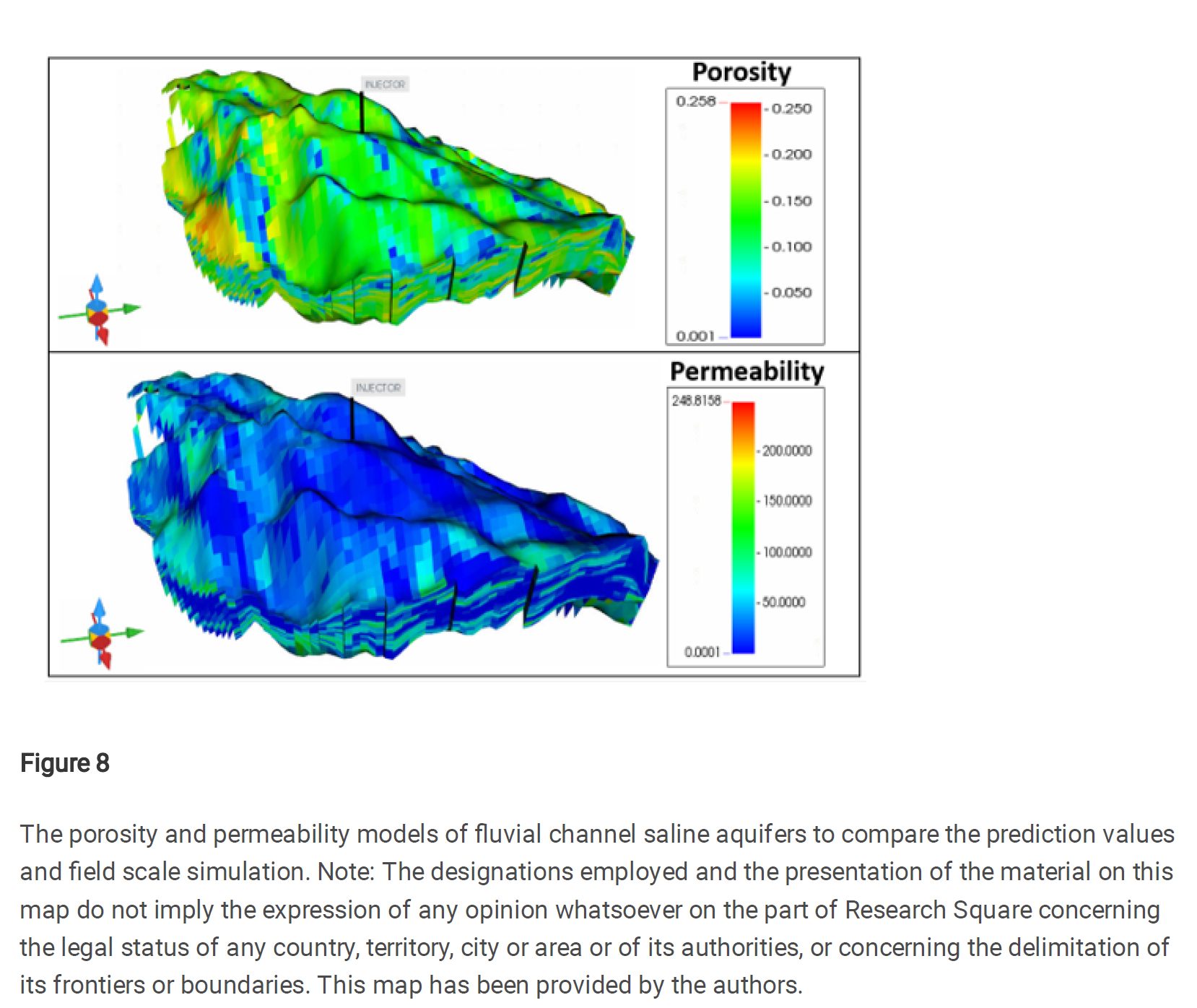
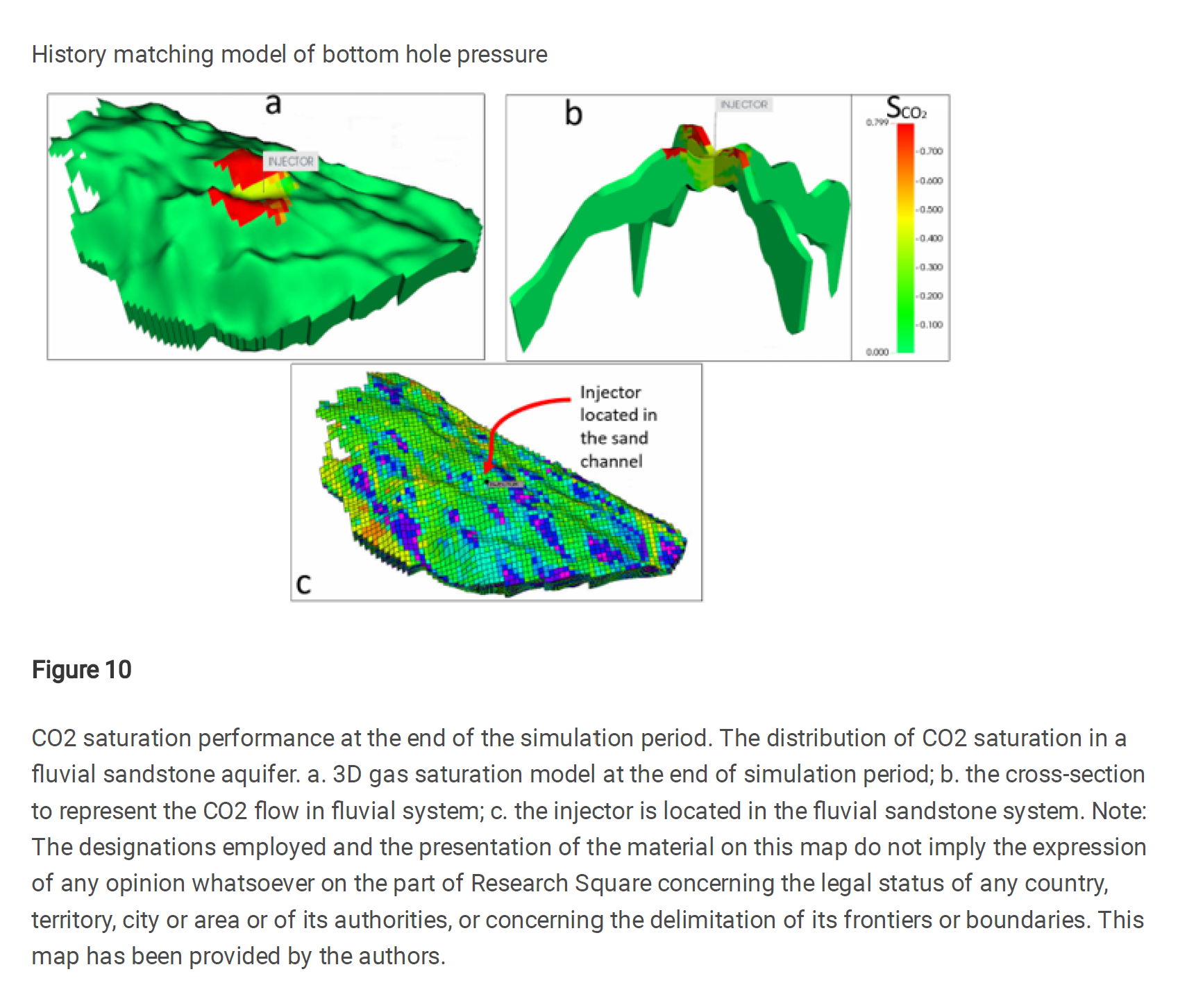
首先,通过使用地质参数、岩石物理特性和其他物理特性数据等不确定变量,创建了一个训练数据集。随后进行了总共101次油藏模拟样本,并收集了束缚空间捕集、溶解捕集和累计注入CO₂的数据。
预测结果显示,三个机器学习(ML)模型的性能排序为:GPR、SVM和RF。这些模型可用于预测深层盐水层中的CO₂捕集效率。其中,GPR模型表现出色,具有最高的相关系数(R² = 0.992)和最低的均方根误差(RMSE = 0.00491)。
通过在越南近海的一个实际油藏中验证了GPR模型的准确性和稳定性。预测模型在模拟场景与预测固定指数之间取得了很好的一致性。这些研究结果表明,GPR机器学习模型可以作为一个可靠的预测工具,支持数值模拟来估计地下CO₂固定的性能。
Abstract and Figures
Deep saline formations are considered as potential sites for geological carbon storage (GCS). To better understand the CO 2 trapping mechanism in saline aquifers, it is necessary to develop robust tools to evaluate CO 2 trapping efficiency. This paper introduces the application of Gaussian process regression (GPR), support vector machine (SVM), and random forest (RF) to predict CO 2 trapping efficiency in saline formations. First, the uncertainty variables, including geologic parameters, petrophysical properties, and other physical characteristics data were utilized to create a training dataset. A total of 101 reservoir simulation samples were then performed, and the residual trapping, solubility trapping, and cumulative CO 2 injection were collected.
The predicted results indicate that three machine learning (ML) models that evaluate performance from high to low: GPR, SVM, and RF can be selected to predict the CO 2 trapping efficiency in deep saline formations. The GPR model has an excellent CO 2 trapping prediction efficiency with the highest correlation factor (R ² = 0.992) and lowest root mean square error (RMSE = 0.00491). The accuracy and stability of the GPR models were verified for an actual reservoir in offshore Vietnam. The predictive models obtained a good agreement between the simulated field and the predicted trapping index. These findings indicate that the GPR ML models can support the numerical simulation as a robust predictive tool for estimating the performance of CO 2 trapping in the subsurface.