Completion Performance Evaluation in Multilateral Wells Incorporating Single and Multiple Types of Flow Control Devices Using Grey Wolf Optimizer
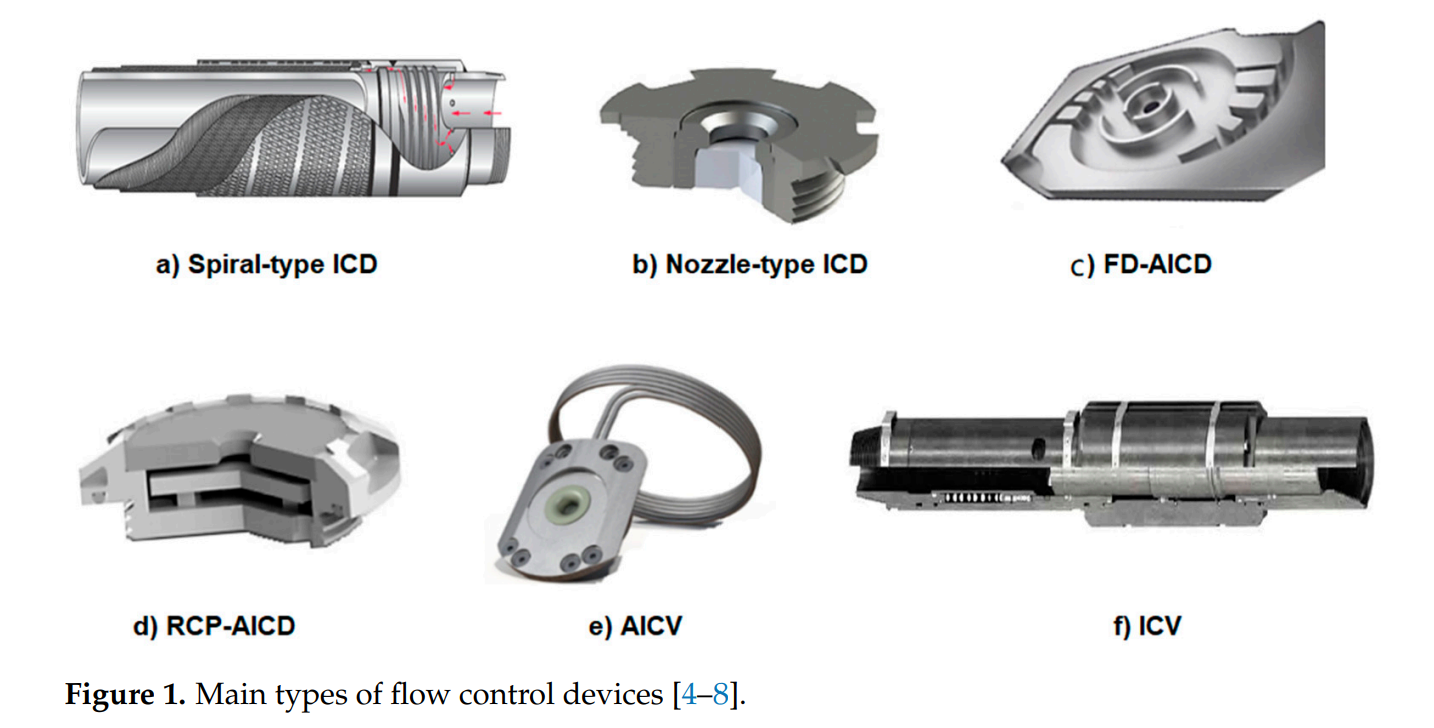
随着油气行业对多分支井(MLWs)的采用趋势增加,这些井的完井技术中结合了多种流量控制装置(FCDs)。在实际应用中,被动流量控制装置(ICDs)或自动流量控制装置(AICDs)被放置在侧向井段中,而间隔控制阀(ICVs)安装在侧向连接处,以调节每个侧向井段的总流量。尽管现场应用的结果看起来很有希望,但这种特定的井下完井组合的有效性尚未经过与使用单一流量控制装置类型的替代完井方法的比较测试。此外,这类完井的设计和当前评估主要基于分析工具,这些工具忽略了动态储层行为、长期生产影响以及不同装置之间的相关效应。
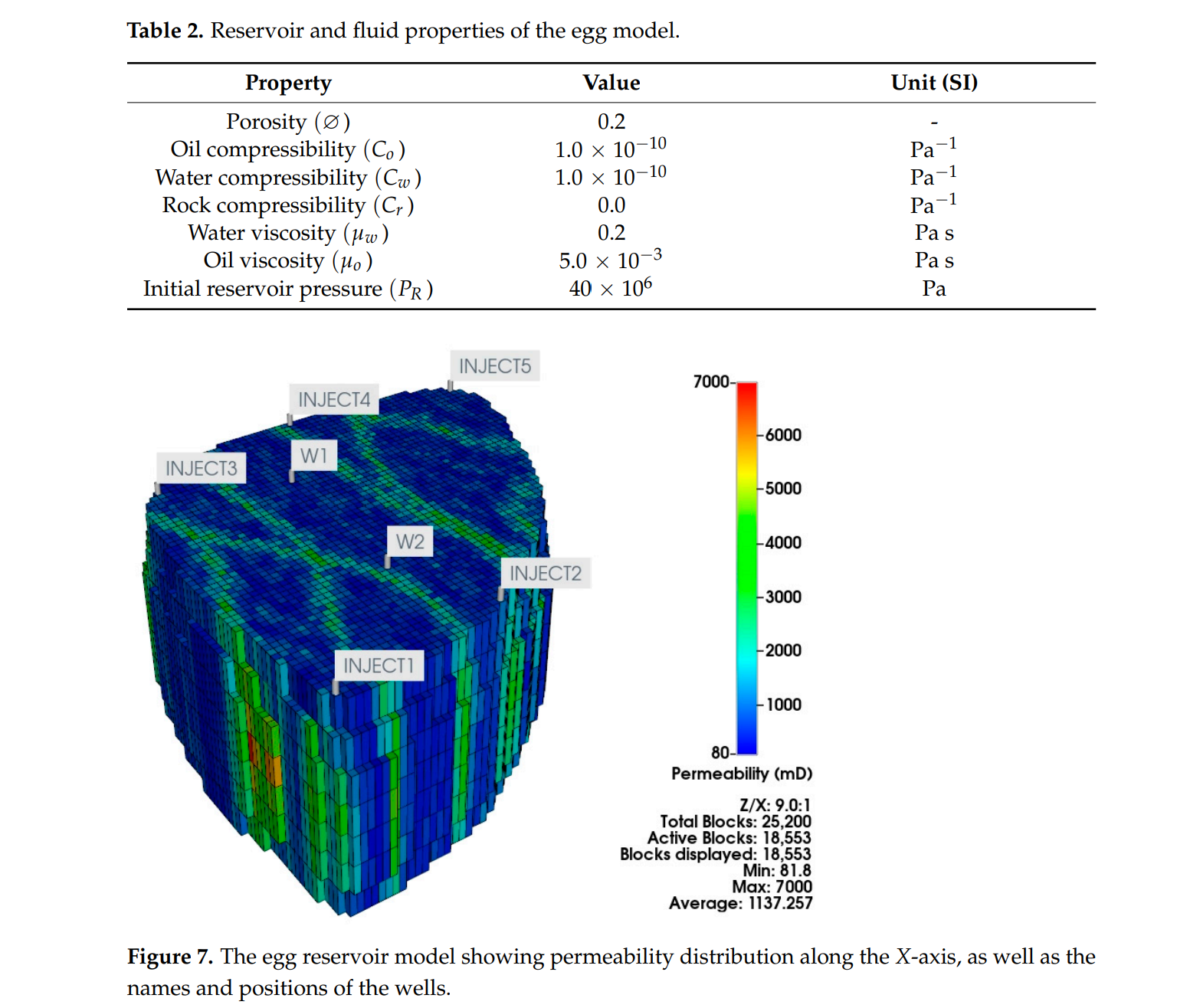
本研究探索了在多分支井中集成各种类型的流量控制装置的潜力,采用数值储层模拟器进行动态优化过程,同时使用灰狼优化器(GWO)作为优化算法。使用Egg基准储层模型,并开发了两个双侧向井。这些井作为实施和测试22个不同完井案例的基础,考虑了单一类型和多种类型的流量控制装置在反应性和主动性管理策略下的完井情况。这项全面的调查旨在阐明这些创新完井方法在优化井和储层性能方面的优势和局限性。
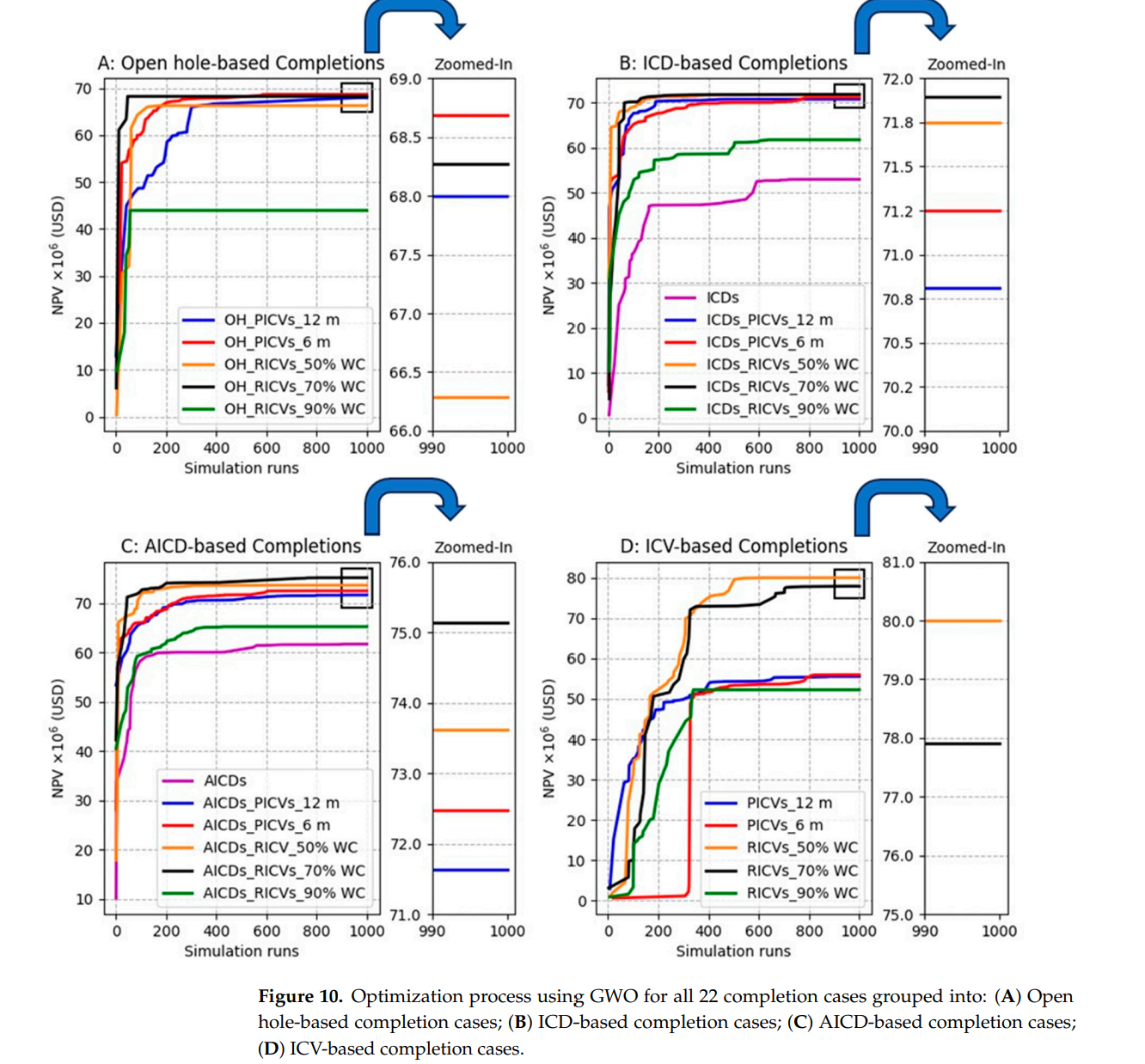
研究结果表明,在多分支井完井中结合使用多种类型的FCDs可以显著提高井的性能,并且可以超过包括ICDs或AICDs的单类型完井。然而,这种增强取决于在侧向井段内实施的装置类型以及用于控制侧向连接处ICVs的控制策略。基于多种类型FCD的完井的最佳性能是通过结合AICDs和反应性ICVs实现的,实现了约7500万美元的利润。这代表了与单一类型ICDs和AICDs安装相比,目标函数分别增加了42%和22%。
ICD和AICD在个别应用中的最优设置可能与与ICVs结合时的最优设置显著不同。这突出了不同装置(控制变量)之间的强相关性,证明了使用任何常见、简化的分析或标准顺序优化方法,这些方法不探索装置之间的相互依赖性,将在此类完井案例中导致次优解决方案。值得注意的是,仅安装ICVs的ICV基础完井,在ICVs反应性控制时表现出色,实现了令人印象深刻的8000万美元NPV,与单一类型ICDs和AICDs安装相比,目标函数分别增加了53%和30%。
CMG软件的应用情况:
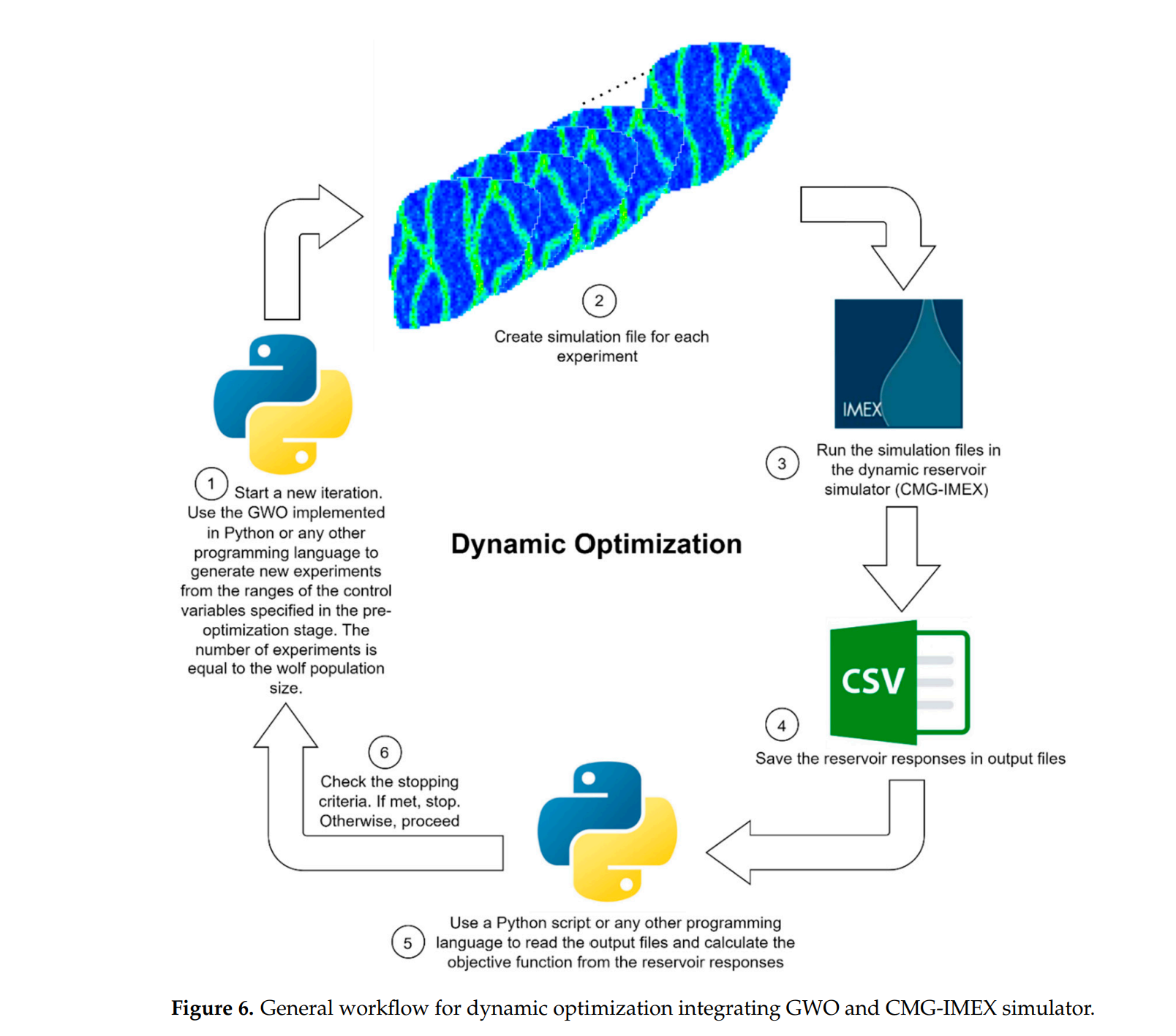
在本研究中,我们采用了CMG-IMEX软件的iSegWellTM模块来模拟先进的井完井技术,这一过程基于多段井(MSW)的概念。CMG-IMEX作为一个功能强大的数值储层模拟器,被用于评估净现值(NPV)目标函数。通过与灰狼优化器(GWO)的动态优化过程集成,我们能够确定每种完井情况下的最优流量控制装置(FCDs)设置。
此外,CMG-IMEX软件也被用于模拟间隔控制阀(ICV)的压降、被动流量控制装置(ICD)和自动流量控制装置(AICD)的性能。这些设备的控制是通过TS-EQSETTING关键字来实现的。在研究中,我们还特别使用了CMG-IMEX的VALVE SUBCRIT关键字来模拟ICV的控制和响应机制,以及SPIRAL关键字来模拟ICD和AICD的压降效果。
通过这些高级模拟技术的应用,本研究能够深入分析和评估多分支井中不同完井策略的性能,为油气行业提供了关于如何优化井完井设计的宝贵见解。
Abstract:
There has been a tendency in oil and gas industry towards the adoption of multilateral wells (MLWs) with completions that incorporate multiple types of flow control devices (FCDs). In this completion technique, passive inflow control devices (ICDs) or autonomous inflow control devices (AICDs) are positioned within the laterals, while interval control valves (ICVs) are installed at lateral junctions to regulate the overall flow from each lateral. While the outcomes observed in real field applications appear promising, the efficacy of this specific downhole completion combination has yet to undergo comparative testing against alternative completion methods that employ a singular flow control device type. Additionally, the design and current evaluations of such completions are predominantly based on analytical tools that overlook dynamic reservoir behavior, long-term production impacts, and the correlation effects among different devices. In this study, we explore the potential of integrating various types of flow control devices within multilateral wells, employing dynamic optimization process using numerical reservoir simulator while the Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) is used as optimization algorithm. The Egg benchmark reservoir model is utilized and developed with two dual-lateral wells. These wells serve as the foundation for implementing and testing 22 distinct completion cases considering single-type and multiple types of flow control devices under reactive and proactive management strategies. This comprehensive investigation aims to shed light on the advantages and limitations of these innovative completion methods in optimizing well and reservoir performance. Our findings revealed that the incorporation of multiple types of FCDs in multilateral well completions significantly enhance well performance and can surpass single-type completions including ICDs or AICDs. However, this enhancement depends on the type of the device implemented inside the lateral and the control strategy that is used to control the ICVs at the lateral junctions. The best performance of multiple-type FCD-based completion was achieved through combining AICDs with reactive ICVs which achieved around 75 million USD profit. This represents 42% and 22% increase in the objective function compared to single-type ICDs and AICDs installations, respectively. The optimal settings for ICD and AICD in individual applications may significantly differ from the optimal settings when combined with ICVs. This highlights a strong correlation between the different devices (control variables), proving that using either a common, simplified analytical, or a standard sequential optimization approach that do not explore this inter-dependence between devices would result in sub-optimal solutions in such completion cases. Notably, the ICVbased completion, where only ICVs are installed with lateral completion, demonstrated superior performance, particularly when ICVs are reactively controlled, resulting in an impressive 80 million USD NPV which represents 53% and 30% increase in the objective function compared to single-type ICDs and AICDs installations, respectively.
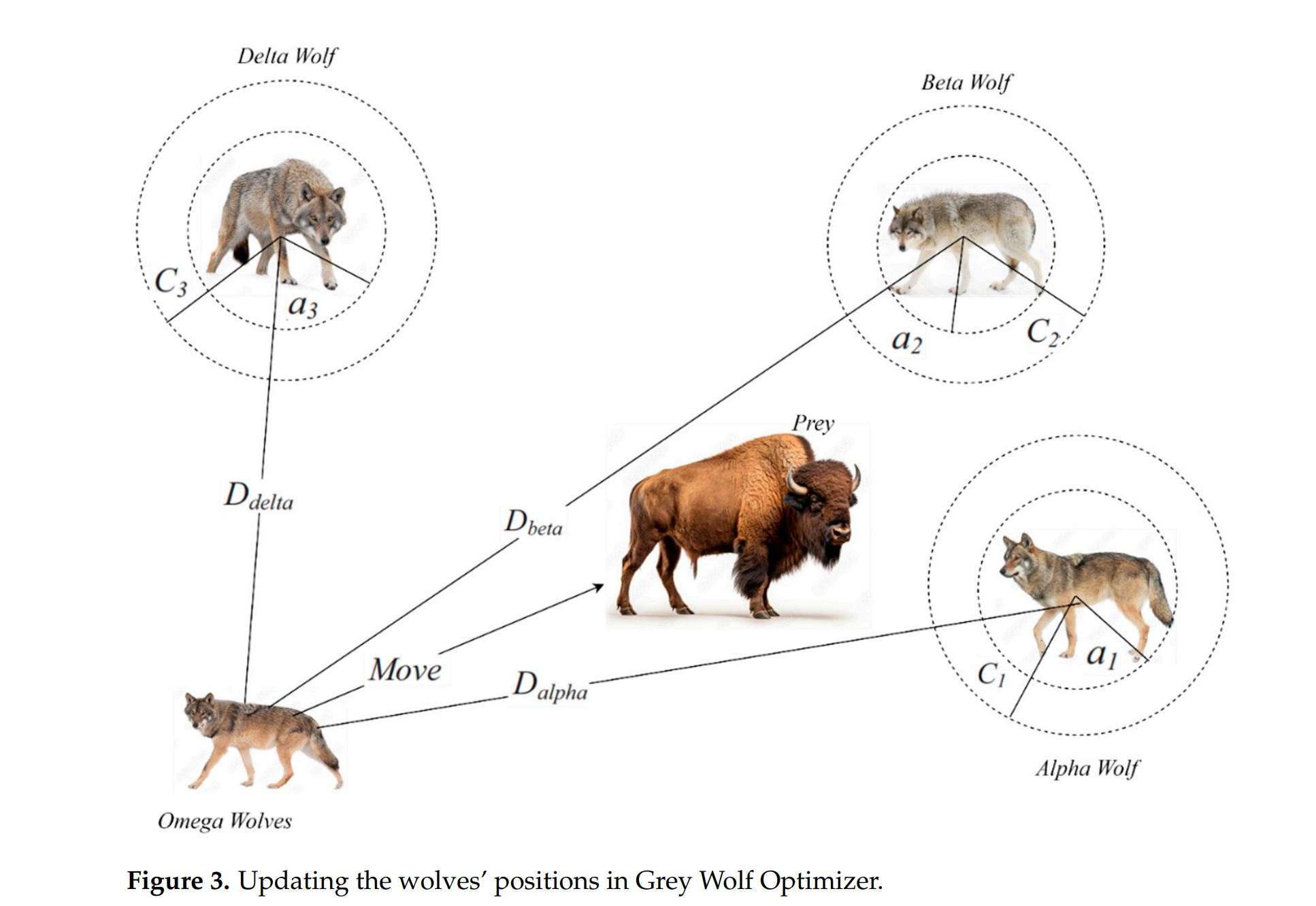
灰狼优化器(Grey Wolf Optimizer,简称GWO)是一种模拟自然界中灰狼社会等级和狩猎行为的优化算法。这种算法由Seyedali Mirjalili等人在2014年提出,它属于群体智能优化算法,通常用于解决全局优化问题。 GWO算法的基本思想是模仿灰狼群的领导结构和狩猎策略,其中包括α(Alpha,领导者)、β(Beta,次领导者)、δ(Delta,追随者)和ω(Omega,最底层成员)四种角色。在搜索最优解的过程中,狼群成员根据这些角色的位置更新自己的位置,通过追踪、包围和攻击猎物的策略来逼近最优解。 GWO算法的主要特点包括:
- 群体智能:算法中包含了多个搜索代理(即“狼”),它们共同协作以找到最优解。
- 社会等级:狼群中的每个成员根据其适应度被分配到不同的社会等级中。
- 狩猎策略:算法模拟了灰狼群的狩猎行为,包括对猎物的追踪、包围和攻击。
- 参数更新:狼群成员的位置通过数学模型更新,这些模型受到狼群社会结构和狩猎行为的影响。
- 全局搜索能力:GWO在搜索过程中能够平衡探索(exploration)和开发(exploitation)的平衡,以避免陷入局部最优解。 GWO算法因其简单、鲁棒和高效的特点,已被广泛应用于多个领域的优化问题,如函数优化、神经网络训练、模式识别、机器学习以及工程设计等。在上述提供的文章摘要中,GWO被用于优化多分支井中流量控制装置的配置,以提高油气井的生产效率和经济效益。
作者单位:
- 英国赫瑞瓦特大学地质能源工程研究所,爱丁堡
- 挪威东南部大学过程、能源与环境技术系,波什格伦
