CO2 Storage and Evaluation of Important Parameters Affecting the CO2 Plume Distribution: Simulation and Sensitivity Analysis
本研究的主要目标是识别和分析影响储层中CO2羽流扩展的关键参数。了解碳封存的地下动力学将有助于更好地规划地下过程,模拟模型使用商业软件CMG开发。研究了30年注入期和170年注入后期的羽流动态,包括羽流体积和羽流几何形状。此外,评估了不同捕集机制在储存过程中的贡献。此外,进行了敏感性分析,以评估包括孔隙度、渗透率、注入速度和注入井底压力在内的变量的影响。
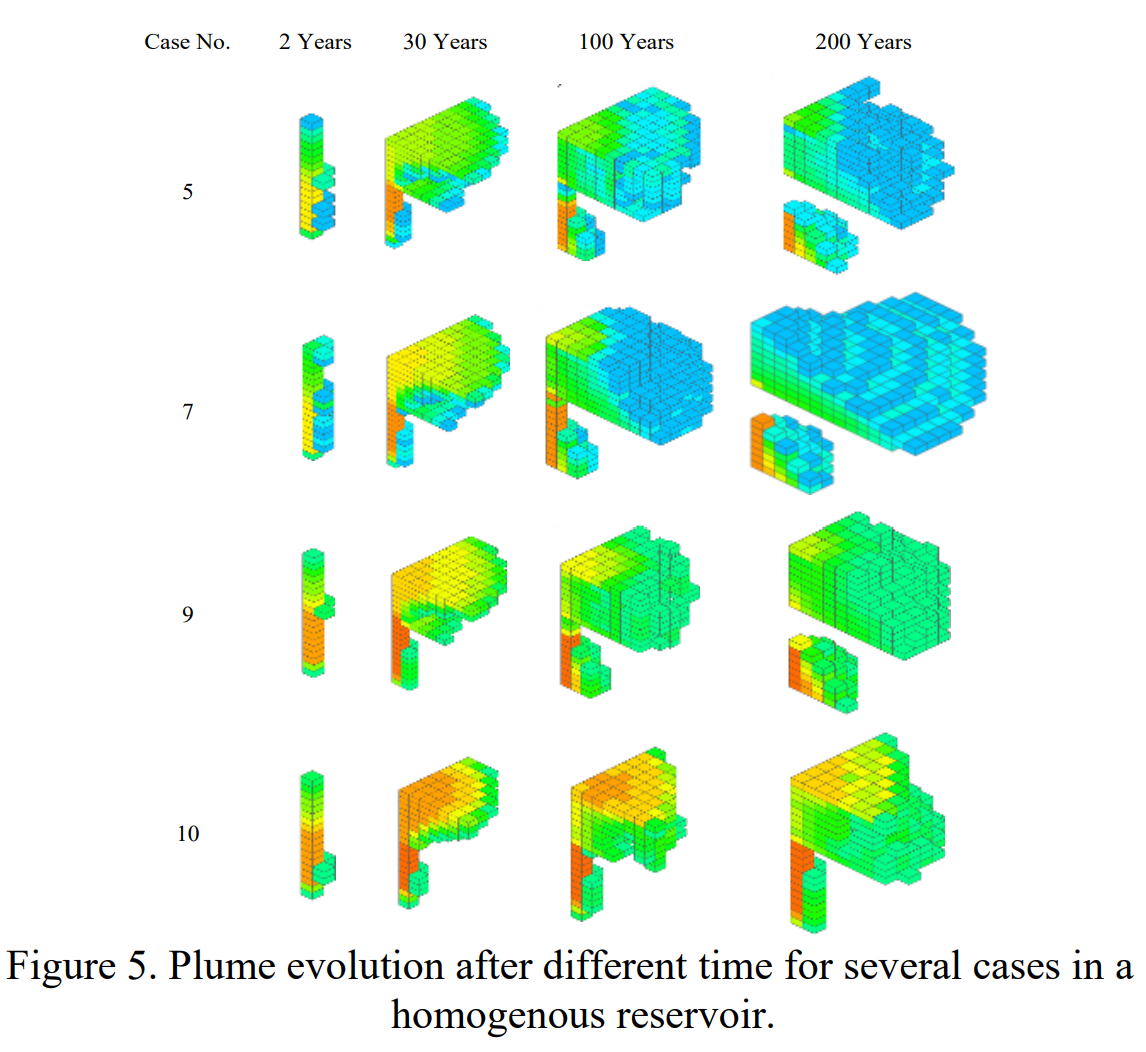
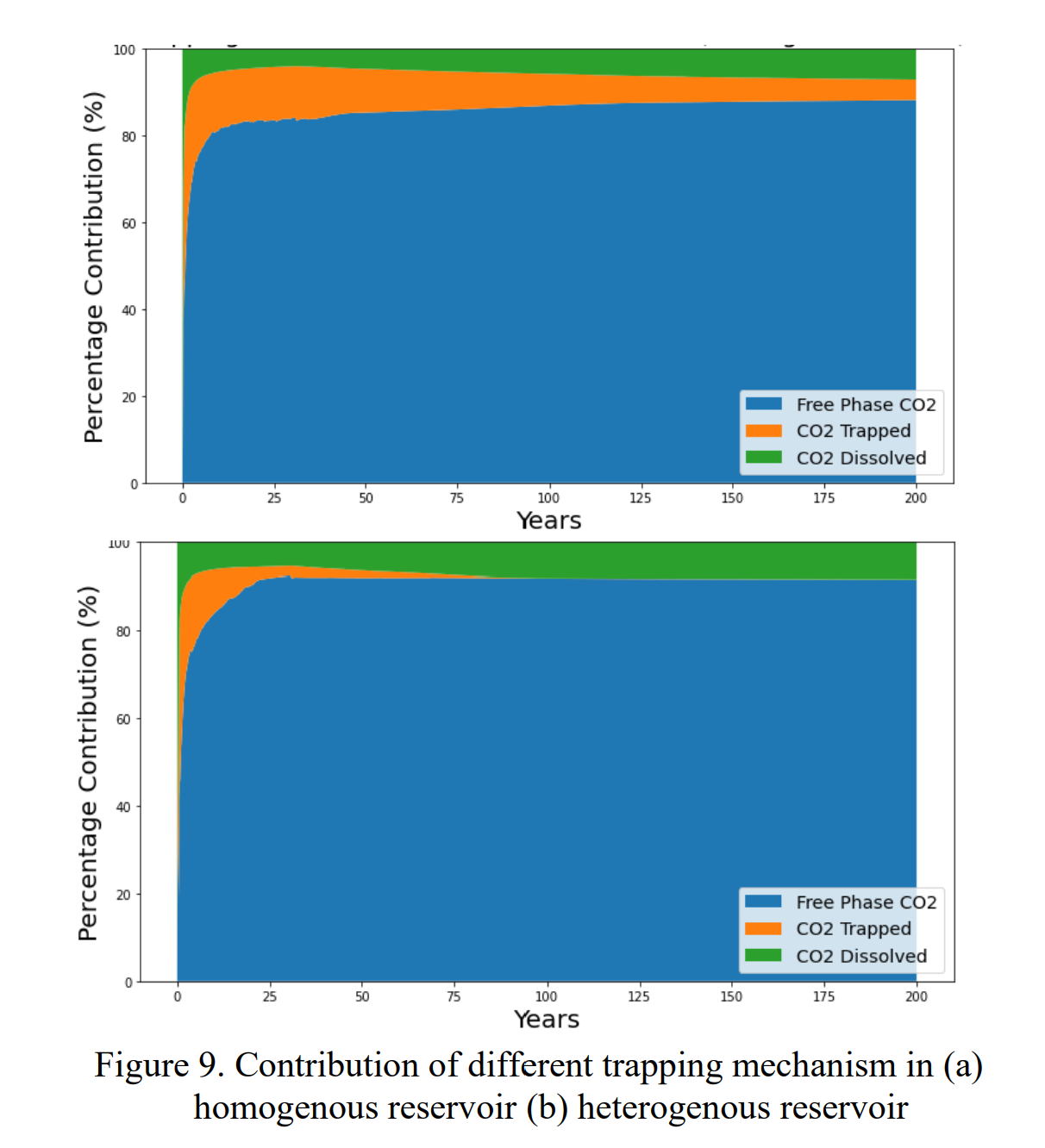
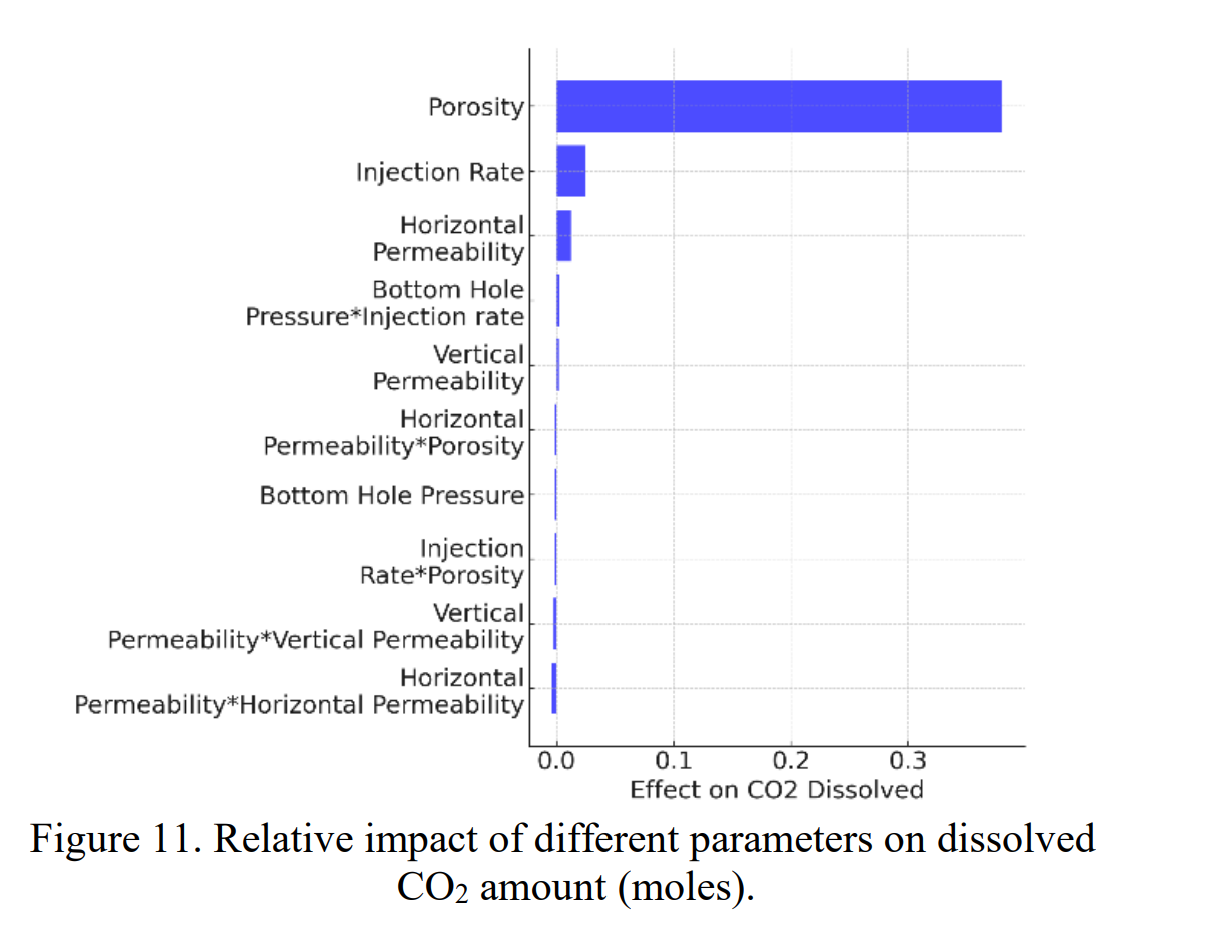
模拟结果表明,CO2羽流在注入期间以增加的速度传播,并在注入结束后以相对较低的速度继续分散。当水平渗透率大于垂直渗透率时,羽流的水平扩散显著大于垂直传播。此外,羽流体积与注入的CO2量呈线性关系。就储存效率而言,最常见的CO2是自由相超临界CO2,占储存CO2的约80%,其余为构造或残留捕集和溶解的CO2。从均质储层的敏感性分析中可以得出结论,水平渗透率对CO2的构造和残留捕获影响最大(42%),而孔隙度对CO2的溶解影响最大(38%),有助于溶解捕集机制。
CMG软件应用情况
本研究使用CMG(Computer Modelling Group Ltd.)软件进行模拟设置、求解系统和结果分析。CMG的五个模块被用于开发模拟模型,以研究CO2运移,并进行敏感性分析,以了解不同参数对储存能力的影响。各个模块的具体应用总结如下:
- GEM:
- GEM是CMG的核心模块,用于建立和求解复杂的地质模型。它支持多种物理场的模拟,包括流体流动、热传导和化学反应。在本研究中,GEM用于模拟CO2在储层中的迁移和羽流发展。
- Builder:
- Builder模块用于创建和编辑地质模型的结构和属性。它允许用户定义储层的几何形状、网格划分以及岩石和流体的物理特性。在本研究中,Builder用于构建CO2储存模拟所需的3D储层模型。
- cEdit(Command Editor):
- cEdit是一个命令行编辑器,用于输入和修改模拟参数。它允许用户通过文本命令来控制模拟过程,包括注入速度、压力条件和其他操作参数。在本研究中,cEdit用于设置CO2注入井的操作参数和约束条件。
- CMOST(CMG’s Optimization and Sensitivity Analysis Tool):
- CMOST模块用于执行敏感性分析和优化研究。它通过实验设计(DoE)方法系统地变化输入参数并运行多次模拟,以评估不同参数对模拟结果的影响。在本研究中,CMOST用于分析孔隙度、渗透率、注入速度等参数对CO2捕集和溶解的影响。
- Results:
- Results模块用于分析和可视化模拟结果。它提供了多种工具来查看和解释模拟数据,包括羽流体积、压力分布和流体性质等。在本研究中,Results模块用于评估不同捕获机制的贡献以及储层参数对CO2储存效率的影响。

Abstract
Carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) offers a potential solution to mitigate the effects of anthropogenic CO2 and to reduce the direct CO2 emissions from stationary sources into the atmosphere. The captured CO2 is injected into deep saline-water saturated formations or in depleted oil and gas fields, or into the oil fields for storage and/or enhanced oil recovery (EOR). The primary objective of this study is to identify and analyze the critical parameters affecting CO2 plume development in the reservoir. Understanding the subsurface dynamics of carbon sequestration will facilitate to plan the subsurface process better. The simulation models are developed using the commercial software Computer Modelling Group, CMG. The plume dynamics that include plume volume and plume geometry over 30 years of injection and 170 years of post-injection period is investigated. Additionally, the contribution of different trapping mechanisms over the time horizon in the storage process is assessed. Moreover, a sensitivity analysis is done for evaluating the impact of variables including porosity, permeability, injection rate, and injector bottom hole pressure. The simulation results show that CO2 plume propagates at an increased rate during the injection period and continues to disperse at a comparatively reduced rate after the injection ends. Additionally, the plume volume shows a linear relationship with the injected CO2 amount. In terms of storage efficiency, the most prevalent CO2 is free phase super critical CO2 that contributes around 80% of the stored CO2 whereas the rest are structurally or residually trapped and dissolved CO2. From the sensitivity analysis in a homogenous reservoir, it can be concluded that the horizontal permeability is impacting the most (42%) for structural and residual trapping of CO2 whereas porosity impacts the most (38%) for dissolution of CO2 contributing to solubility trapping mechanism.
Key phrases: CCUS, CO2 injection rate, CO2 storage, CO2 trapping mechanism, Plume dynamics, sensitivity
作者单位
挪威东南大学过程、能源与环境技术系
