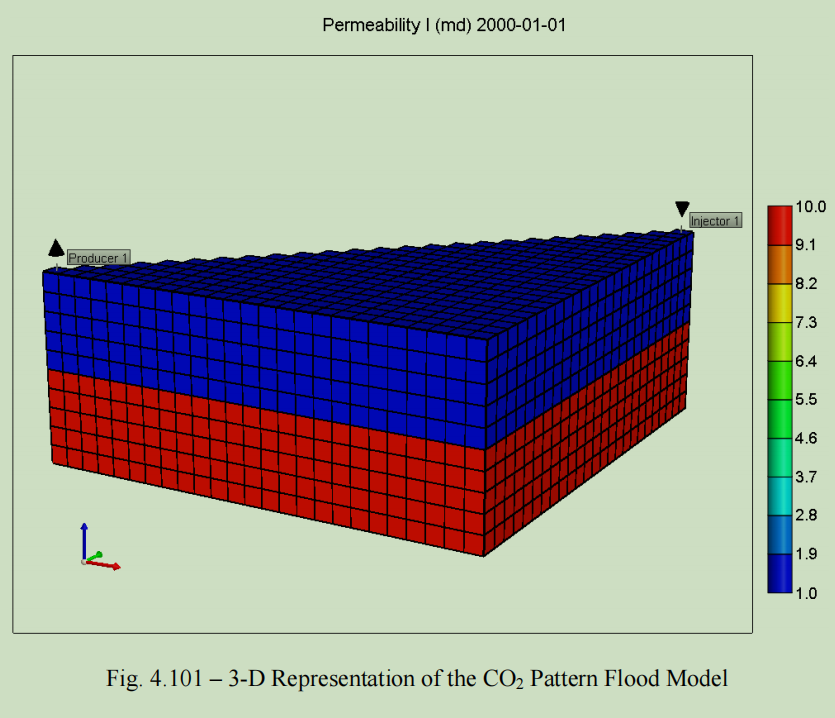
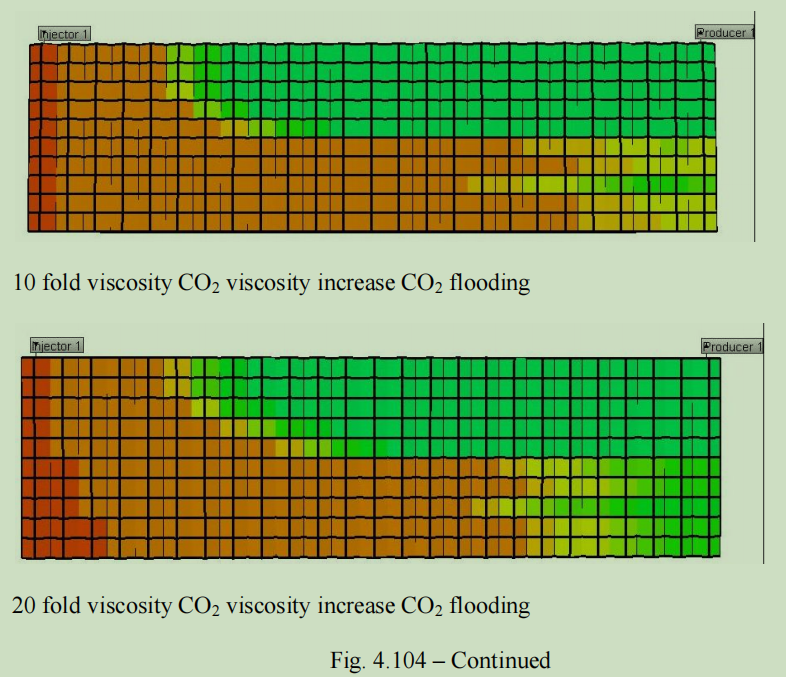
CO2被广泛用作非混相和混相驱油过程,以实现三次采油。CO2驱的应用存在一些问题,尤其是当储层中存在非均质物性时,如裂缝和高渗通道。驱替过程中,二氧化碳将形成指进,同时油藏残余大量剩余油/捕集油。早期气体突破时CO2相关项目中的一个非常普遍的问题,降低了CO2驱的整体波及效率。本研究旨在利用交联凝胶调剖和CO2增粘剂技术提高CO2驱油效率。通过岩心实验研究,探讨应用CO2运移速度控制技术的可能性,并进行了相应的模拟工作。
在实验室研究中,CO2 岩心驱替系统与CT(计算机扫描)集成,获得岩芯中CO2饱和度分布的实时岩心图像。该系统被应用于交联聚合物凝胶处理和CO2增粘剂研究,并生成具有鲜明的相位对比图像。对于凝胶调剖研究,通过应用交联凝胶消除渗透率对比,并将CO2改道到低渗透区域以获得增量采油,取得了有希望的结果;借助CT图像,研究了凝胶强度与泄漏程度的关系。对于CO2增粘剂研究,测试了几种潜在的增粘剂化学品,发现PVAc(聚醋酸乙烯酯)/甲苯组合效果最好。后续研究表明,就驱替效率而言,增稠CO2优于纯CO2。本研究时CO2传质速度控制技术的一项初步探索,并为未来研究提供方向。
STUDY OF CO2 MOBILITY CONTROL USING CROSS-LINKED GEL CONFORMANCE CONTROL AND CO2 VISCOSIFIERS IN HETEROGENEOUS MEDIA
ABSTRACT
Study of CO2 Mobility Control Using Cross-linked Gel Conformance Control and CO2
Viscosifiers in Heterogeneous Media. (August 2010)
Shuzong Cai, B.S., Peking University; M.S., New York University
Chair of Advisory Committee: Dr. David S. Schechter
CO2 has been widely used as a displacement fluid in both immiscible and miscible displacement processes to obtain tertiary recovery from the field. There are several problems associated with the application of CO2 flooding, especially when there is a significant presence of heterogeneous elements, such as fractures, channels and high permeability streaks within the reservoir. With flooding, CO2 will finger through the target zone while leaving most of the residual/trapped oil untouched. As a result, early gas breakthrough has been a very common problem in CO2-related projects, reducing the overall sweep efficiency of CO2 flooding. This research aims at improving the CO2 flood efficiency using cross-linked gel conformance control and CO2 viscosifier technique. A series of coreflood experiment studies have been performed to investigate the possibility of applying CO2 mobility control techniques. Corresponding simulation works have also been carried out to predict the benefits of applying CO2 mobility control techniques in the field.
In the laboratory study, the CO2 coreflood system was integrated with the CT (Computed Tomography)-scanner and obtained real-time coreflood images of the CO2 saturation distributions in the core. This system was applied to the research of both cross-linked polymer gel treatment and CO2 viscosifier study and produced images with sharp phase contrasts. For the gel conformance study, promising results were obtained by applying cross-linked gel to eliminate permeability contrast and diverting CO2 into low permeability regions to obtain incremental oil recovery; also studied were the gel strength in terms of leak-off extent with the aid of CT (Computed Tomography) images. For the CO2 viscosifier research, we tested several potential viscosifier chemicals and found out PVAc (Polyvinylacetate)/toluene combination to be the most promising. The follow-up study clearly demonstrates the superiority of viscosified CO2 over neat CO2 in terms of sweep efficiency. This research serves as a preliminary study in understanding advanced CO2 mobility control techniques and will provide insights to future studies on this topic.