Effect of fracture design parameters on the well performance in a hydraulically fractured shale gas reservoir
Abstract
This study investigates the impact of fracture design parameters from the results of sensitivity analysis in a shale gas reservoir. When a shale gas reservoir is hydraulically fractured, the fracture network systems are formed comprising primary and secondary fractures. In the case of low permeability reservoir, especially, the more complex fracture network systems is, the more the productivity is improved. In this study, a sensitivity analysis was carried out to evaluate the impact of fracture design parameters on the well performance in a hydraulically fractured shale gas reservoir using simulation model. The productivity is improved when the secondary fracture conductivity increases or spacing decreases with various conditions of reservoir. It is shown that the determination of whether to increase or decrease secondary fracture growth is required to improve the productivity of shale gas reservoir. Based on the results, a guideline for hydraulic fracturing is proposed.
Keywords:
Shale gas, Fracture design parameter, Multistage fracturing of horizontal wells, Sensitivity analysis
Table 1. Gas production mechanism (Li et al., 2013).
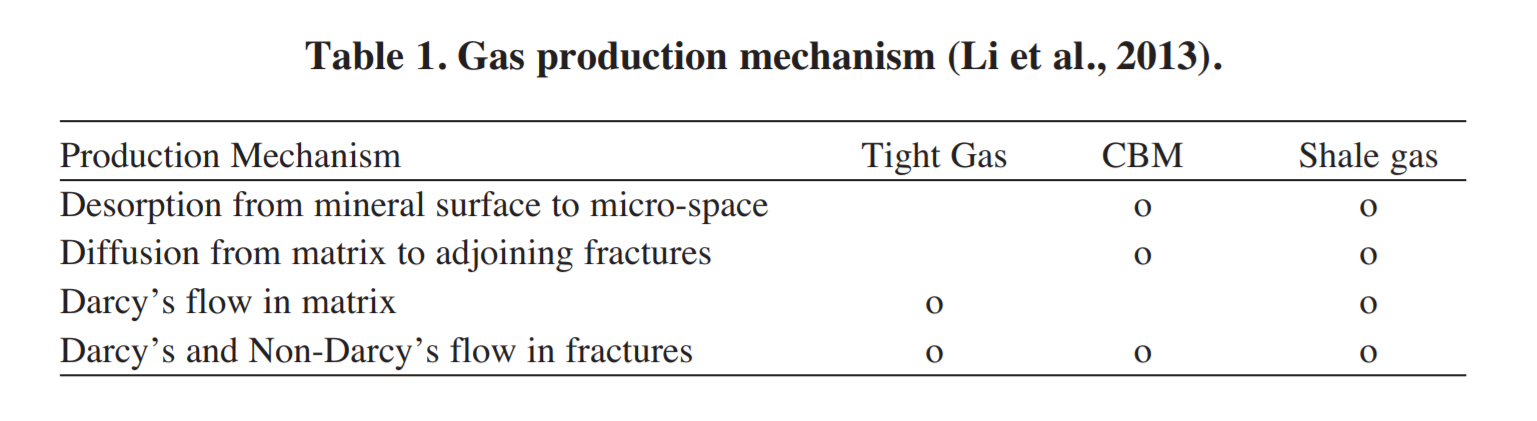
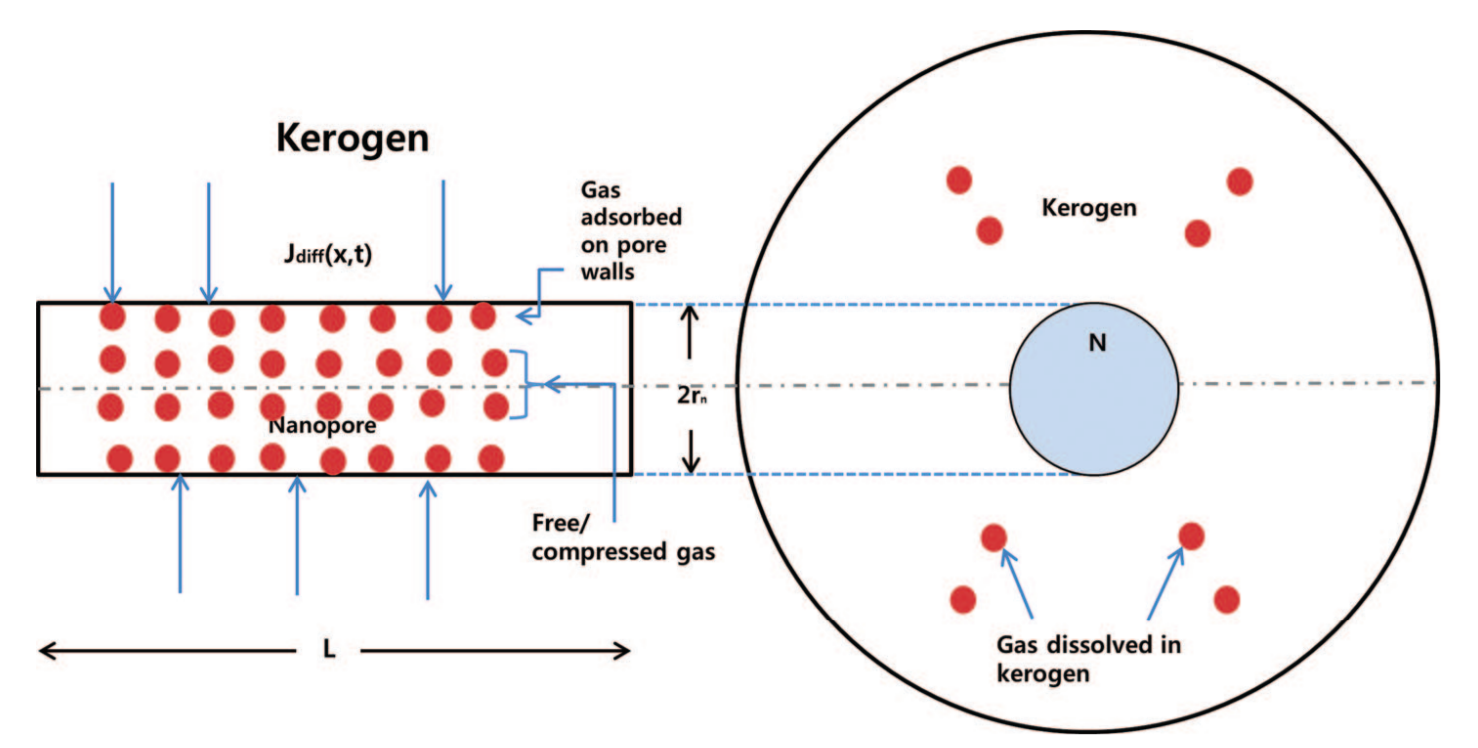 Figure 1. Physical model to model the flow in nanopore (Swami, 2012).
Figure 1. Physical model to model the flow in nanopore (Swami, 2012).