Impact of small-scale heterogeneity on field-scale CO2 migration and trapping
本研究通过实验室实验与矿场尺度数值模拟(使用CMG软件),探讨了沉积地层中小尺度非均质性对CO₂运移和封存的影响。实验采用米级平板反应器模拟具有不同粒度对比的波纹沉积层,发现CO₂的毛管力捕集量高度依赖于非均质性的类型和程度,甚至波纹层理模式的微小变化也会显著改变捕集羽流的规模和饱和度。
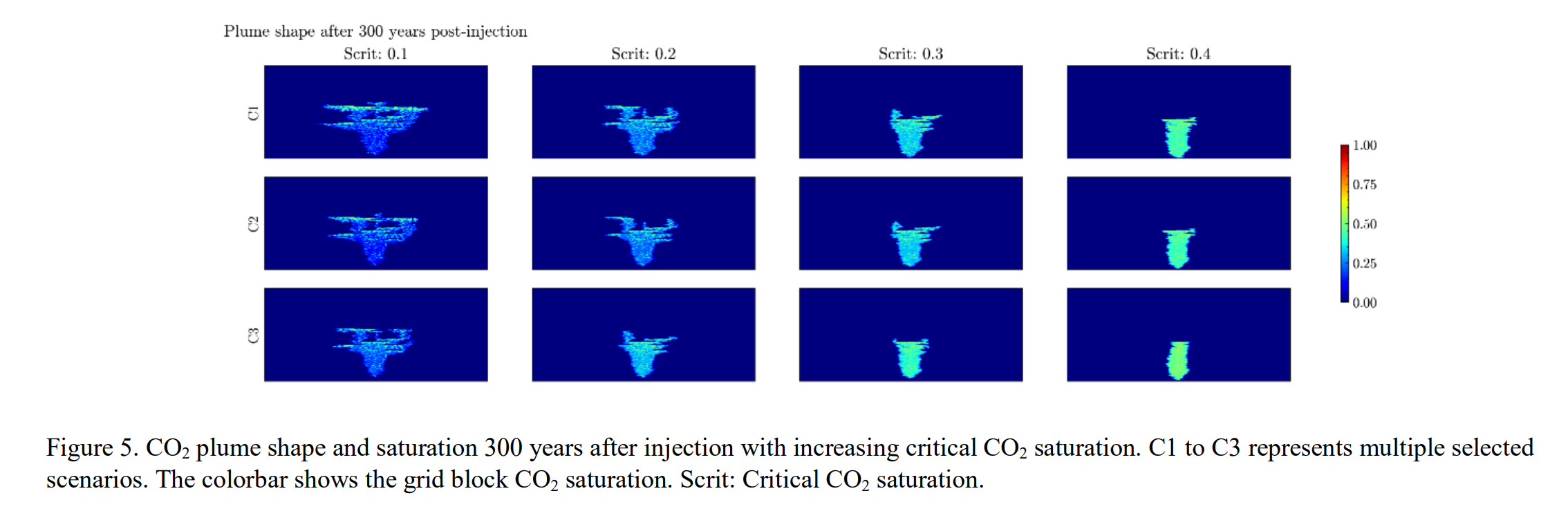
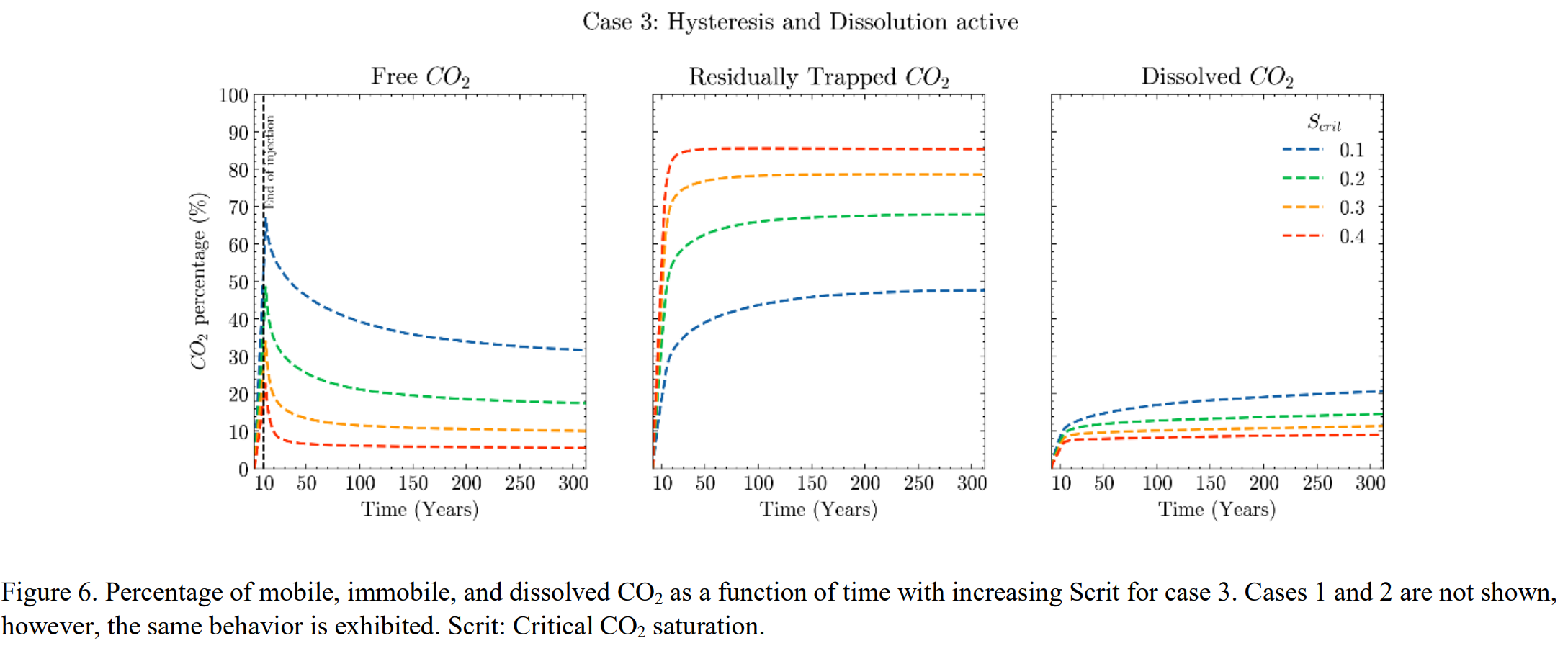
研究提出通过临界CO₂饱和度(即CO₂-水相对渗透率曲线上的首个非零值)量化毛细管非均质捕集效应,并基于实验数据设定了临界饱和度范围(0.1-0.4)进行模拟。结果表明,临界饱和度升高会导致CO₂羽流规模和横向扩展大幅减少,同时影响毛管力捕集与溶解封存的相对贡献。
CMG软件解决方案
- 模型构建
- 采用CMG全物理场油藏模拟器,结合实验室砂箱实验结果,构建包含两种岩相(洁净砂岩和页岩隔层)的二维非均质地层模型(孔隙度和渗透率服从对数正态分布)。
- 通过修改临界CO₂饱和度参数(基于实验测得的突破时非润湿相饱和度),模拟不同非均质性场景下的CO₂运移与封存。
- 模拟方案设计
- 方案C1:不考虑滞后效应和溶解作用,仅研究临界饱和度对残余封存的影响。
- 方案C2:加入溶解作用,分析临界饱和度对溶解封存的影响。
- 方案C3:同时考虑滞后效应和溶解作用,综合评估不同封存机制的相互作用。
结论
- 小尺度非均质性通过改变临界CO₂饱和度显著影响CO₂羽流形态和封存效率,需在场地尺度模拟中精确表征。
- 临界饱和度参数可作为连接实验室观测与矿场模拟的关键桥梁,提升碳封存预测的可靠性。
- 实际碳封存项目中,需结合地层非均质性优化注入策略,以最大化毛管力捕集并降低泄漏风险。



Abstract
Small-scale geological heterogeneities in storage formations can lead to greater CO2 trapping during the capillary- and buoyancy-dominated regime. This increase in trapped saturation is called capillary heterogeneity trapping, also known as local capillary trapping. This study uses both laboratory experiments and field-scale simulations to investigate the impact of small-scale heterogeneity on field-scale CO2 migration and trapping. We conducted experiments using a meter-scale slab chamber with ripple deposits of varying grain size contrasts and incorporated these sand tank results as inputs into field-scale simulations using CMG. Experimental results indicate that CO2 trapping amount is highly dependent on both the type and the degree of small-scale heterogeneity, and even slight changes in the ripple bedform patterns can significantly alter the size and saturation of the trapped plume. Accurately capturing the effects of these heterogeneities is essential for reliable field-scale CO2 storage simulations. Capillary heterogeneity trapping can be modeled using the parameter known as the critical CO2 saturation, which represents the first nonzero value on the CO2 drainage relative permeability curve. We conducted simulations with varying critical saturation values (0.1 to 0.4) to study its impact on CO2 plume dynamics. This value range was selected based on laboratory saturation results. Simulation results show that as critical saturation increases, both the plume size and lateral extent greatly decrease. Finally, critical CO2 saturation also impacts the relative contribution from capillary and dissolution trapping. These results highlight the significant role small-scale heterogeneity plays in CO2 migration and trapping, offering insights for improving storage simulations.
Keywords: CO2 geologic storage, full physics reservoir simulation, small-scale heterogeneity, CO2 capillary and dissolution trapping, multiphase flow in porous media
作者单位
美国德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校,
