Multi-Physics Coupling Mechanisms and Key Development Factors in Enhanced Geothermal Systems for Hot Dry Rock
干热岩(HDR)地热是一种清洁、可再生资源,对实现“双碳”目标具有重要意义。本文以水为工质,构建“温度-应力-流动”全耦合模型,并引入动态基质孔隙度-渗透率关系,利用 CMG 数值模拟平台建立离散裂缝模型,系统评估井网、工程参数及裂缝网络对热采性能的影响。结果表明:
- 垂直单注单采水平井在重力与压差双重驱动下热采量最高,较其他井型高 5 % 以上;
- 基质孔隙度、渗透率越低越有利,可抑制流体滞留与绕流;
- 注-采压差每提高 1 MPa,30 年累计采热量可提高 12.93 %,而注水温度影响极小;
- 均匀裂缝网络优于非均匀“长-短”交替布局,次级裂缝仅早期略增回采率,对总热量贡献不足 1 %。
研究为 HDR-EGS 井位部署、压裂设计提供了理论依据与技术指导。
CMG 软件应用情况
• 软件:CMG-IMEX + 用户自定义 THM 耦合子程序
• 网格:1000 m×550 m×500 m,40×22×20 网格,经独立性与误差测试验证
• 裂缝:采用离散裂缝网络(DFN),显式嵌入主裂缝与次级裂缝
• 耦合:将温度-应力-渗流动态方程写入 CMG 的 USER-DEFINED 模块,实时更新基质孔隙度 φ、渗透率 k、裂缝开度 df
• 算例:单注单采、单注双采、水平/垂直/对角井网对比;注水 200–1000 m³/d,温度 40–80 ℃,压差 8–12 MPa
结论
- 建立了适用于 HDR-EGS 的 THM 全耦合模型,温度场解析解验证误差 <1 %。
- 井网优化:垂直单注单采水平井长期效益最佳,可避免早期热突破。
- 储层与工程参数:低孔隙度(0.5 %)、低渗透率(0.01 mD)及高注-采压差(12 MPa)有利于提高采热量。
- 裂缝工程:压裂施工应保证裂缝长度均匀,次级裂缝对最终热量贡献有限。
作者单位:中国石油大学(北京)石油工程学院
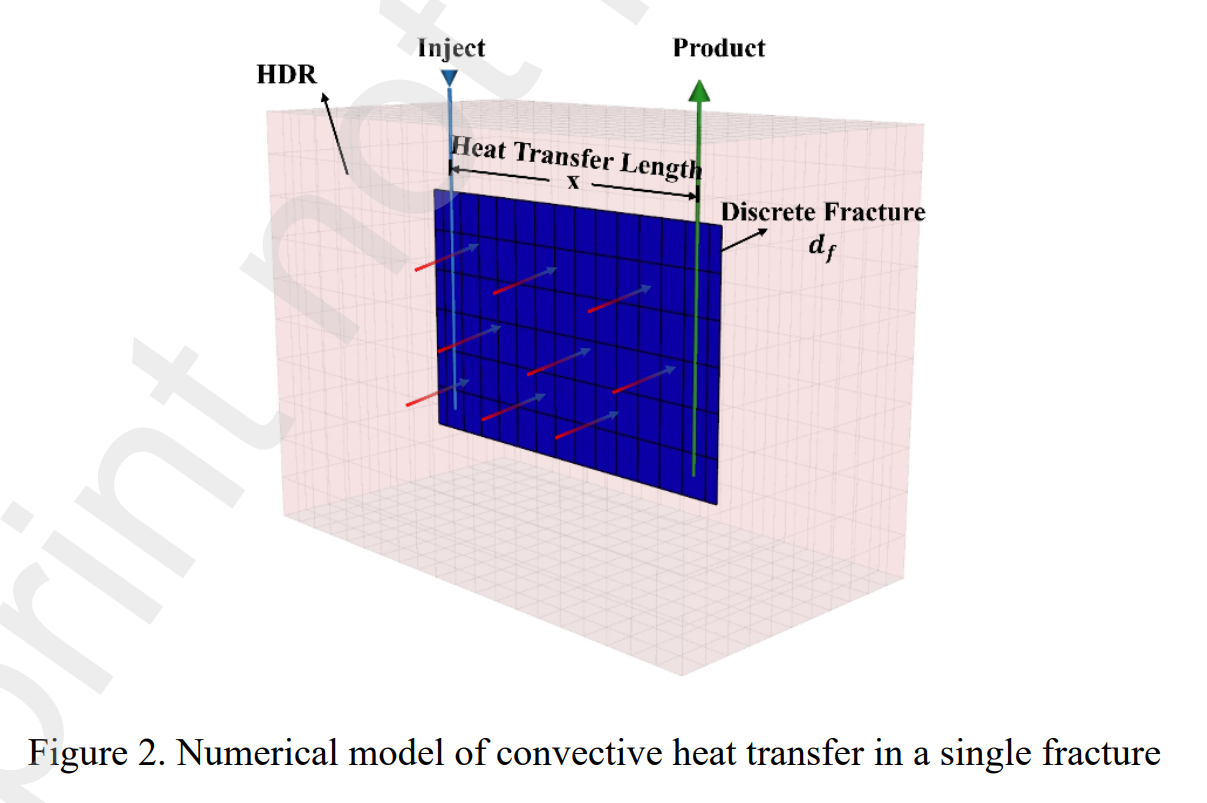
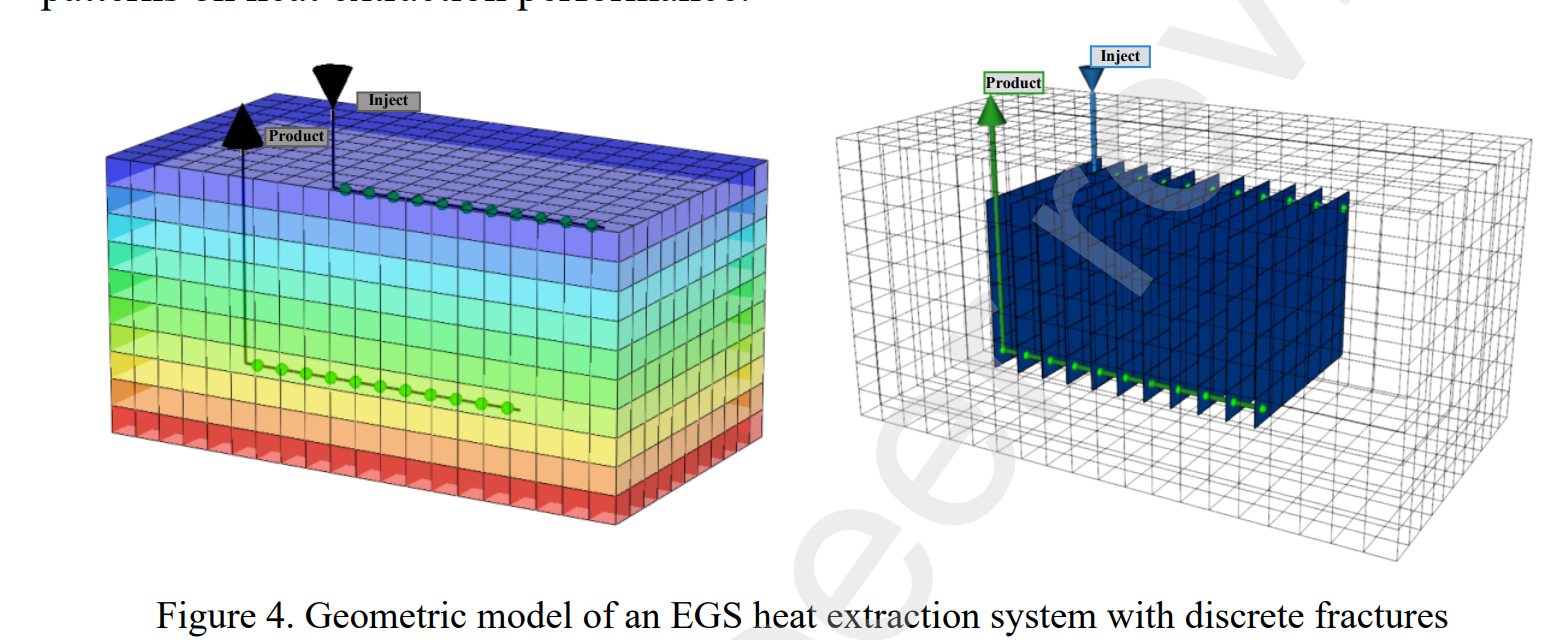
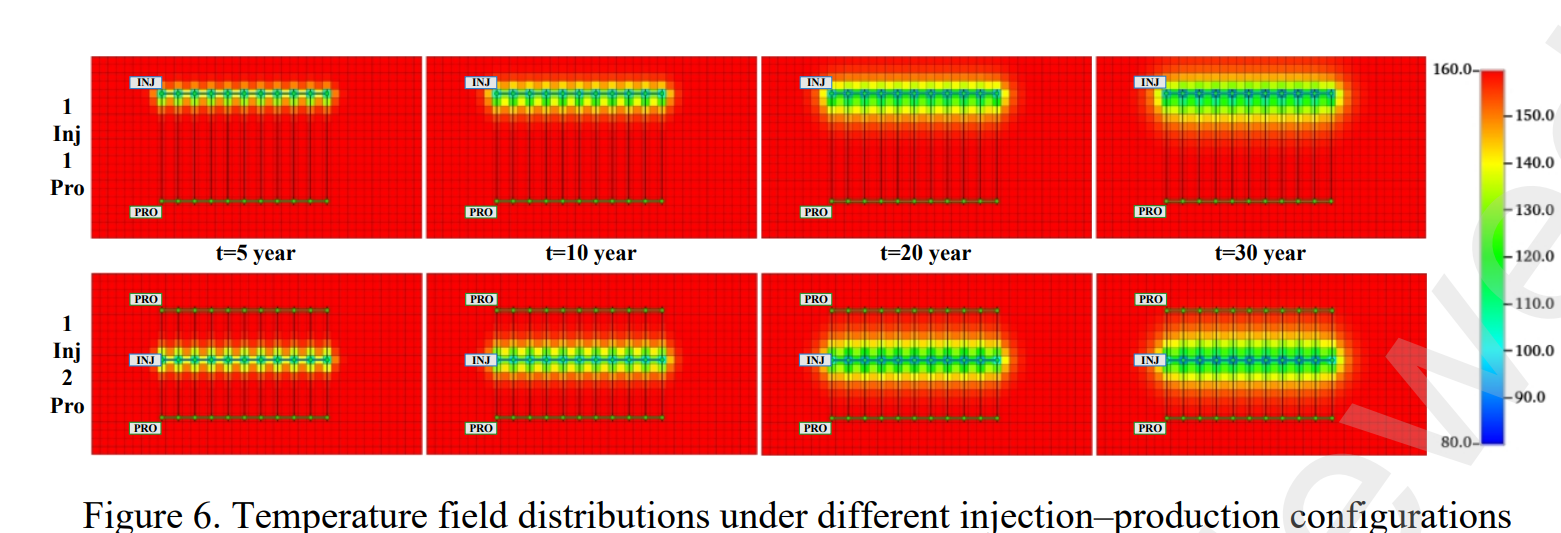
Abstract
Hot dry rock (HDR) geothermal energy is a clean, renewable resource whose efficient development is essential for advancing energy transition and achieving green, low-carbon objectives. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS), which extract heat by hydraulically connecting injection and production wells, have emerged as the primary technological approach for HDR exploitation. This study systematically investigates the development mechanisms and key influencing factors of EGS using H₂O as the working fluid, through integrated theoretical modeling and numerical simulation. By introducing a dynamic matrix porosity–permeability model to modify the governing equations, a multi-physics coupled model better aligned with practical EGS development is established. Based on this, a discrete-fracture numerical model is developed to analyze the impacts of well configuration, development parameters, and fracture network structure on thermal performance. Results show that, driven by pressure gradients and gravity, a vertically aligned single-injection single-production horizontal well achieves superior heat extraction, with cumulative output exceeding other configurations by over 5%. Sensitivity analysis shows that increased matrix porosity and permeability reduce heat recovery due to fluid entrapment and flow diversion, whereas for engineering parameters, injection temperature has limited impact on thermal performance, while the injection–production pressure differential significantly enhances system efficiency. Further analysis shows that a uniformly distributed fracture network improves thermal performance, while secondary fractures enhance fluid recovery but contribute little to total heat extraction. This study deepens the understanding of multi-physics coupling in EGS and offers theoretical and technical support for optimizing development and achieving carbon peaking and neutrality goals.
Keywords: EGS, Multi-physics Coupling, Sensitivity analysis, Well pattern, Injection-Production Strategy
