Effects of Aqueous Solubility and Geochemistry on CO2 Injection for Shale Gas Reservoirs
CMG软件的应用情况
中文作者单位
-
韩国国家石油公司
-
汉阳大学地球资源与环境工程系
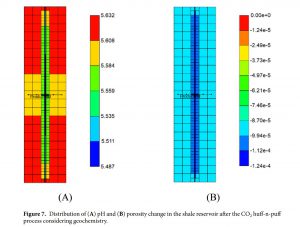
In shale gas reservoirs, CH4 and CO2 have finite aqueous solubilities at high-pressure conditions and their dissolution in water affect the determination of the original gas in place and the CO2 sequestration. In addition, the dissolution of CO2 decreases the pH of connate water, and the geochemical reactions may thus occur in carbonate-rich shale reservoirs. The comprehensive simulations of this work quantify the effects of aqueous solubility and geochemistry on the performance CO2 huff-n-puff process in shale gas reservoir. Accounting for the aqueous solubility of CH4 increases the initial natural gas storage and natural gas production. The effect of the aqueous solubility of CO2 enables to sequester additional CO2 via solubility trapping. Considering the geochemical reactions, the application of the CO2 huff-n-puff process causes the dissolution of carbonate minerals and increases the porosity enhancing the gas flow and the gas recovery. Incorporation of geochemistry also predicts the less CO2 sequestration capacity.
Therefore, this study recommends the consideration of aqueous solubility and geochemical reactions for the accurate prediction of gas recovery and CO2 sequestration in shale gas reservoirs during the CO2 huff-n-puff process.