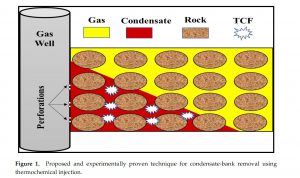
Condensate-Banking Removal and Gas-Production Enhancement Using Thermochemical Injection: A Field-Scale Simulation
井筒附近凝析液的积累已知会将气体产量减少高达80%。为了减轻凝析液银行的影响并提高气体产量,采用了多种方法。本文介绍了一种现场规模的模拟研究,使用热化学处理策略去除致密气藏中的凝析液损害,并通过原位生成的热量和压力来增强气体回收。研究使用了组分模拟器来评估所建议处理方法在减少凝析液损害和提高气体回收方面的有效性。与代表行业标准气体注入策略的基准案例相比,模拟研究表明,热化学处理近井筒区域可显著提高烃类回收性能。对于所研究的情景,热化学的应用将生产平台期从参考气体注入案例的104天延长至683天,即生产平台时间增加了6.5倍,气体回收率从25%提高到89%。回收率的提高归因于毛细管压力和凝析液粘度的降低。本研究对于设计和实施致密气藏中的热化学处理至关重要。
CMG软件的应用情况
在本文中,使用了Computer Modelling Group (CMG)软件中的高级状态方程(EoS)组分和非常规模拟器(GEM)来构建气藏模型。该模型基于文献中收集的数据,模拟了一个1平方公里的笛卡尔网格覆盖的正方形区域。模型考虑了垂直异质性,定义了四个渗透率从5到315 mD不等的层。此外,还使用了CMG软件中的相对渗透率曲线生成工具,基于Corey模型生成了水相和油相的相对渗透率曲线。这些工具和模型帮助研究人员模拟了热化学处理对气藏中凝析液银行和气体产量的影响。
中文作者单位
-
国王法赫德国立石油与矿物大学石油工程与地质科学学院,沙特阿拉伯达兰31261;电子邮件:g201205100@kfupm.edu.sa (A.H.);mohamed.abdalla@kfupm.edu.sa (M.A.);mmahmoud@kfupm.edu.sa (M.M.);aamajed@kfupm.edu.sa (A.A.-M.)
-
高级研究中心(EXPEC ARC),沙特阿拉伯达兰31311;电子邮件:ayman.nakhli@aramco.com
-
对应作者:Guenther Glatz,电子邮件:guenther@kfupm.edu.sa
Abstract
Condensate-liquid accumulation in the vicinity of a well is known to curtail gas production up to 80%. Numerous approaches are employed to mitigate condensate banking and improve gas productivity. In this work, a field-scale simulation is presented for condensate damage removal in tight reservoirs using a thermochemical treatment strategy where heat and pressure are generated in situ. The impact of thermochemical injection on the gas recovery is also elucidated. A compositional simulator was utilized to assess the effectiveness of the suggested treatment on reducing the condensate damage and, thereby, improve the gas recovery. Compared to the base case, represented by an industry-standard gas injection strategy, simulation studies suggest a significantly improved hydrocarbon recovery performance upon thermochemical treatment of the near-wellbore zone. For the scenarios investigated, the application of thermochemicals allowed for an extension of the production plateau from 104 days, as determined for the reference gas injection case, to 683 days. This represents a 6.5-fold increase in production plateau time, boosting gas recovery from 25 to 89%. The improved recovery is attributed to the reduction of both capillary pressure and condensate viscosity. The presented work is crucial for designing and implementing thermochemical treatments in tight-gas reservoirs.
Keywords: tight reservoirs; gas recovery; thermochemical treatment; field-scale simulation