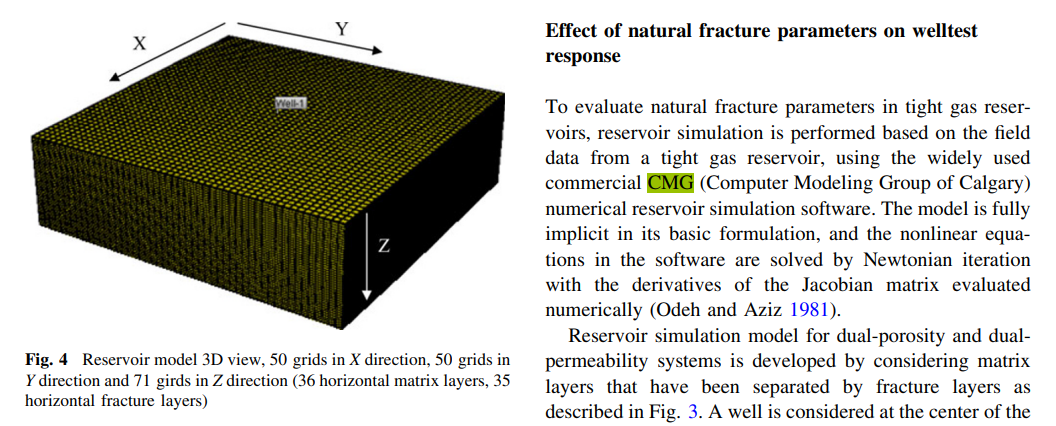
Characterizing natural fractures productivity in tight gas reservoirs
CMG软件的应用情况
作者单位
Abstract
Tight formations normally have production problems mainly due to very low matrix permeability and various forms of formation damage that occur during drilling completion and production operation. In naturally fractured tight gas reservoirs, gas is mainly stored in the rock matrix with very low permeability, and the natural fractures have the main contribution on total gas production. Therefore, identifying natural fractures characteristics in the tight formations is essential for well productivity evaluations. Well testing and logging are the common tools employed to evaluate well productivity. Use of image log can provide fracture static parameters, and welltest analysis can provide data related to reservoir dynamic parameters. However, due to the low matrix permeability and complexity of the formation in naturally fractured tight gas reservoirs, welltest data are affected by long wellbore storage effect that masks the reservoir response to pressure change, and it may fail to provide dual-porosity dual-permeability models dynamic characteristics such as fracture permeability, fracture storativity ratio and interporosity flow coefficient. Therefore, application of welltest and image log data in naturally fractured tight gas reservoirs for meaningful results may not be well understood and the data may be difficult to interpret. This paper presents the estimation of fracture permeability in naturally fractured tight gas formations, by integration of welltest analysis resultsand image log data based on Kazemi’s simplified model. Reservoir simulation of dual-porosity and dual-permeability systems and sensitivity analysis are performed for different matrix and fracture parameters to understand the relationship between natural fractures parameters with welltest permeability. The simulation results confirmed reliability of the proposed correlation for fracture permeability estimation. A field example is also shown to demonstrate application of welltest analysis and image log data processing results in estimating average permeability of natural fractures for the tight gas reservoir.
Keywords :Fracture permeability Tight gas reservoirs Natural fractures characterisation Welltest analysis