Polymer Assisted Carbon dioxide (CO₂) Enhanced Oil Recovery in Naturally Fractured Oil Reservoirs
本研究探讨了在天然裂缝油藏中应用聚合物辅助二氧化碳吞吐技术作为调控手段,以解决水产量高和二氧化碳驱替效率低的问题。研究采用CMG GEM组分模拟器设计并分析了多种聚合物辅助二氧化碳提高采收率方案。结果表明,在吞吐过程中引入聚合物调控可降低含水率、气体产率和气油比,同时提高原油采收率。研究强调了聚合物调控在增强二氧化碳吞吐效果方面的潜力,并深入理解了影响该工艺的物理过程。研究还发现,用于提高采收率的聚合物材料具有成本低、环保(特别是可生物降解和生物基聚合物)等优势。
CMG软件应用情况
本研究使用CMG GEM组分模拟器进行数值模拟研究,主要应用包括:
模型构建:
建立了89×29×1的笛卡尔网格系统,模拟了Eagle Ford页岩油藏的天然裂缝系统(图25-27展示了网格构建和属性设置)
模拟方案:
- 初始油藏自然衰竭589天
- 进行1个月聚合物注入后关井1个月使聚合物定型
- 实施3-5个周期的二氧化碳吞吐(每个周期包括6个月注入、6个月焖井和6个月生产)
- 在五周期系统中,第二周期后重新注入聚合物
参数分析:
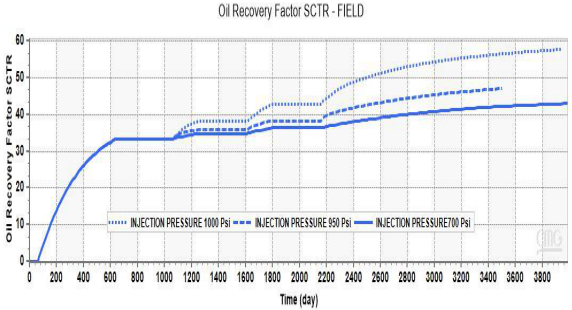
研究了聚合物摩尔比、油藏孔隙度、渗透率、气油比等参数的影响(图58-60展示了注入压力、孔隙度和注入速率的影响)
主要结论
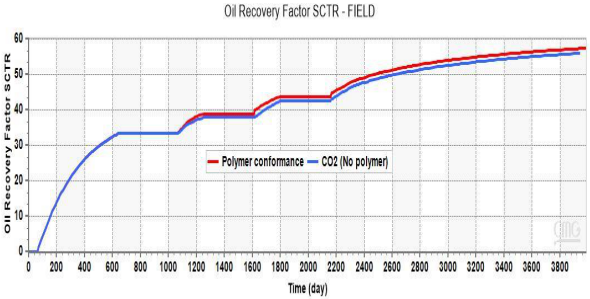
在三周期吞吐系统中,聚合物调控使原油采收率提高了约1.5%,同时降低了含水率、气体产率和气油比(图61-65展示了对比结果)
- 在五周期系统中,第二周期后重新注入聚合物可有效应对调控失效问题,改善第三至第五周期的生产效果(图76-80展示了二次调控效果)
- 增加聚合物浓度可增强调控效果,但过高浓度会抑制采收率提高
- 二氧化碳利用因子分析显示,无聚合物调控时利用因子更高(0.442 bbl/Mscf),表明聚合物调控减少了气窜损失
- 扩散物理效应(0.0005 m²/s扩散系数)对提高采收率有显著贡献
作者单位: 英国朴茨茅斯大学电气与机械工程学院
Abstract
Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) in naturally fractured reservoirs presents significant challenges, particularly when addressing water production and the inefficiency of CO₂ displacement due to finger channeling. This research explores polymer-assisted CO₂ huff-n-puff processes to address these issues as a conformance control strategy. The motivation stems from the critical need to improve oil recovery while minimizing water cut and optimizing injected gas utilization in reservoirs, which is vital for the sustainability of oil extraction practices.
The study employs a compositional reservoir simulator (CMG GEM) to design and analyse various scenarios of polymer-assisted carbon dioxide (CO₂) enhanced oil recovery. The methodology involves initial reservoir depletion for 589 days, followed by a one-month polymer injection phase, during which the polymer is allowed to set by shutting the well. Subsequently, a huff-n-puff process is conducted, iteratively increased from three to five cycles, with additional polymer injections introduced after the second cycle. Key parameters such as polymer molar ratio, reservoir porosity, permeability, gas-oil ratio (GOR), and gas production rates were evaluated to assess the effectiveness of this approach.
The results demonstrate a reduction in percentage water cut, gas production rate, and gas oil ratio, with a consequent increase in oil recovery factor when polymer conformance was introduced in the huff-n-puff process. These effects, therefore, highlight the potential of polymer conformance as a viable method to enhance CO₂ huff-n-puff in an enhanced oil recovery operation. A rigorous understanding of the physical processes influencing these operations was achieved, along with insights into the effects of various parameters on maximizing hydrocarbon recovery while effectively minimizing water production. These findings contribute to the growing knowledge on conformance control and provide valuable insights for optimizing oil recovery processes in naturally fractured reservoirs. There is also a belief that polymer materials used in enhanced oil recovery are cheap and eco-friendly, especially biodegradable and bio-based, environmentally friendly polymers. This also further reiterates its advantages and importance in this research.
Keywords: Enhanced oil recovery; carbon dioxide huff-n-puff; polymer conformance, polymer injection, oil reservoir, gas-oil-ratio, water cut.
