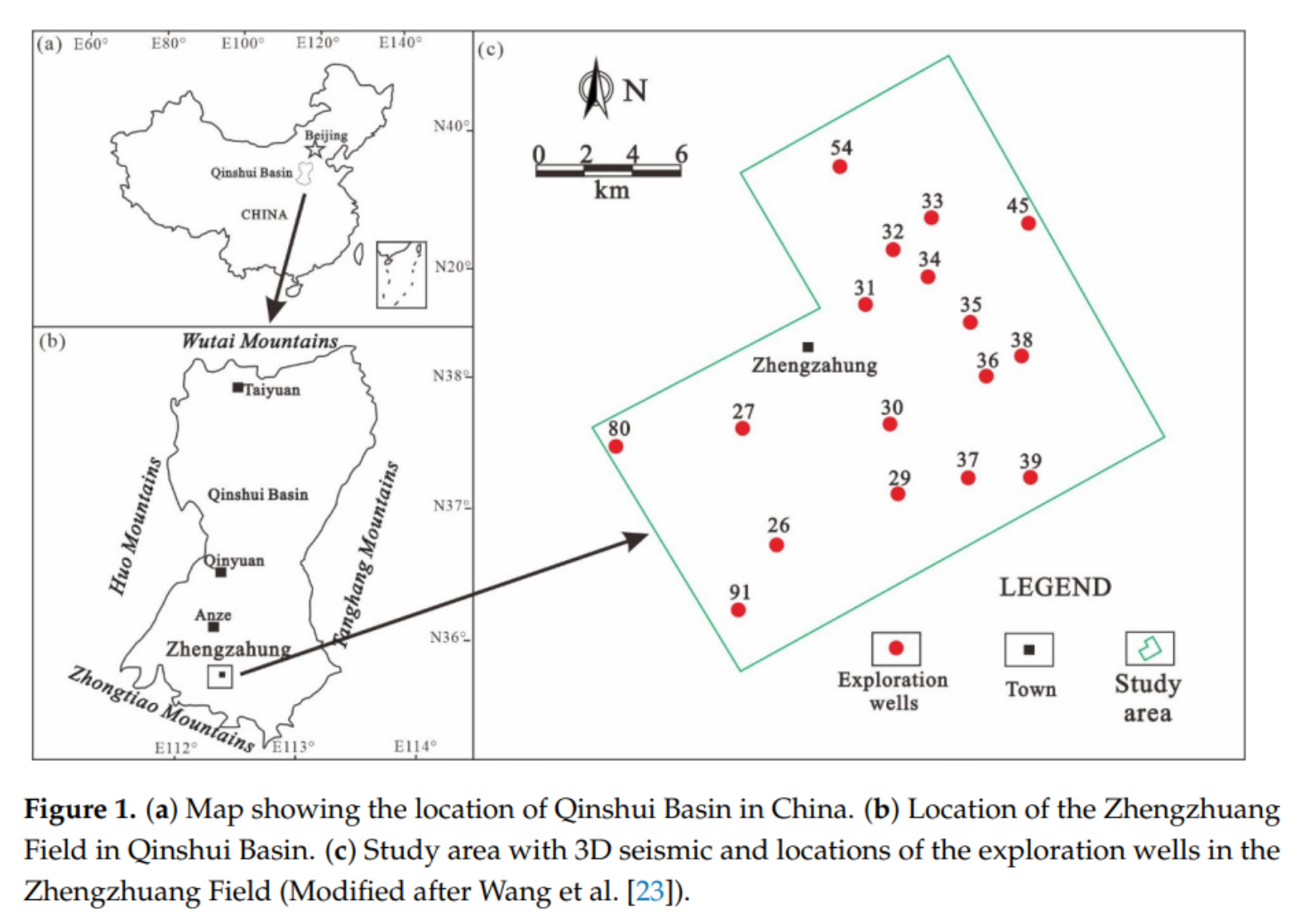
Integrated 3D Geological Modeling, Stress Field Modeling, and Production Simulation for CBM Development Optimization in Zhengzhuang Block, Southern Qinshui Basin
郑庄区块是沁水盆地重要煤层气(CBM)开发区,优质资源枯竭后剩余储层地质复杂。本文融合 94.85 km² 三维地震、973 口井资料,在 Petrel 平台完成山西组 3 号煤层高分辨率三维地质建模;利用有限元方法建立地应力场模型,识别西南区为压裂有利区;继而采用 CMG-IMEX 建立 27 口井典型井组双孔双渗模型,经历史拟合后评价剩余气分布,并构建权重多指标评价体系,将资源划分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ三类。研究结果为井网优化、压裂方案及剩余气动用提供了技术依据。
CMG 软件应用情况
• 模块:CMG-IMEX(2021 版)
• 模型:4650 m×4675 m,平面网格 25 m×25 m;纵向 20 层,双孔双渗(DUALPERM)
• 机理:考虑 Langmuir 等温吸附/解吸、气-水两相流动、基质-裂缝间扩散与达西流动耦合
• 拟合:以定井底流压方式对 27 口井 4–5 年产气、产水历史进行自动/手动历史拟合
– 累计产气量最大误差 15.2 %(拟合精度 >84.8 %)
– 累计产水量最大误差 11.6 %(拟合精度 >88.4 %)
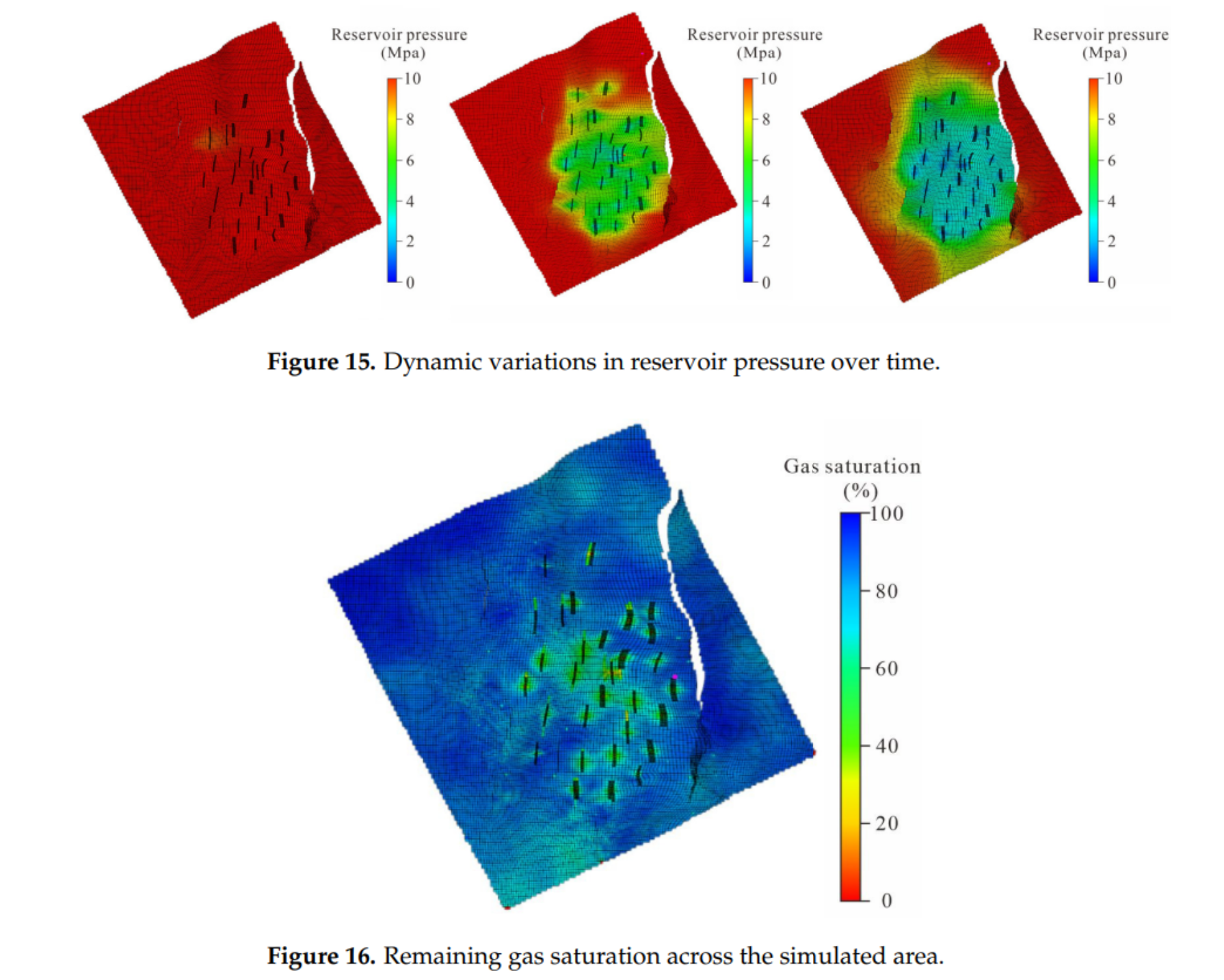
• 应用:基于拟合结果提取剩余气饱和度与压力场,用于区块剩余资源潜力评价
结论
- 三维地质模型揭示 3 号煤岩相以半亮煤为主,孔隙度 1.3–12 %,渗透率 0.01–1 mD,强非均质受断裂控制。
- 地应力场呈显著各向异性(σH/σh 梯度 0.0344/0.0215 MPa/m),西南部为压裂改造有利区。
- CMG 历史拟合成功再现早期快速降压、后期稳压规律,中央剩余压力约 3 MPa。
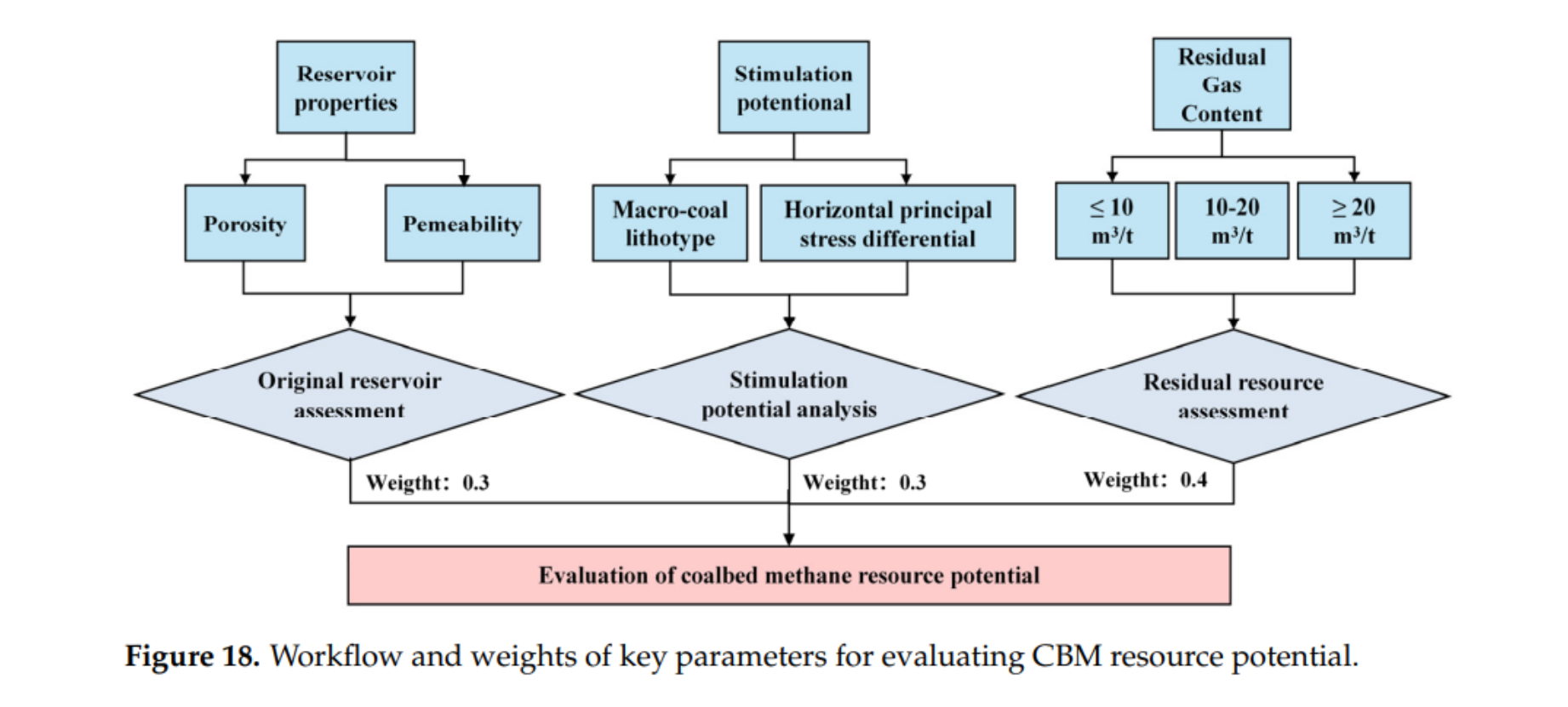
- 剩余气 14–33.5 m³/t,集中于西部、东南部构造高部位;多指标评价将区块划分为:
– Ⅰ类(西南):高孔渗、高残余气(≥20 m³/t),优先开发;
– Ⅱ类:中等条件,过渡区;
– Ⅲ类:低孔渗、低含气,需技术突破。
作者单位:中石油华北油田分公司
Abstract
The Zhengzhuang Block in the Qinshui Basin is one of the important coalbed methane (CBM) development areas in China. As high-quality CBM resources become depleted, remaining reserves exhibit complex geological characteristics requiring advanced development strategies. In this study, a multidisciplinary workflow integrating 3D geological modeling (94.85 km2 seismic data, 973 wells), geomechanical stress analysis, and production simulation was developed to optimize development of the Permian No. 3 coal seam. Structural architecture and reservoir heterogeneity were characterized through Petrel-based modeling, while finite-element analysis identified stress anisotropy with favorable stimulation zones concentrated in southwestern sectors. Computer Modeling Group (CMG) simulations of a 27-well group revealed a rapid initial pressure decline followed by a stabilization phase. A weighted multi-criteria evaluation framework classified resources into three tiers: type I (southwestern sector: 28–33.5 m3/t residual gas content, 0.8–1.0 mD permeability, 8–12% porosity), type II (northern/central: 20–26 m3/t residual gas content, 0.5–0.6 mD permeability, 5–8% porosity), and type III (<20 m3/t residual gas content, <0.4 mD permeability, <4% porosity). The integrated methodology provides a technical foundation for optimizing well patterns, enhancing hydraulic fracturing efficacy, and improving residual gas recovery in heterogeneous CBM reservoirs.
