Modeling of surfactant and surfactant–polymer flooding for enhanced oil recovery using STARS (CMG) software
CMG软件的应用情况
作者单位
Abstract
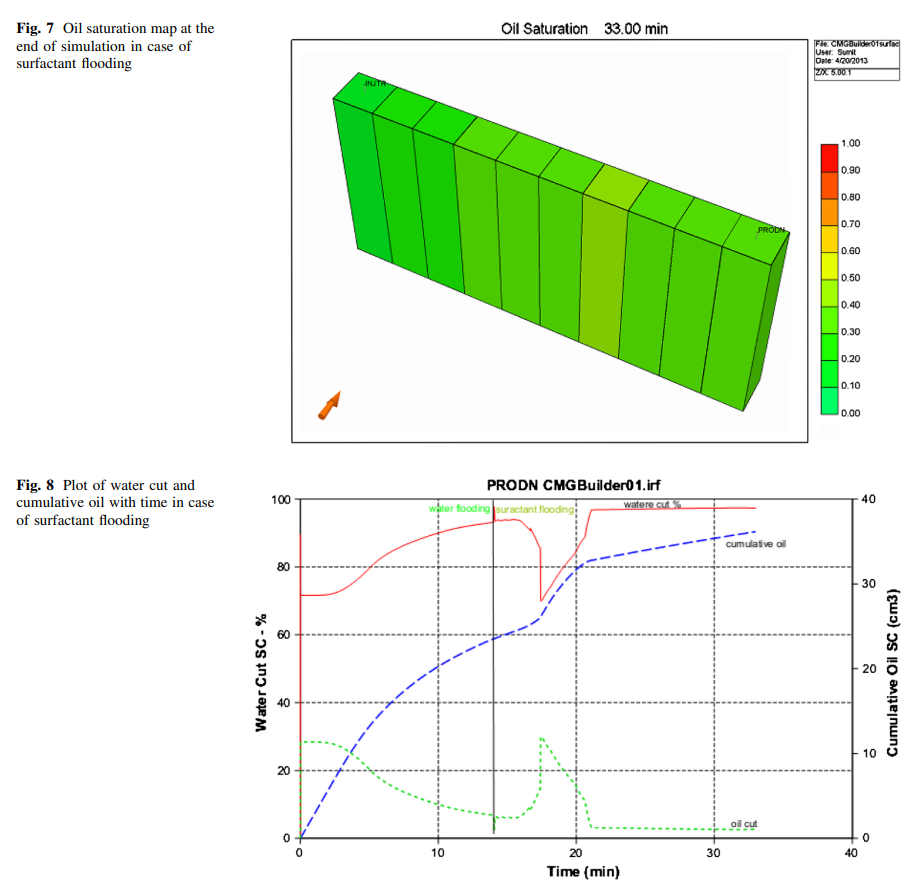
Chemical flooding methods are now getting importance in enhanced oil recovery to recover the trapped oil after conventional recovery. Investigation has been made to characterize the surfactant solution in terms of its ability to reduce the surface tension and the interaction between surfactant and polymer in its aqueous solution. A series of flooding experiments have been carried out to find the additional recovery using surfactant and surfactant–polymer slug. Approximately 0.5 pore volume (PV) surfactant (sodium dodecylsulfate) slug was injected in surfactant flooding, while 0.3 PV surfactant slug and 0.2 PV polymer (partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide) slug were injected for surfactant–polymer flooding. In each case, chase water was used to maintain the pressure gradient. The present work sought to determine whether or not acommercially available simulator could accurately simulate results from core flooding experiments. The adherence to physically realistic input values with respect to experimentally derived parameters was of primary importance during the development of the models. When specific values were not available for certain simulation parameters, a reasonable range of assumptions was made and both the water cut and cumulative oil production were successfully matched. Ultimately, understanding how to simulate the surfactant and polymer behavior on a core scale will improve the ability to model polymer floods on the field scale.


表面活性剂驱: 0.5 PV十二烷基硫酸钠段塞。
表面活性剂-聚合物驱: 0.3 PV 表面活性剂段塞+ 0.2 PV 部分水解聚丙烯酰胺段塞。