Enhanced Oil Recovery from a Low Pressure Tight Oil Reservoir in Ordos Basin
本研究聚焦于中国鄂尔多斯盆地的一个大型沉积盆地,该盆地拥有丰富的油气储量。与巴肯形成相比,研究区域的压力较低,可能导致初级采收率不高。通过模拟研究,结果表明在这样一个低压力储层中,初级采收率并不高效,建议通过注水或注气来提高油气采收率。与水相比,气体更适合于提高研究区域的油气采收率。在所有研究的气体中,甲烷(CH4)和分离器气体是更好的选择。通过储层模拟还研究了异质性的影响。随着储层异质性的增加,油气采收率会降低。然而,注气仍然可以显著提高油气采收率。已建立地质模型以预测气体注入情况下的案例研究表现。
CMG软件的应用情况
在本研究中,CMG软件被用于建立和模拟地质模型,以及进行储层模拟和油气采收率的预测。具体来说,CMG GEM软件用于储层模拟,CMG WINPROP用于计算最小混相压力(MMP),这些计算对于确定CH4和CO2的MMP至关重要,进而评估气体注入提高油气采收率的潜力。
Abstract
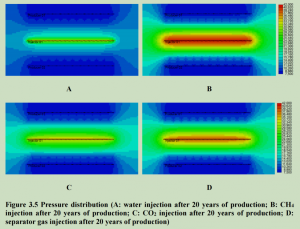
As one of the biggest sedimentary basins in China, abundant oil reserves exist in the Ordos Basin. Compared with Bakken formation, the pressure of the study area is quite low, which may results in inefficient primary recovery. The primary recovery in the study area has been studied through simulation. The results indicate that primary recovery is not efficient in such a low pressure reservoir. Water or gas should be injected to enhance the oil recovery. Compared with water, gas is more suitable for improving the oil recovery from the study area. Among all gases investigated, CH4 and separator gas are a better choice. The effects of heterogeneity have also been studied by reservoir simulation. As reservoir heterogeneity increases, oil recovery will decrease. However, gas injection can still highly improve the oil recovery. A geological model has been built to predict the gas injection performance in case studies.
Simulator: GEM
作者单位
文章作者韩佳贝,隶属于加拿大卡尔加里大学化学与石油工程研究生项目。
