Geochemical Modelling of the Fracturing Fluid Transport in Shale Reservoirs
Abstract
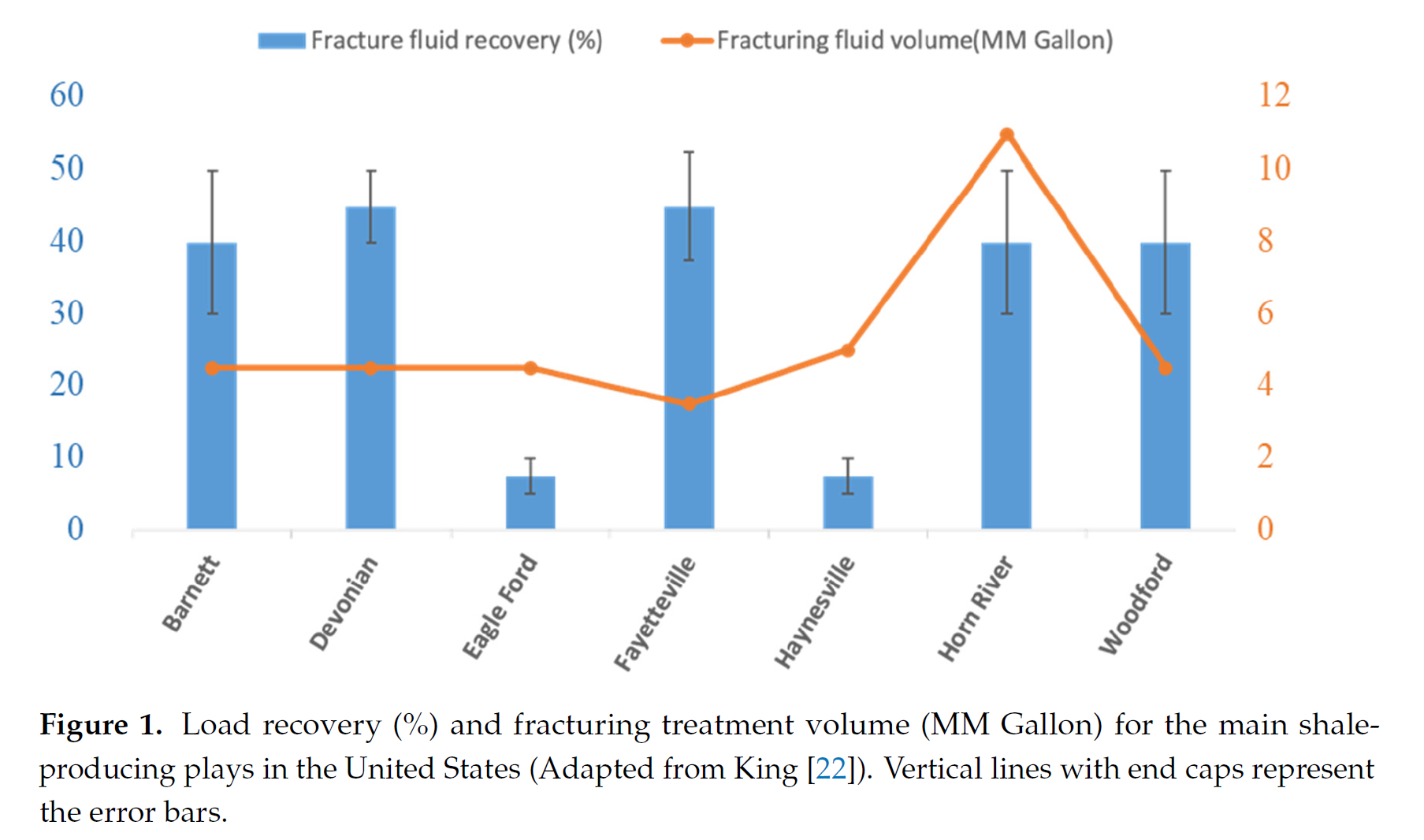
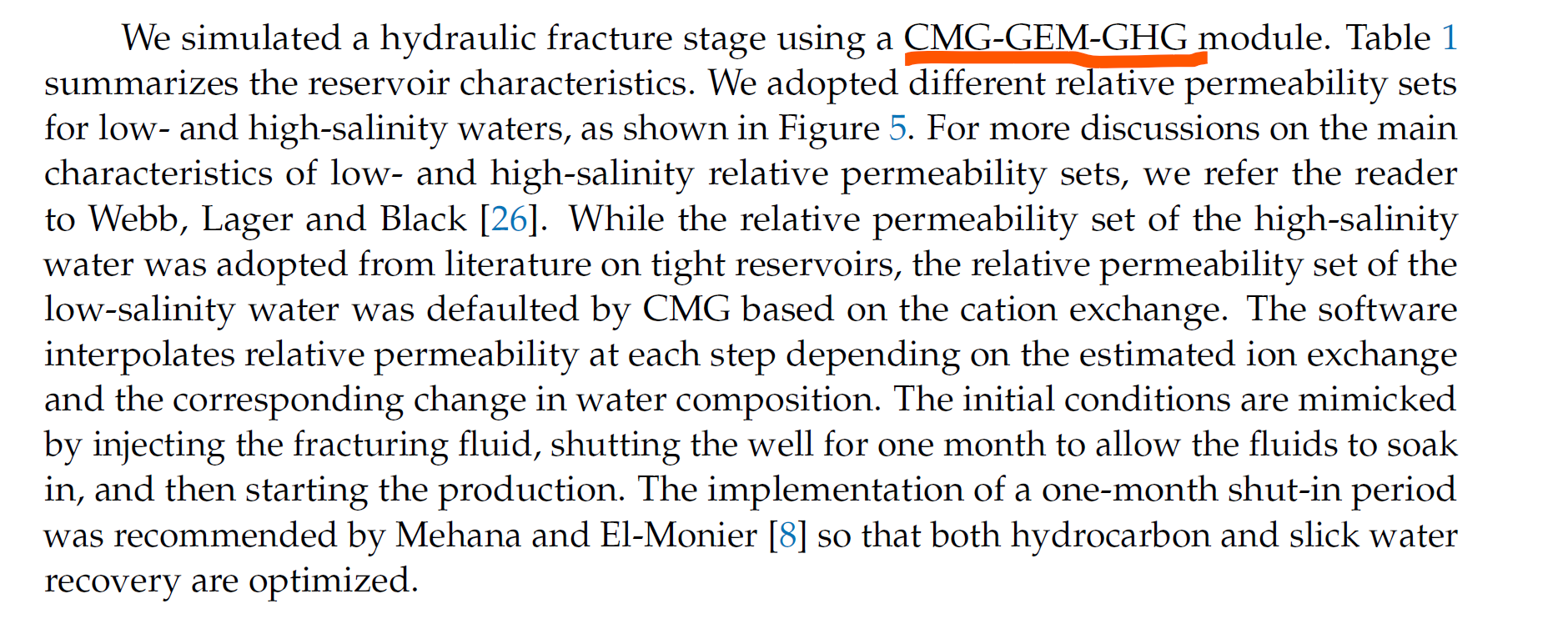
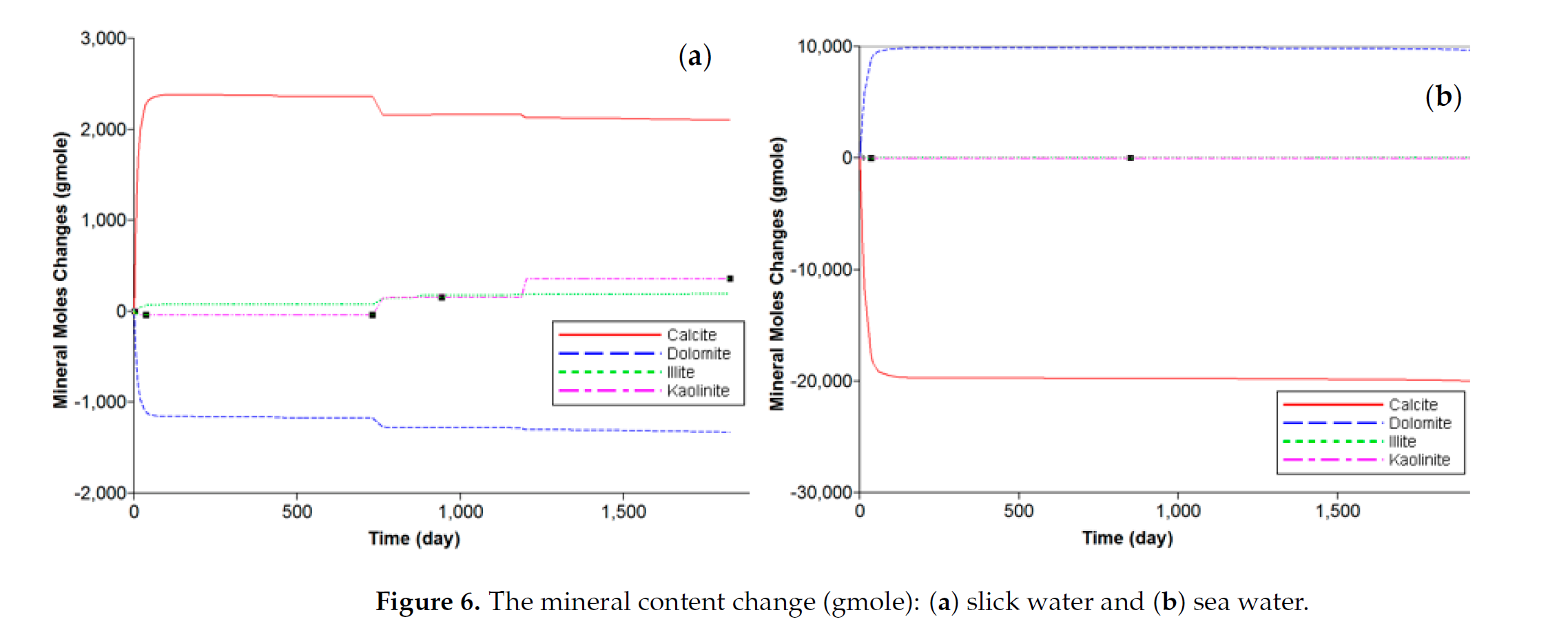
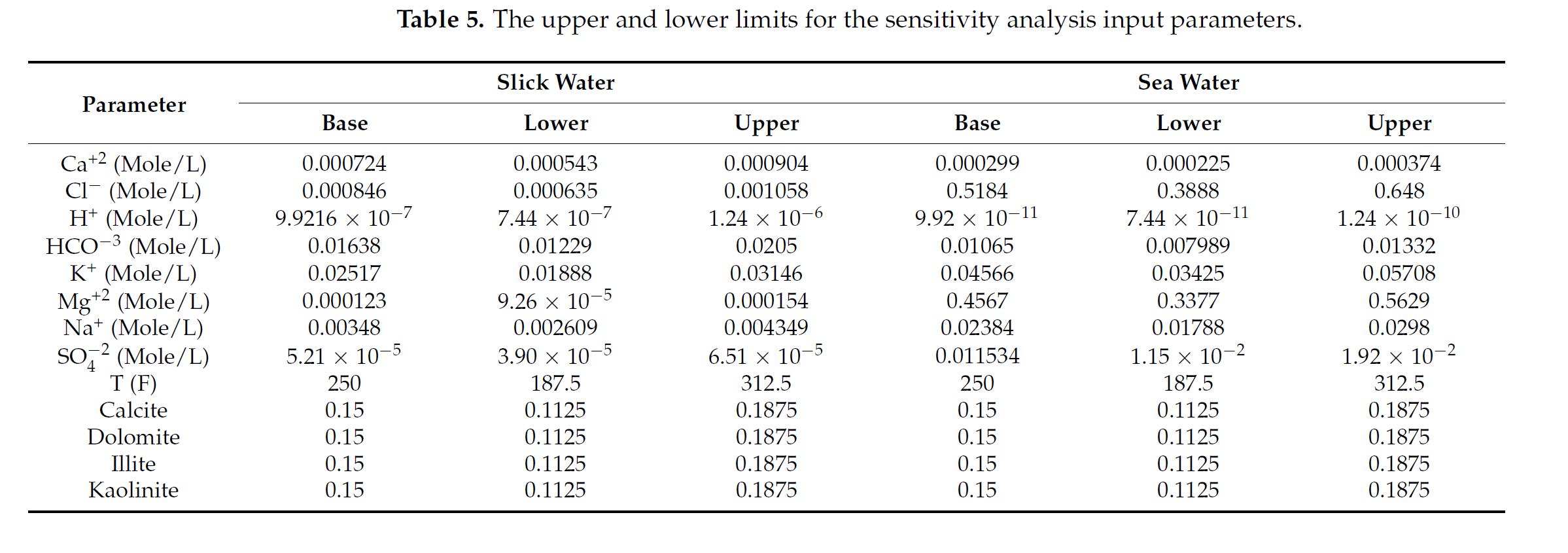
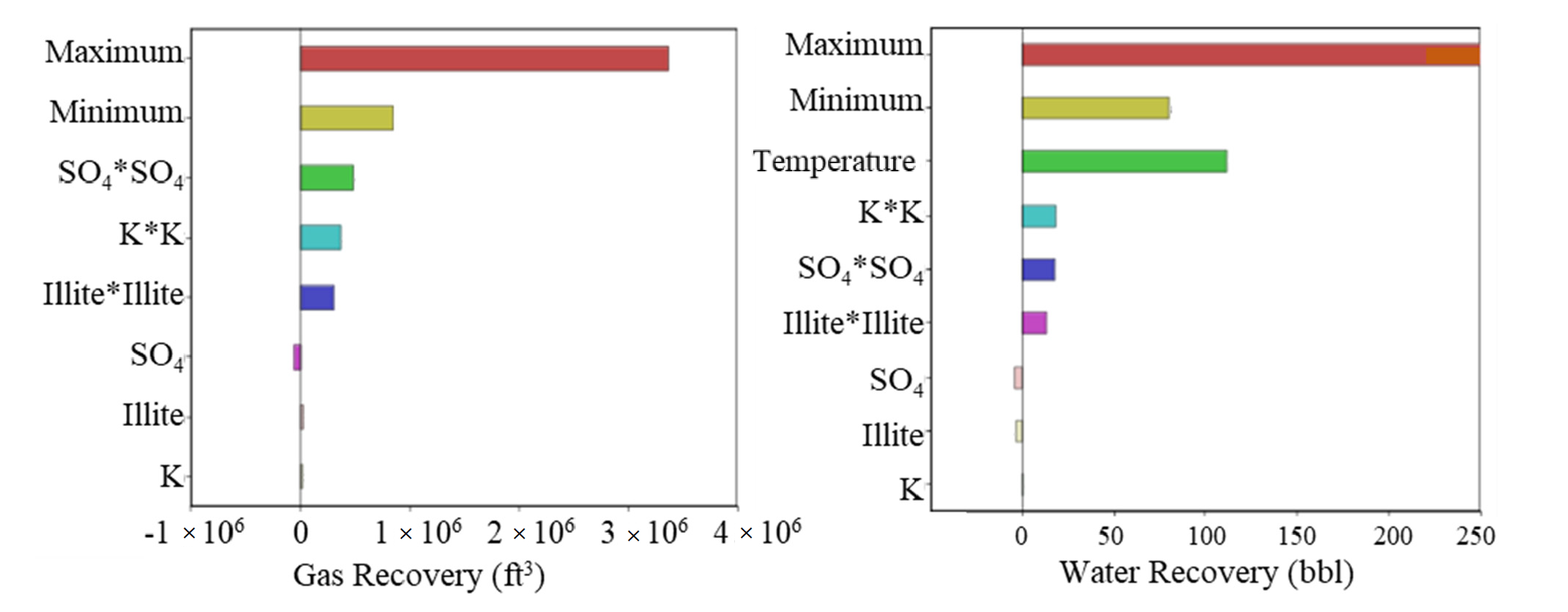
Field operations report that at least half of the fracturing fluid used in shale reservoirs is trapped. These trapped fluids can trigger various geochemical interactions. However, the impact of these interactions on well performance is still elusive. We modeled a hydraulic fracture stage where we simulated the initial conditions by injecting the fracturing fluid and shutting the well to allow the fluids to soak into the formation. Our results suggest a positive correlation between the dissolution and precipitation rates and the carbonate content of the rock. In addition, we observed that gas and load recovery are overestimated when geochemical interactions are overlooked. We also observed promising results for sea water as a good alternative fracturing fluid. Moreover, we observed better performance for cases with lower-saline connate water. The reactions of carbonates outweigh the reactions of clays in most cases. Sensitivity analysis suggests that the concentration of SO4, K and Na ions in the fracturing fluid, and the illite and calcite mineral content, along with the reservoir temperature, are the key factors affecting well performance. In conclusion, geochemical interactions should be considered for properly modeling the fate of the fracturing fluids and their impact on well performance.
Keywords: geochemical modeling; shale reservoirs; hydraulic fracture
洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室计算地球科学小组