The Employment Of CMG-STARS To Simulate Alkaline/Ionic Liquid/Polymer (AILP) Flooding Results
本研究旨在通过CMG-STARS软件模拟实验结果,以实现对实验室规模化学驱油的历程匹配。研究中进行了一些化学驱油实验,以获得额外的残余油饱和度(RF)。在建立模型过程中,最具有挑战性的因素是纯聚合物粘度和油水相对渗透率曲线。为了解决信息不足的问题,我们做出了一系列合理的假设,并调整特定值,以成功匹配累积产油量、水切、油切和压力降曲线。最终,理解如何在实验室规模模拟化学驱油性能将为模拟工业规模化学驱油提供可能性。
CMG软件的应用情况
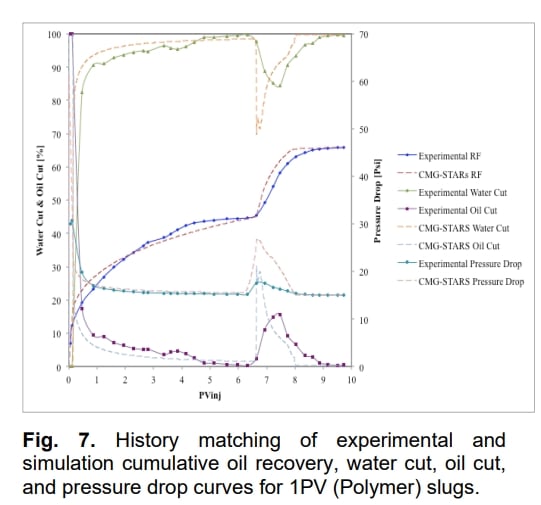
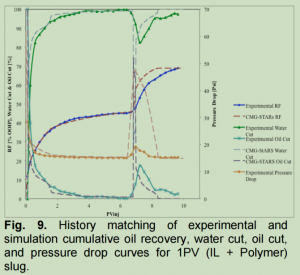
CMG-STARS软件被用于构建非热化学驱油实验的历程匹配。通过水驱和化学驱(碱性/离子液体/聚合物)实现了历程匹配,选择了累积油回收量、油切、水切、生产率和压差作为历程匹配的指标。在成功实现历程匹配后,研究了实验室中无法研究的各种条件对提高残余油饱和度的影响。

Abstract
One of the most successful enhanced oil recovery techniques, nowadays, is chemical (Alkaline/Surfactant/Polymer) flooding and modeling the experimental results of these experiments is one of the most difficult challenges. For that, this study has been conducted to obtain the history matching of the laboratory scale results employing STARS. Some of the chemical flooding experiments have been done to get additional RF. We noticed that the most challenging factors throughout building up the models were the pure polymer viscosity and oil-water relative permeability curves. Also, a fair range of assumptions was made to address the unavailability of any information and adjust the particular values to end up with a successful match of cumulatively produced oil, water cut, oil cut, and pressure drop curves. Finally, understanding how to model the chemical flooding performance in laboratory scale will develop the possibility of simulating chemical floods in industrial scale.
Keywords
CMG-STARS; AILP flooding; history matching; sensitivity study; oil viscosity; slug injection time.
作者单位
文章的作者来自加拿大里贾纳大学石油系统工程系(Department of Petroleum Systems Engineering, University of Regina, Regina, Canada)和过程系统工程系(Department of Process Systems Engineering, University of Regina, Regina, Canada)。

