Sensitivity analysis of low salinity waterflood alternating immiscible CO2 injection (Immiscible CO2-LSWAG) performance using machine learning application in sandstone reservoir
本研究采用数值模拟和机器技术相结合的方法,对砂岩储层中非混相CO2-LSWAG注入技术的效果进行了全面研究。此外,对各种注入和储层参数进行了详细的敏感性分析,以深入了解它们对过程的影响。为了预测原油采收率(RF),研究使用了1000个实验设计在初始油湿条件下。
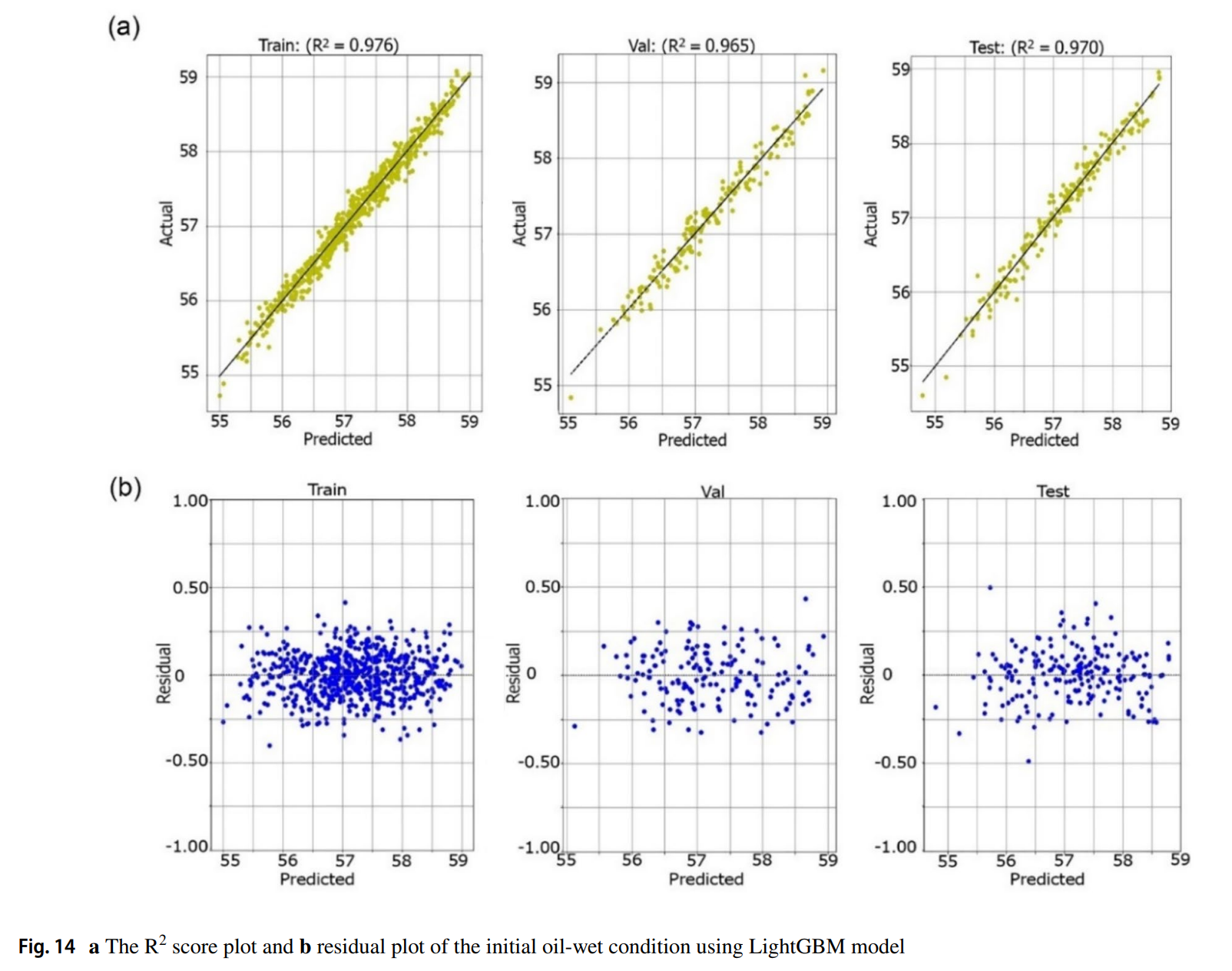
数值模拟结果表明,不混相CO2-LSWAG注入比传统的非混相CO2和低矿化度水注入效果更好,从而获得更高的采收率。本研究中使用的Catboost和LightGBM机器学习模型产生了高于0.95的R2分数,并且预测结果与实际结果之间的误差较低。这表明机器学习模型可以提供比数值模拟更快、更准确的替代方案。机器学习模型的敏感性分析结果揭示了影响油RF的主要因素是注入水的化学成分和注入速率。总之,本研究利用机器学习进行非混相CO2-LSWAG性能的敏感性分析,主要发现包括识别影响参数和CatBoost和LightGBM算法的高预测准确性。结果有助于通过关注主要影响因素,加快现场试验的决策制定,未来研究建议扩大应用范围。
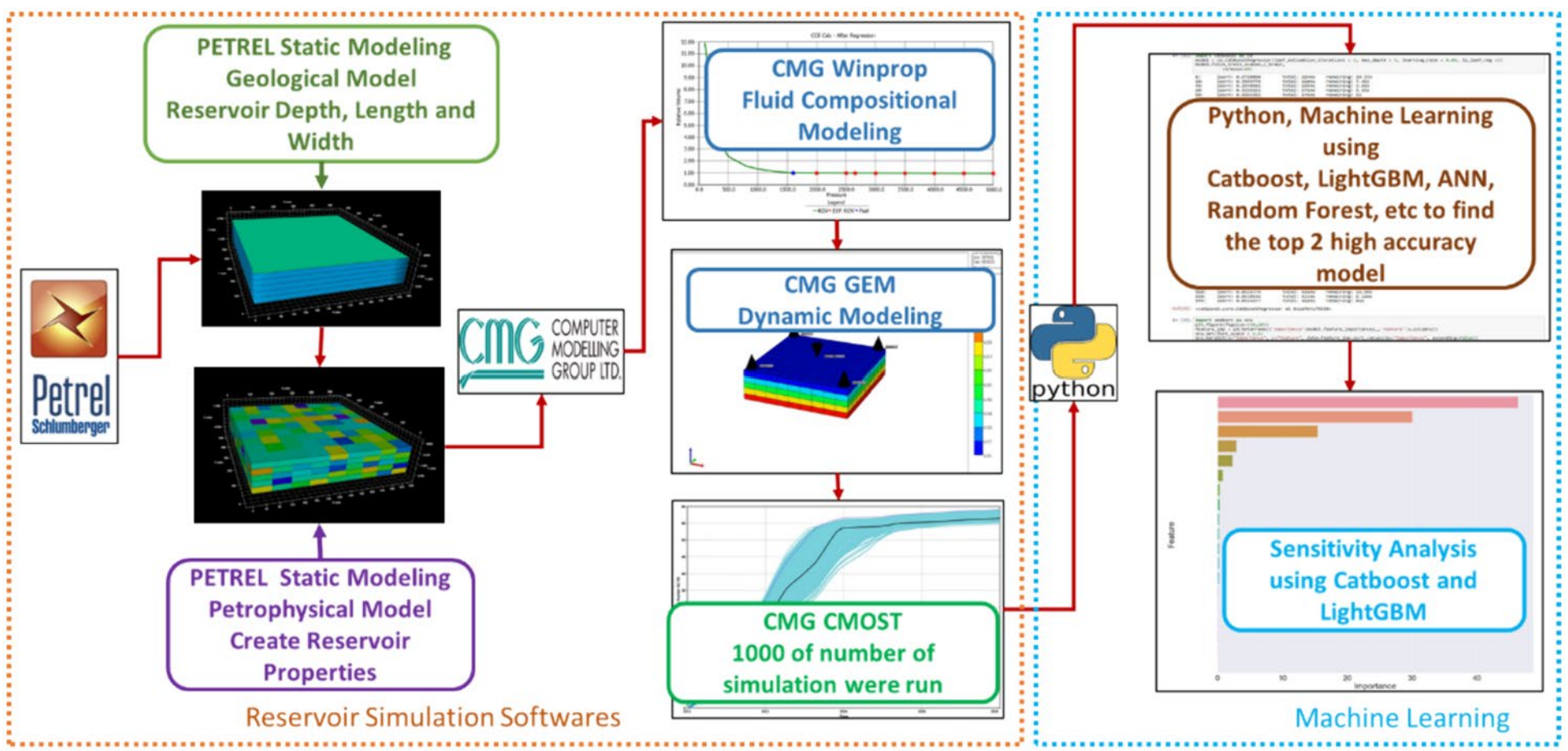
CMG软件应用情况:
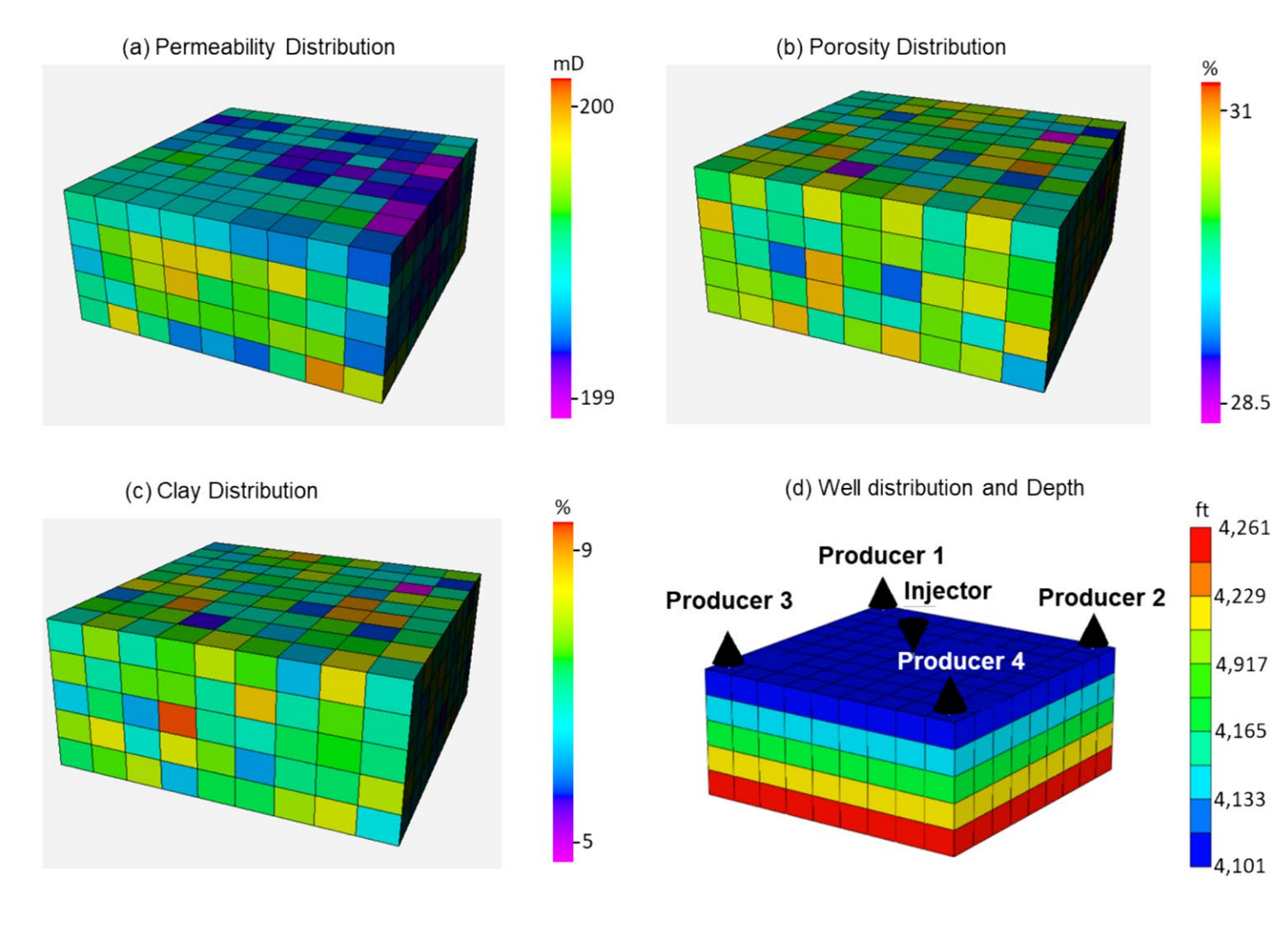
在本研究中,CMG软件被用于构建数值储层模拟,特别是CMG Winprop用于创建组分模型中的流体属性,CMG GEM用于建立岩石属性、储层条件和不混相CO2-LSWAG注入计划以预测采收率。CMG CMOST产生了1000个初始油湿砂的数据样本,输入特征包括影响不混相CO2-LSWAG注入的参数,输出特征代表采收率。最后,将机器学习技术应用于数据集,进行模型训练和测试,以预测采收率并进行敏感性分析。
Abstract
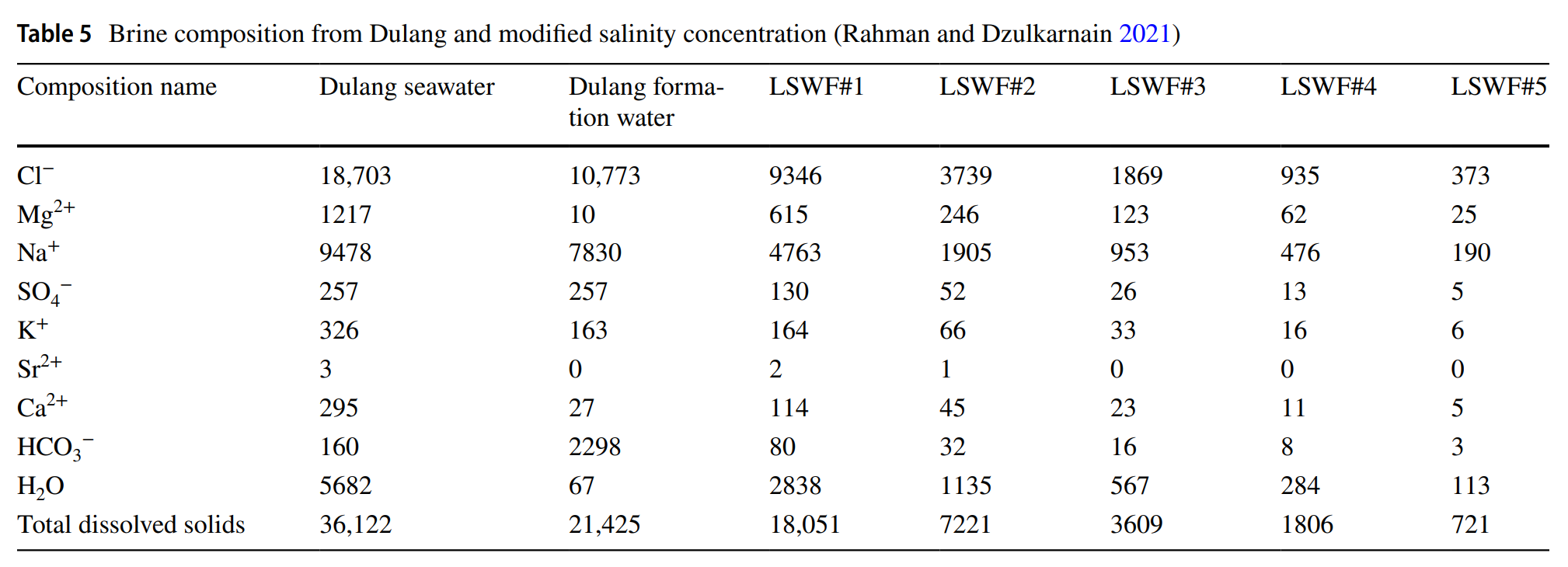
Low salinity water alternating immiscible gas CO2 (Immiscible CO2-LSWAG) injection is a popular technique for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) that combines the benefits of low salinity and immiscible CO2 flooding to increase and accelerate oil production. This approach modifies the displacement properties of the reservoir, resulting in higher sweep efficiency and greater oil production. The current study employs a combination of numerical and machine learning techniques to comprehensively investigate the performance of immiscible CO2-LSWAG injection in a sandstone reservoir. Furthermore, a detailed sensitivity analysis of various injection and reservoir parameters is conducted to gain deeper insights into their impact on the process. In order to predict the oil recovery factor (RF), the study employs 1000 experimental designs on initial oil-wet. The numerical simulation results indicate that immiscible CO2-LSWAG injection outperforms conventional immiscible CO2 and low salinity waterflood injection, resulting in a higher oil RF. The machine learning models of Catboost and LightGBM used in this study produced R2 scores higher than 0.95 with lower errors between the predicted and actual results. This indicates that machine learning models can provide a faster and more accurate alternative to numerical simulation. The sensitivity analysis results from the machine learning model reveal that the major contributing factors to oil RF are the chemical composition of the injected water and the injection rate. In summary, this study leverages machine learning for sensitivity analysis in immiscible CO2-LSWAG performance in oil-wet sandstone reservoirs. Key findings include the identification of top influencing parameters and high predictive accuracy of CatBoost and LightGBM algorithms. The results facilitate quick decision-making for field trials by focusing on major contributing factors, with future research suggested for broader applications.
