Endurance Primary Store Geochemical Model & Report
本文是关于Endurance储层的地球化学模型和报告,旨在为Net Zero Teesside (NZT)项目和Northern Endurance Partnership (NEP)项目提供地下CO2储存的地球化学模拟和解释。这些项目计划在2020年代中期促进Humber和Teesside工业集群的脱碳。报告详细介绍了使用PHREEQC和Geochemist’s Workbench (GWB)软件包进行的地球化学模拟,以及定制概念模型来定义地下系统并预测其对CO2注入的响应。模拟结果表明,向Endurance结构注入超临界CO2不太可能对储层或粘土或卤水封隔层造成负面影响,化学过程造成损害的风险非常低。此外,报告还探讨了井筒附近的地球化学过程,以及通过周期性淡水冲洗来测试缓解方案的有效性。
CMG软件的应用情况:
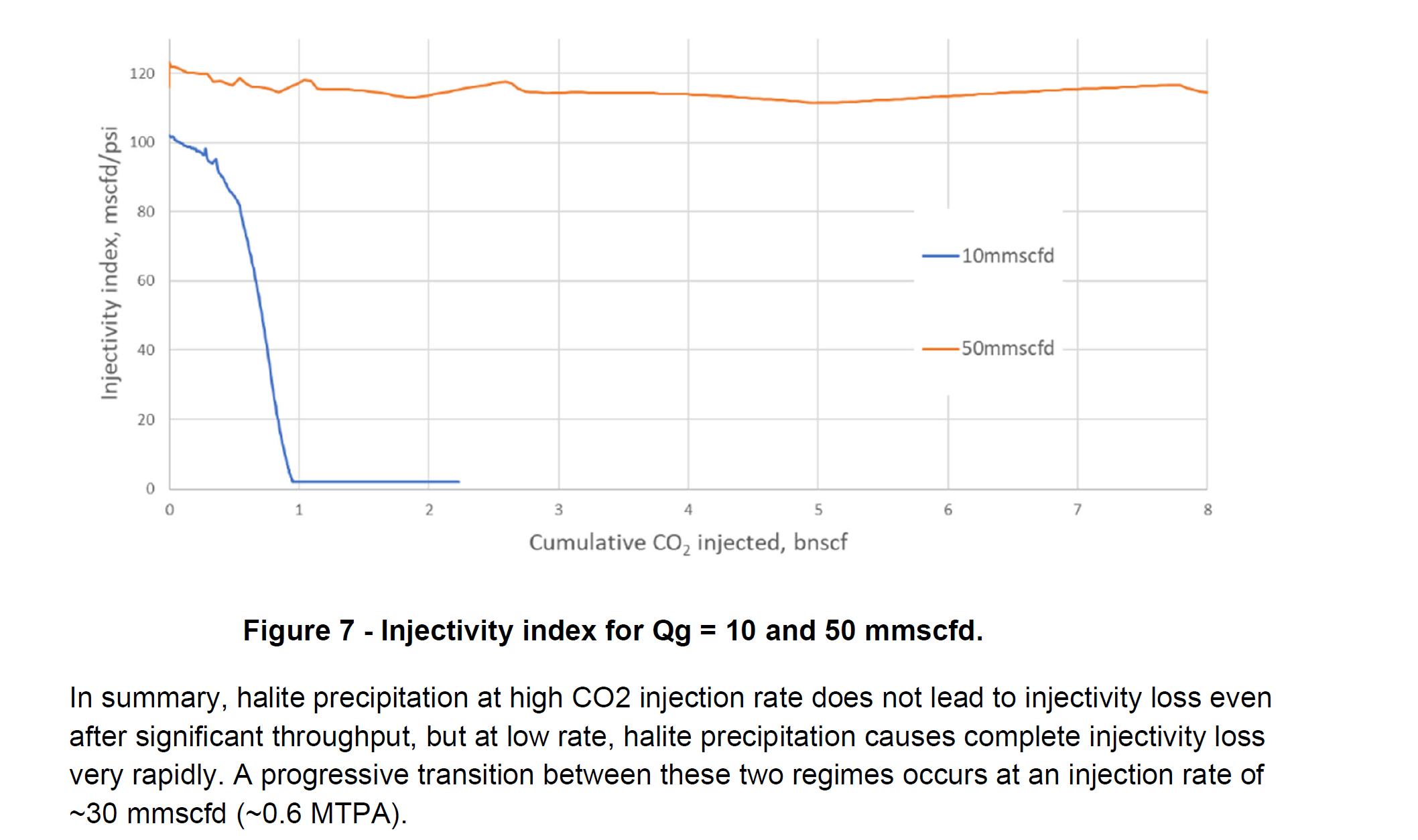
CMG的GEM™储层模拟器被用于模拟井筒附近的耦合传质、相互溶解度和地球化学效应。该模型提供了对现象的机理分析,评估了不确定性的影响,并测试了缓解方案(盐水冲洗)。GEM™允许在状态方程(EoS)中包含水组分,从而严格处理盐水蒸发。模型参数基于Endurance储层的特性,包括半径、高度、单元尺寸、压力、底部温度、孔隙度、渗透率等。通过模型,研究了不同注入速率下的盐析和沉淀机制,以及不确定性对这些机制的影响,并通过周期性淡水冲洗来缓解注入能力损失。此外,模型还考虑了储层层状渗透率分布对注入能力损失的影响。
结论:
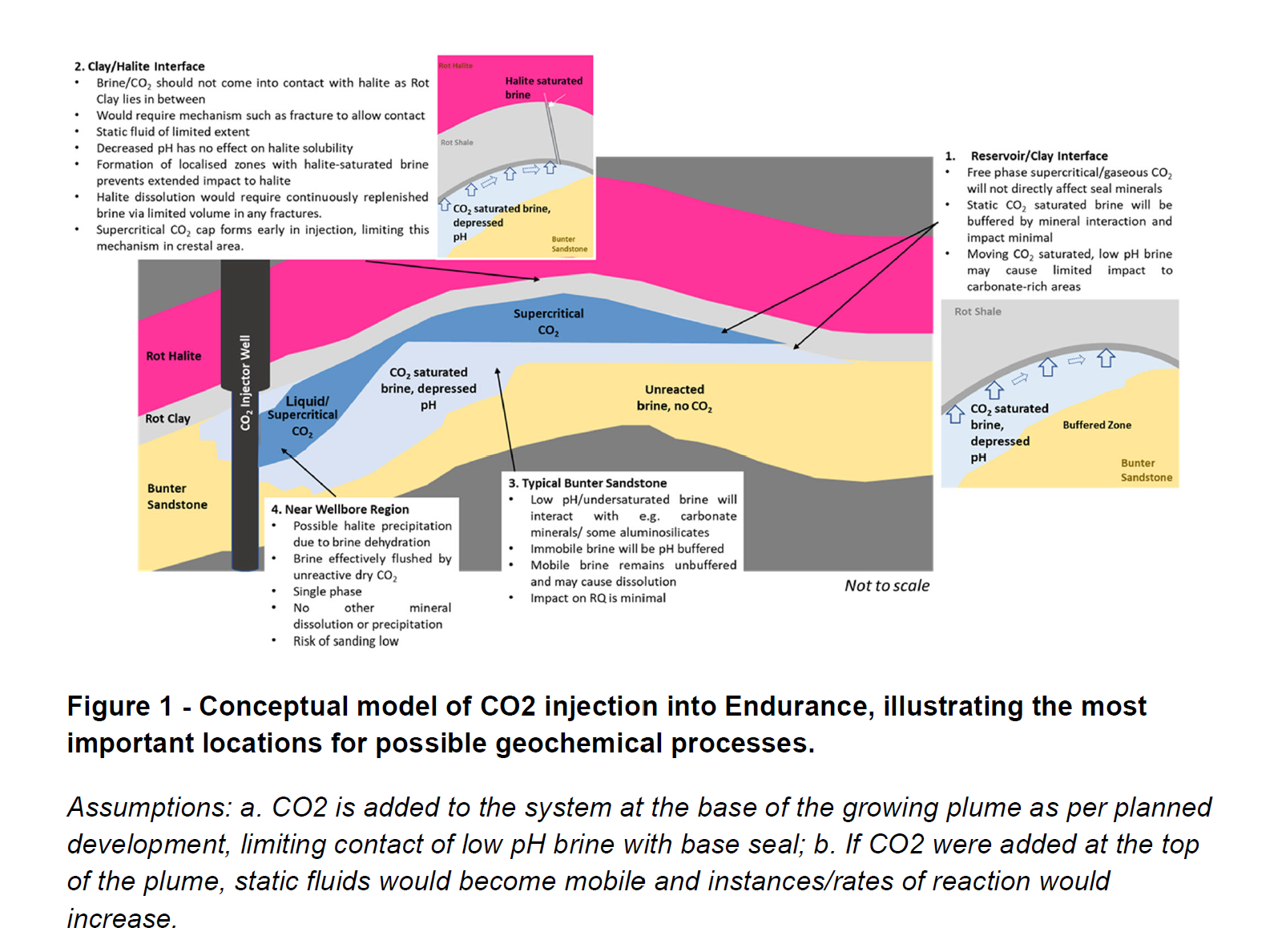
报告总结了地球化学模拟与概念模型结合的结果,指出在Endurance储层注入超临界CO2不太可能对储层或封隔层造成负面影响。CO2溶解会导致pH值下降,但这一过程会被碳酸盐矿物的缓冲作用所缓解。在井筒附近区域,由于CO2和盐水的互溶性,几乎完全蒸发的盐水意味着不太可能发生化学反应,从而极大限制了通过水泥溶解引起的砂化风险。在储层/封隔层界面,粘土矿物的存在对矿物溶解的可能性影响很小,因此不会影响封隔层的完整性。如果酸性储层盐水到达粘土/卤水界面,预测会有一些盐水溶解,但这种情况会迅速饱和,形成边界层,之后不会再有更多的卤水溶解,因此对卤水完整性的风险也是有限的。此外,模拟过程还可以用来预测任何产生的水的有毒/危险物质的分布,这将影响其处理、处置或排放的决策。
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to summarize the work program completed on geochemical aspects of the integrated subsurface description of the Endurance store. This follows previous studies such as those completed as part of the White Rose project. Early analysis of previous studies highlighted a number of key areas to further advance understanding, which were drawn together and used in the development of geochemical models used to test subsurface uncertainties and assess risk.
Subsurface storage risks can be broadly classified as those relating to containment, capacity, injectivity and monitorability, with those covered by this document focusing on containment and injectivity. Key areas to advance geochemical understanding to assess containment and injectivity uncertainties and risks at the Endurance store were identified as:
CO2 and brine interactions within the reservoir and within the two key sealing formations, the Röt Clay and the Röt Halite, and any impact on containment integrity.
Mechanisms that control halite precipitation within the reservoir following the injection of CO2 and its impact to injectivity, and mitigation effectiveness by periodic fresh-water flushing.
These were investigated via two discrete geochemical modelling and simulation studies.
作者单位:英国石油公司(bp)代表其自身及Northern Endurance Partnership项目合作伙伴编写此报告