Study of the effect of salt deposition on production capacity and storage capacity in underground gas storage
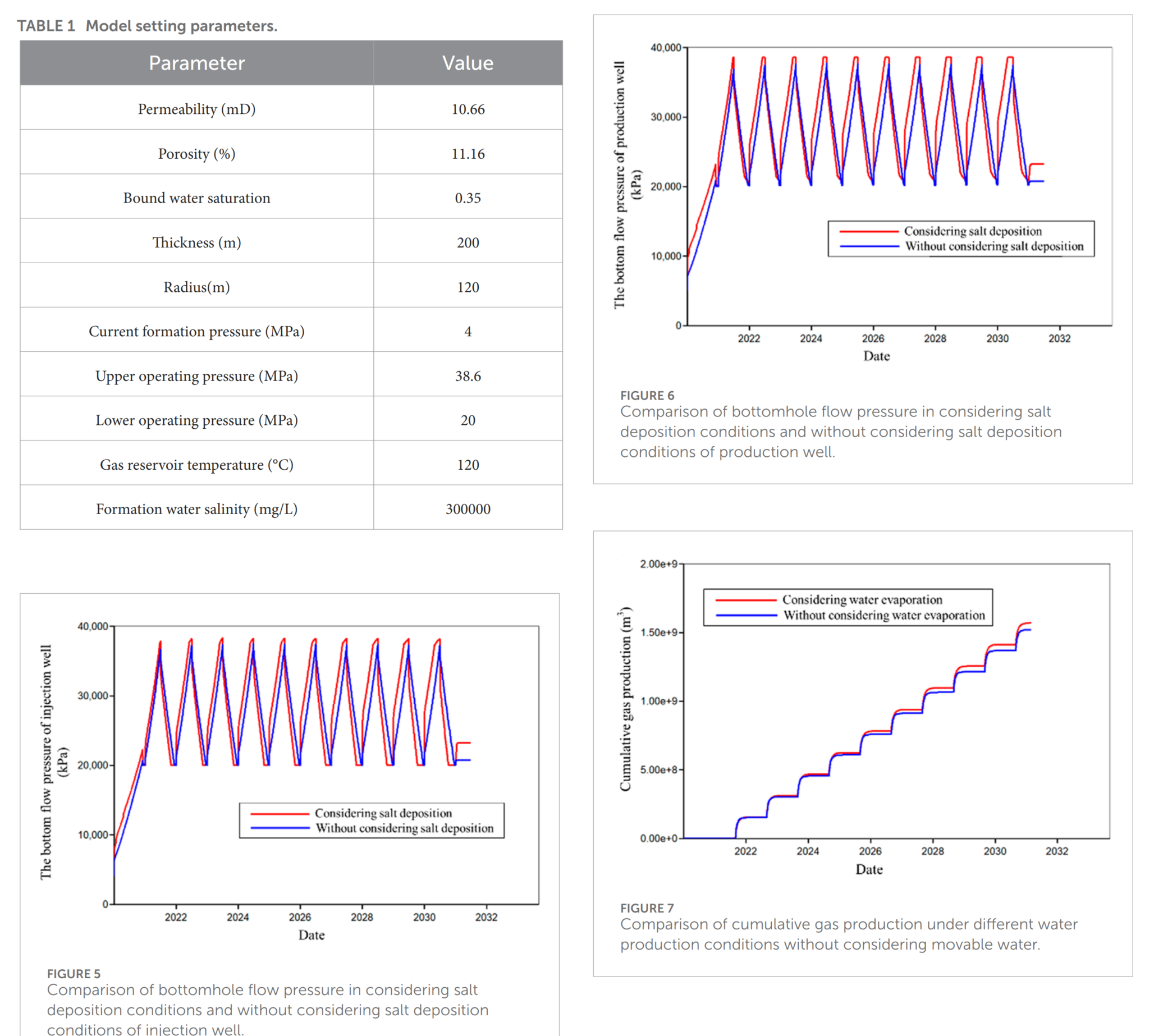
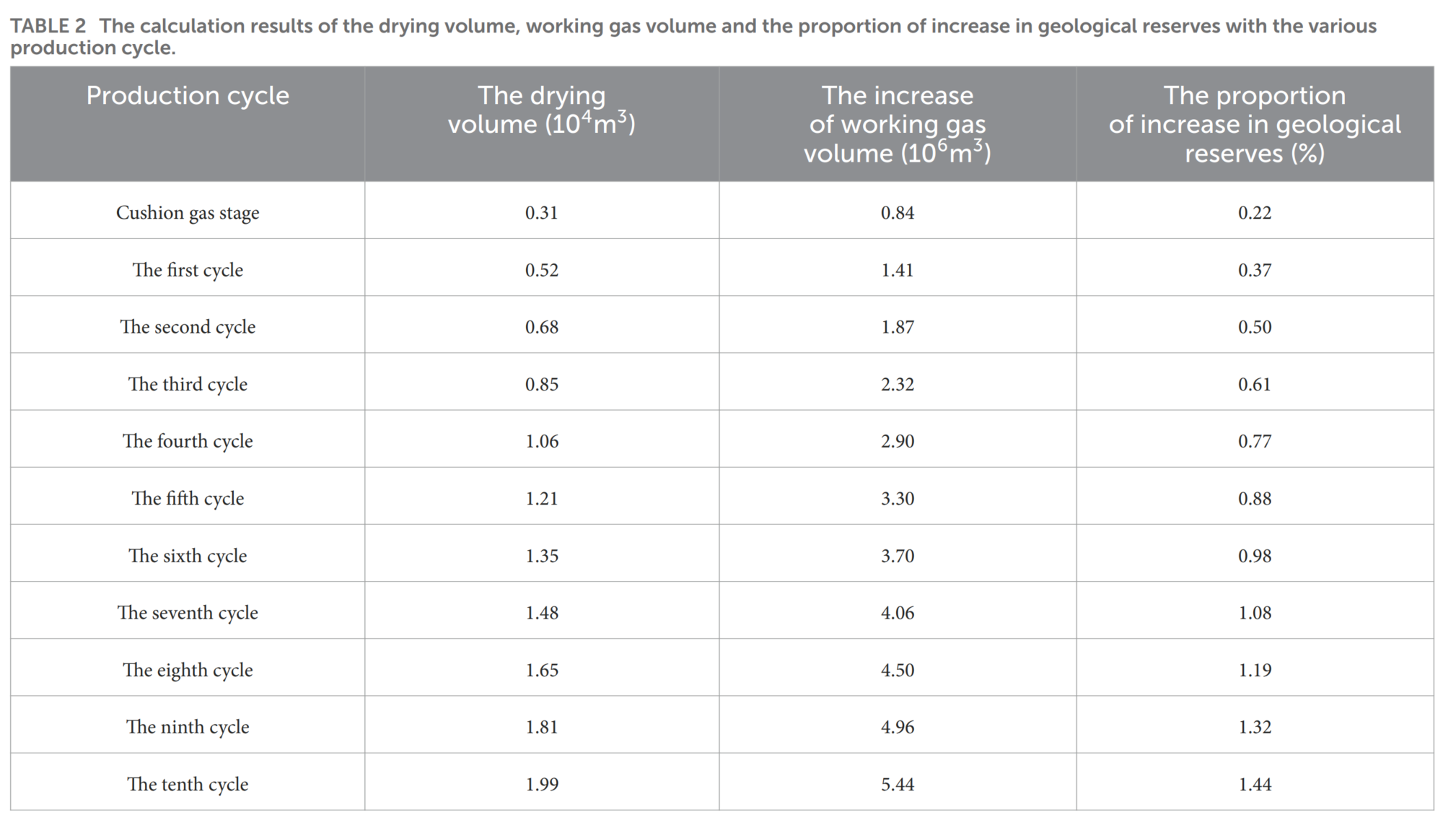
天然气地下储存(UGS)是保证稳定天然气供应最经济有效的手段。在天然气生产过程中,地层水的蒸发导致气体中水分含量增加,剩余地层水的矿化度增加。本研究应用数值模拟分析了盐析对流动压力、生产能力和储存能力的影响。模拟结果表明,在盐析条件下,UGS的最小和最大压力更有可能在多周期生产中达到。在初始水条件下,储层干燥可以提高气体储存能力。在第十周期结束时,储存能力增加了1.4%。研究认为,研究地层水蒸发对储存能力的影响有助于高矿化度UGS中盐析的预防和控制。
CMG软件应用情况:
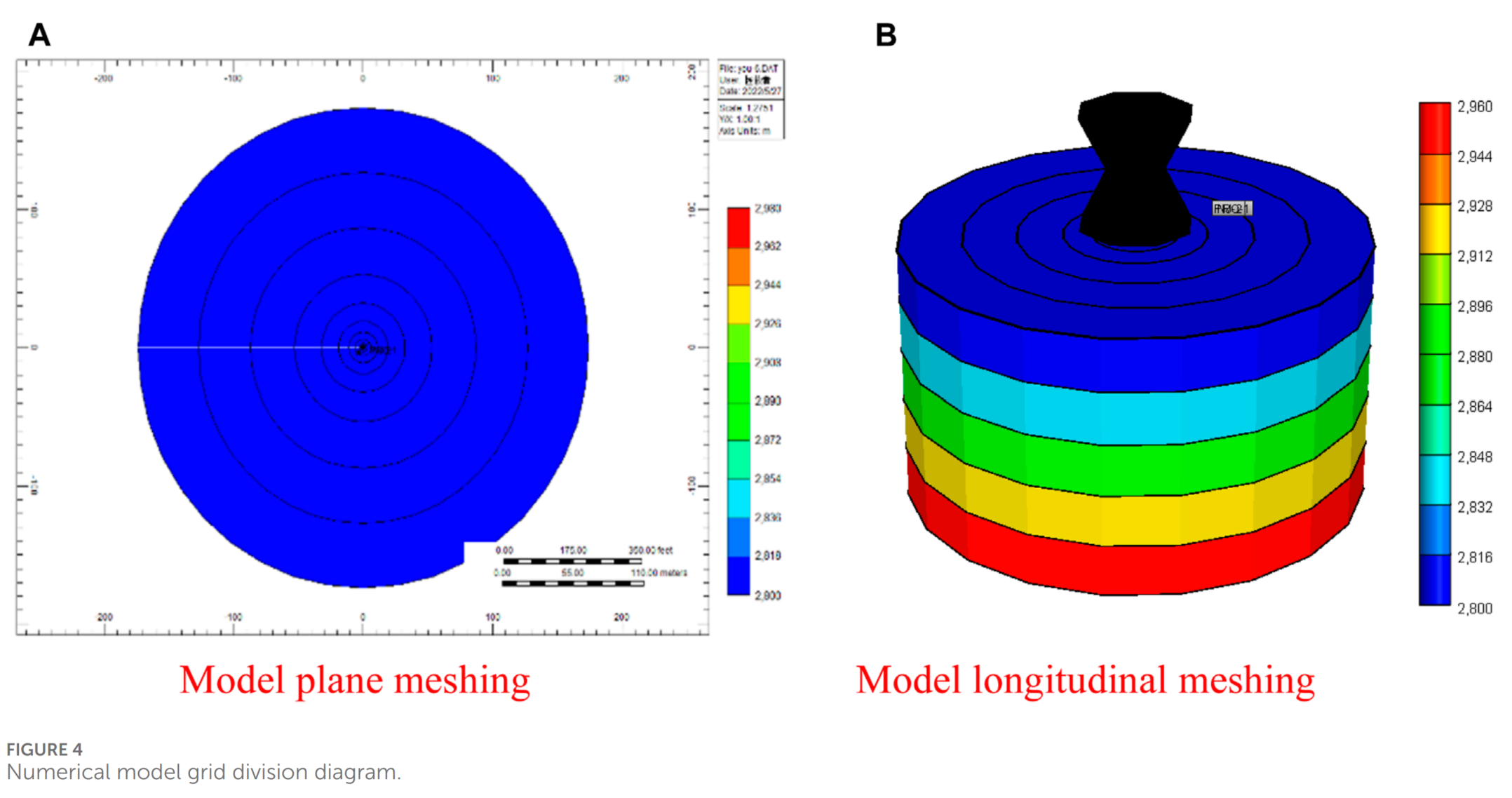
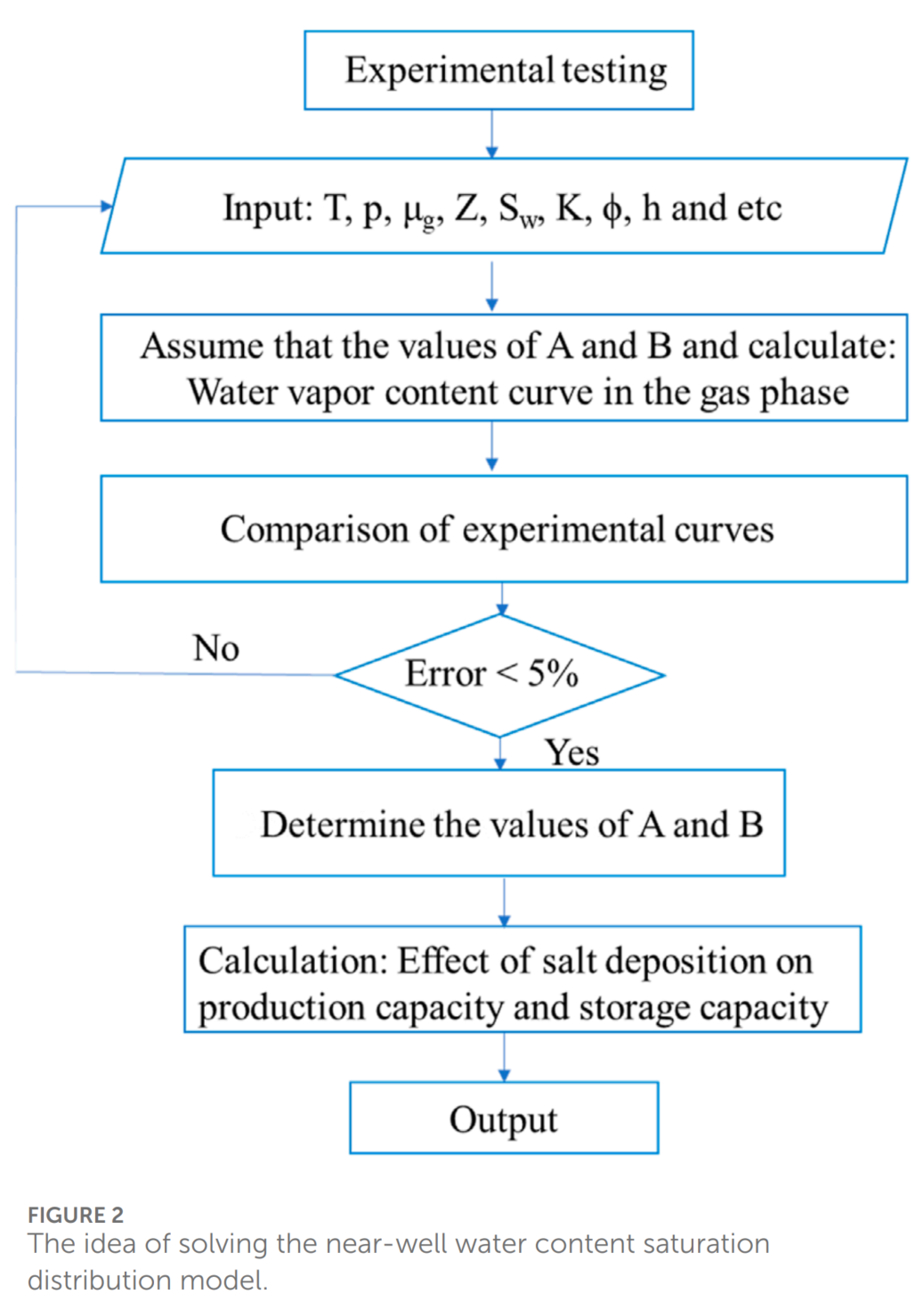
本文使用CMG数值模拟软件来模拟单井多周期生产的UGS的径向机理。该模型用于研究水蒸发和盐析对UGS生产能力和储层容量的影响。模拟中考虑了地层水的矿化度对气体液相平衡和固相沉淀的影响,以及在气体生产期间对气体流动能力和储层储存能力的影响。
作者单位:
- 国家油气管网集团
- 西南石油大学石油工程学院
Abstract:
Underground gas storage (UGS) is the most economical and effective means to guarantee stable gas supply. During gas production process, the evaporation of formation water leads to the increase of water content in the gas, and the salinity of the remaining formation water increases. This work applied numerical simulation to analyze the effect of salt deposition on flowing bottomhole pressure, production capacity and storage capacity. The simulation results show that the minimum and maximum pressure of UGS is more likely to be reached during multi-cycle production under the conditions of salt deposition. Under the initial water condition, reservoir drying can improve the gas storage capacity. At the end of the tenth cycle, the storage capacity increases by 1.4%. It is concluded that the study on the impact of formation water evaporation on storage capacity is helpful for the prevention and control of salt formation water in UGS with high salinity.
