为了缓解环境危机,改善能源结构,世界各国都把目光投向了潜力巨大、污染小的干热岩地热资源。强化地热系统产生的地热具有复杂的多场耦合过程,研究地热储层的时空演化具有重要意义。本文建立了一个实用的数值模型来模拟EGS中的采热过程,并对地热储层的热流(TH)、热流固(THM)、及热流固化(THMC)耦合进行了比较分析。
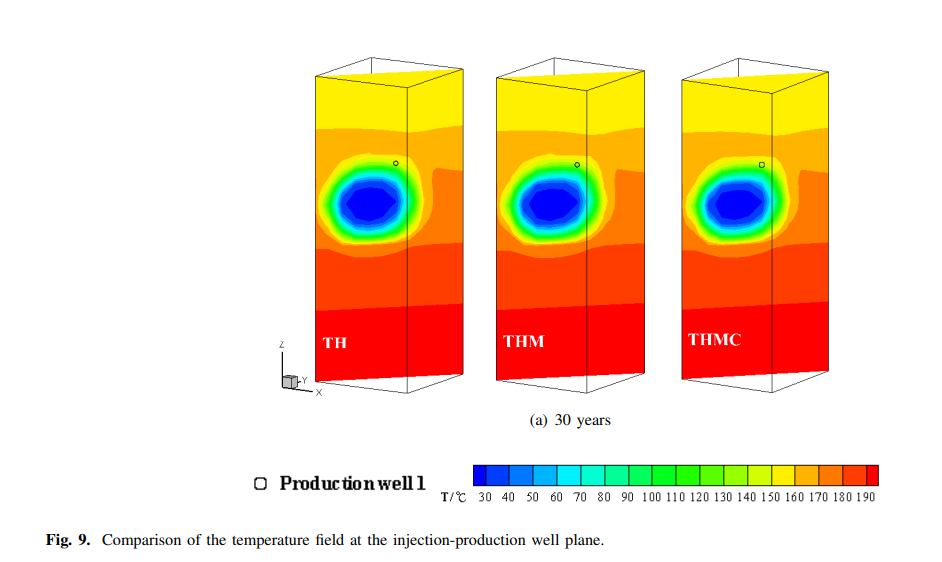
进行了分析。结果表明,三种情况下的稳定生产阶段约为5年;然而,与TH和THMC耦合相比,THM耦合的开采年限分别减少了1140天和332天。化学沉淀抵消了机械增强效应,SiO2的沉淀量远大于方解石的溶解量。
Comparison of multi-field coupling numerical simulation in hot dry rock thermal exploitation of enhanced geothermal systems
Abstract:
In order to alleviate the environmental crisis and improve energy structure, countries from all over the world have focused on the hot dry rock geothermal resources with great potential and with little pollution. The geothermal heat production from enhanced geothermal system comes with complex multi-field coupling process, and it is of great significance to study the temporal and spatial evolution of geothermal reservoir. In this work, a practical numerical model is established to simulate the heat production process in EGS, and the comparison of thermal hydraulic (TH), thermal-hydraulic-mechanical (THM) and thermal-hydraulic-mechanical-chemical (THMC) coupling in geothermal reservoir
is analyzed. The results show that the stable production stage of the three cases is approximately 5 years; however, compared with TH and THMC coupling, the service-life for THM coupling decreased by 1140 days and 332 days, respectively. The mechanical enhanced effects are offset by the chemical precipitation, and the precipitation from SiO2 is much larger than the dissolution of calcite.