The Impact of Autonomous Inflow Control Valve on Improved Oil Recovery in a Thin-Oil-Rim Reservoir
文章探讨了在薄油环储层中应用自主流入控制阀(AICV)来提高石油采收率的效果。由于薄油环储层容易受到气锥现象的影响,这会导致油气生产效率降低。AICV技术通过限制气体在突破区域的流入,有助于提升这些储层的石油采收率。研究通过实验和模拟相结合的方法,对比分析了AICV、被动流入控制装置(ICD)和砂筛的性能。实验部分在模拟Troll油气田储层条件下,使用轻质油、天然气和水进行了单相和多相流动实验。模拟研究则利用CMG STARS模拟器,开发了考虑砂筛、AICV和ICD完井的油井模型,以模拟近井筒油生产。研究结果表明,与ICD和砂筛相比,AICV完井能显著减少累计天然气产量,并增加累计石油产量。此外,AICV完井的油井在更长时间内以更有利的气油比(GOR)生产。本研究的创新之处在于对新型AICV进行了多相实验,并将实验数据成功应用于模拟器中,提出了AICV/ICD模拟的流程,并通过模拟结果验证了实验AICV性能结果的准确性。
CMG软件的应用情况
在本研究中,CMG STARS模拟器被用来模拟ICD和AICV在轻质油储层中的性能,并评估它们对提高石油采收率的贡献。STARS模拟器能够处理涉及多相和多组分的复杂油藏模拟,特别适合模拟装备有ICD和AICV等复杂完井技术的油井。模拟时,采用了先进的FlexWell(FW)灵活井模型,该模型考虑了井筒与储层之间的动态相互作用,并通过耦合求解井筒和油藏模型来提高模拟精度。模拟结果揭示了AICV完井在提高石油产量和减少天然气产量方面的显著优势,并与实验数据相符,证明了模拟器中AICV/ICD行为实现的准确性和有效性。
Summary
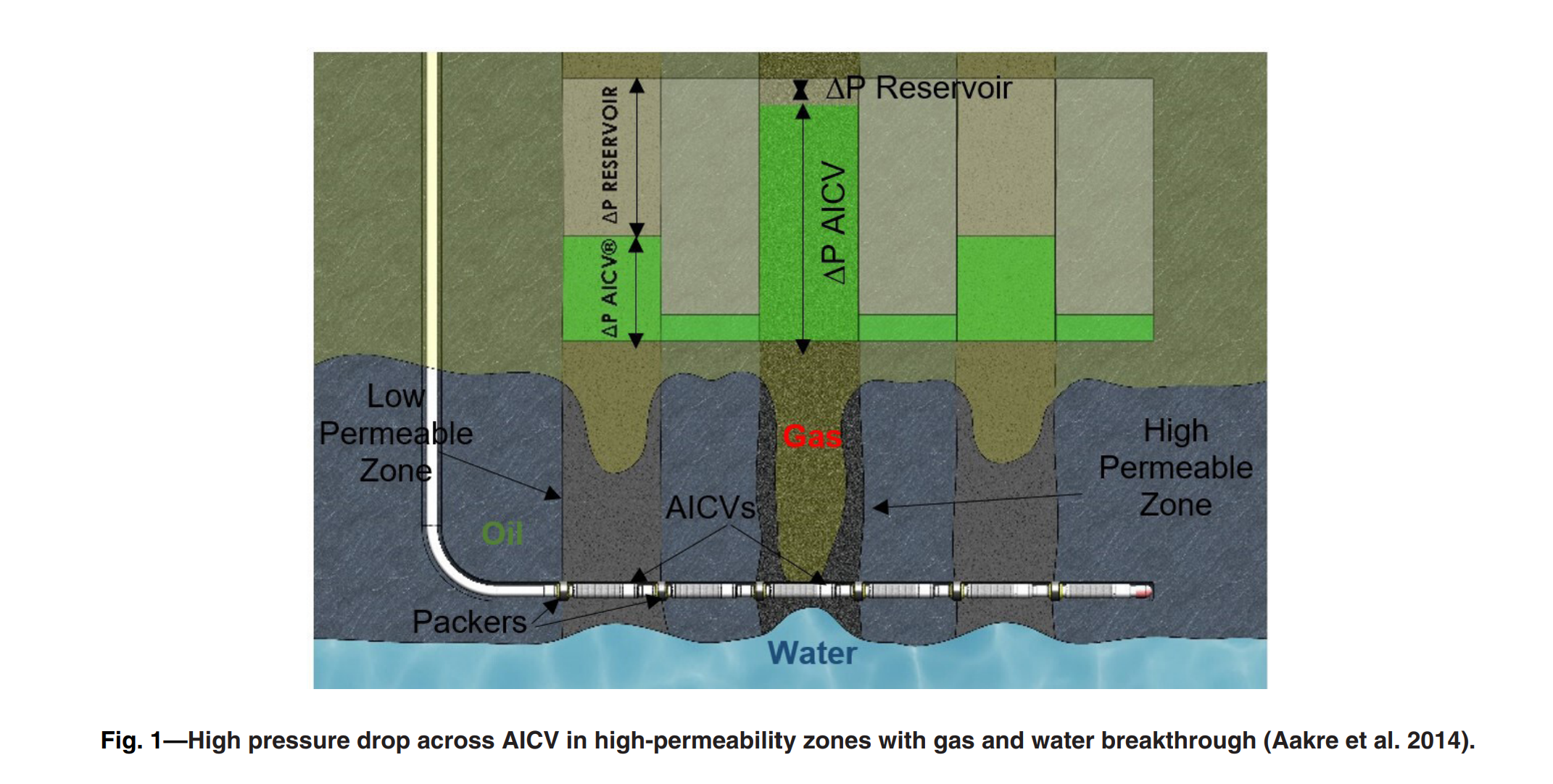
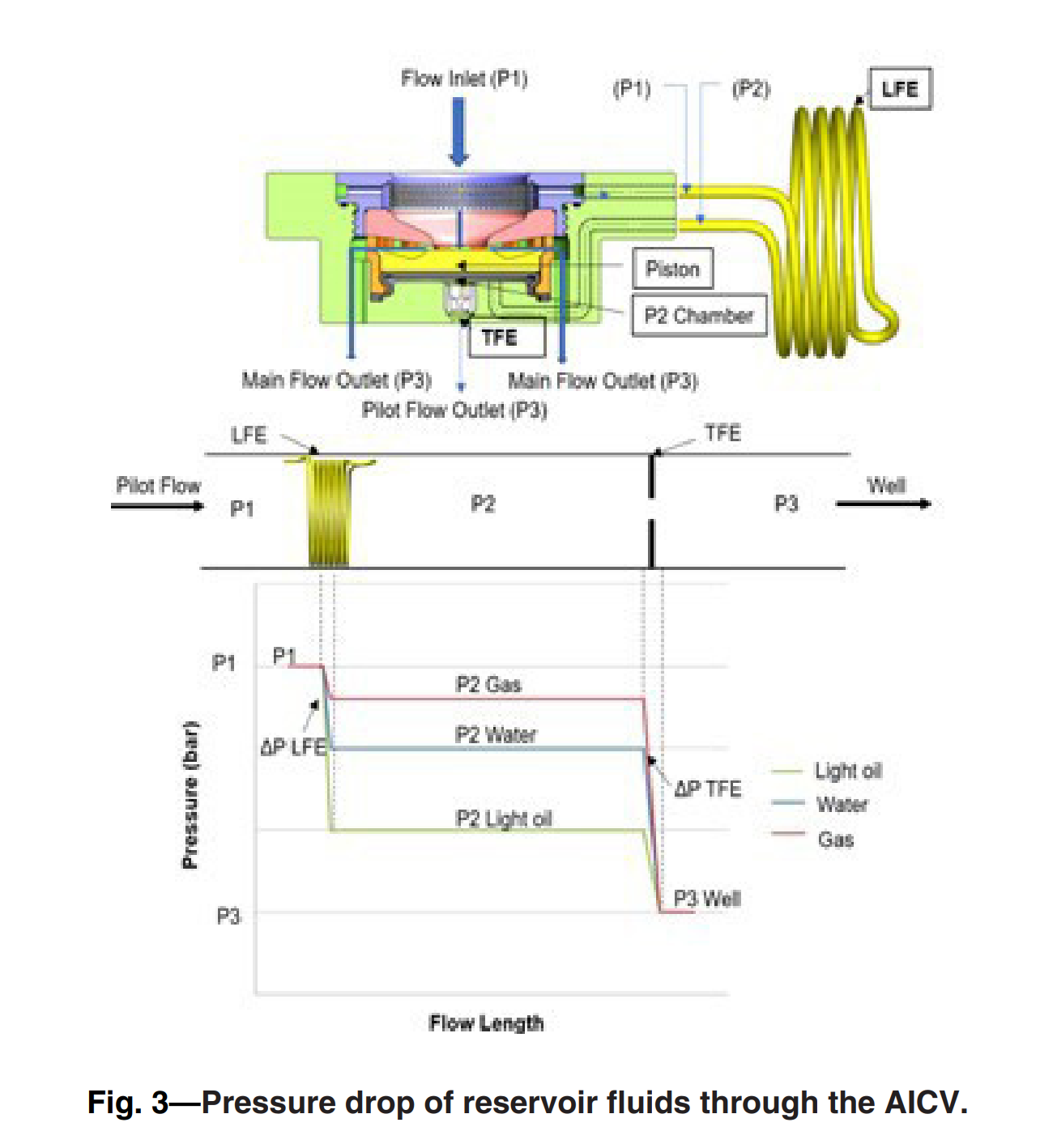
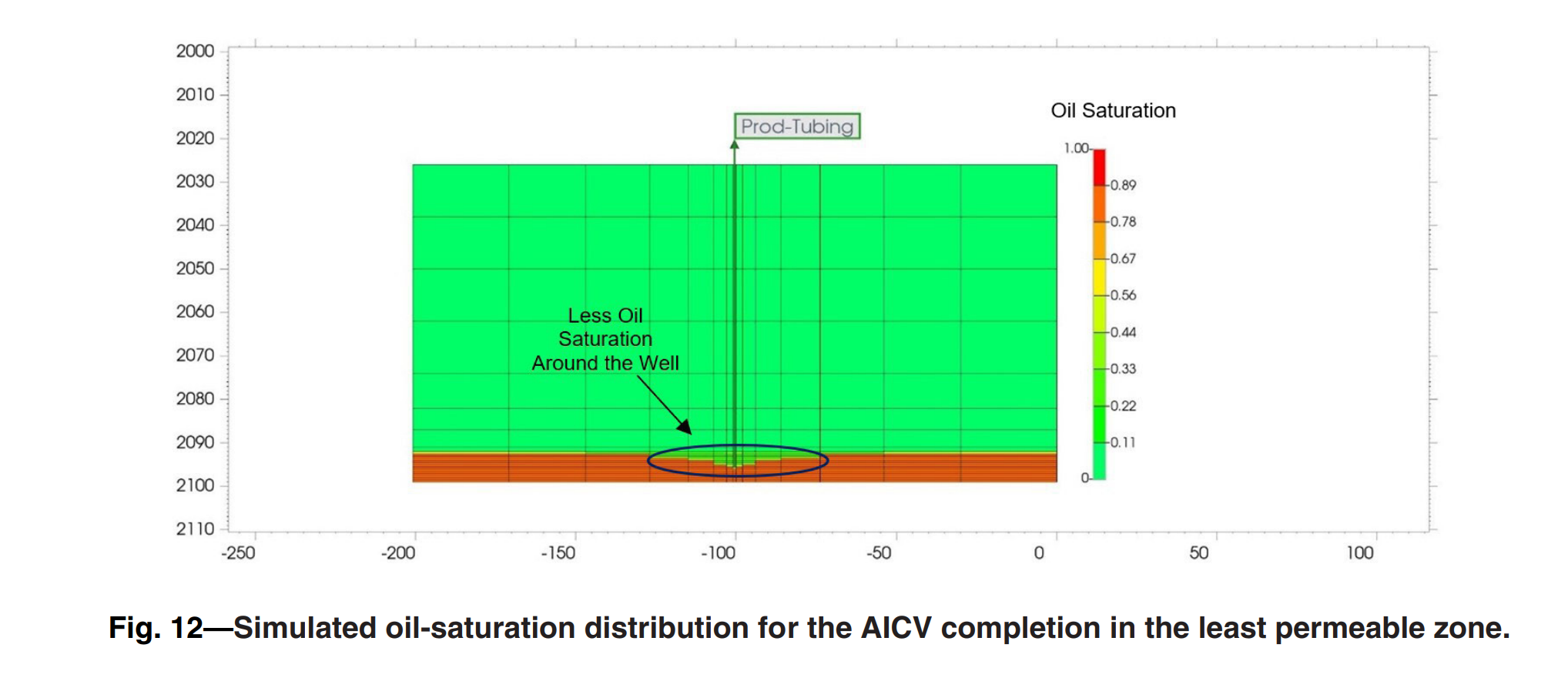
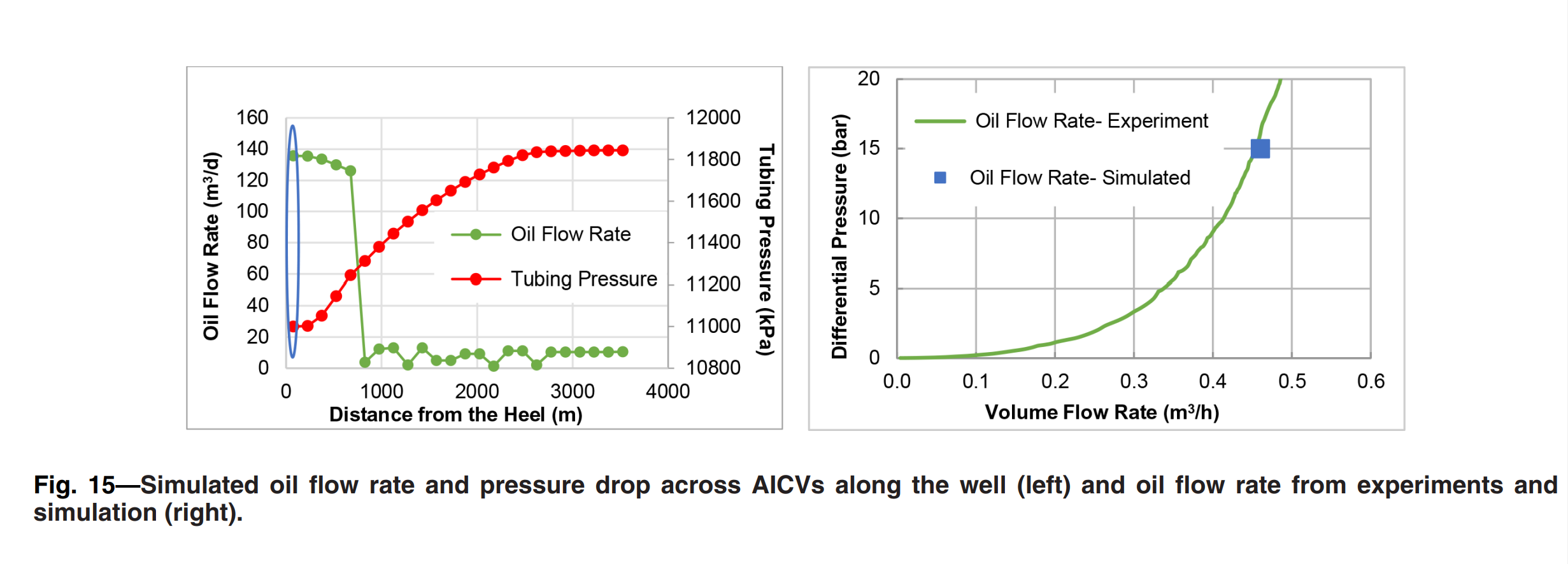
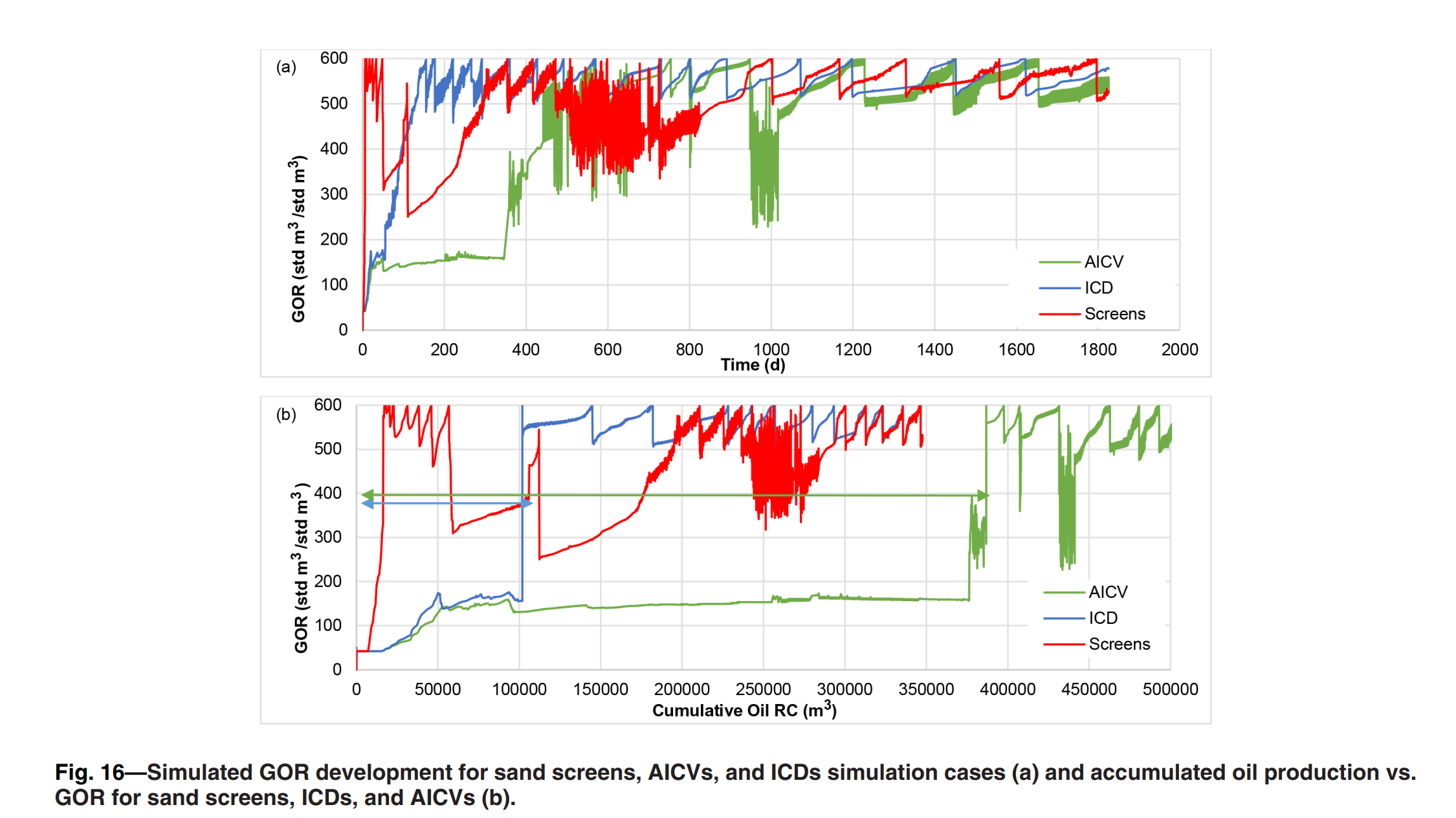
Oil production from thin-oil-rim fields can be challenging as such fields are prone to gas coning. Excessive gas production from these fields results in poor production and recovery. Hence, these resources require advanced recovery methods to improve the oil recovery. One of the recovery methods that is widely used today is advanced inflow control technology such as autonomous inflow control valve (AICV). AICV restricts the inflow of gas in the zones where breakthrough occurs and may consequently improve the recovery from thin-oil-rim fields. This paper presents a performance analysis of AICVs, passive inflow control devices (ICDs), and sand screens based on the results from experiments and simulations. Single- and multiphase-flow experiments are performed with light oil, gas, and water at typical Troll field reservoir conditions (RCs). The obtained data from the experiments are the differential pressure across the device vs. the volume flow rate for the different phases. The results from the experiments confirm the significantly better ability of the AICV to restrict the production of gas, especially at higher gas volume fractions (GVFs). Near-well oil production from a thin-oil-rim field considering sand screens, AICV, and ICD completion is modeled. In this study, the simulation model is developed using the CMG simulator/STARS module. Completion of the well with AICVs reduces the cumulative gas production by 22.5% and 26.7% compared with ICDs and sand screens, respectively. The results also show that AICVs increase the cumulative oil production by 48.7% compared with using ICDs and sand screens. The simulation results confirm that the well completed with AICVs produces at a beneficial gas/oil ratio (GOR) for a longer time compared with the cases with ICDs and sand screens. The novelty of this work is the multiphase experiments of a new AICV and the implementation of the data in the simulator. A workflow for the simulation of AICV/ICD is proposed. The simulated results, which are based on the proposed workflow, agree with the experimental AICV performance results. As it is demonstrated in this work, deploying AICV in the most challenging light oil reservoirs with high GOR can be beneficial with respect to increased production and recovery.

作者单位
- 南东挪威大学
- InflowControl AS公司
