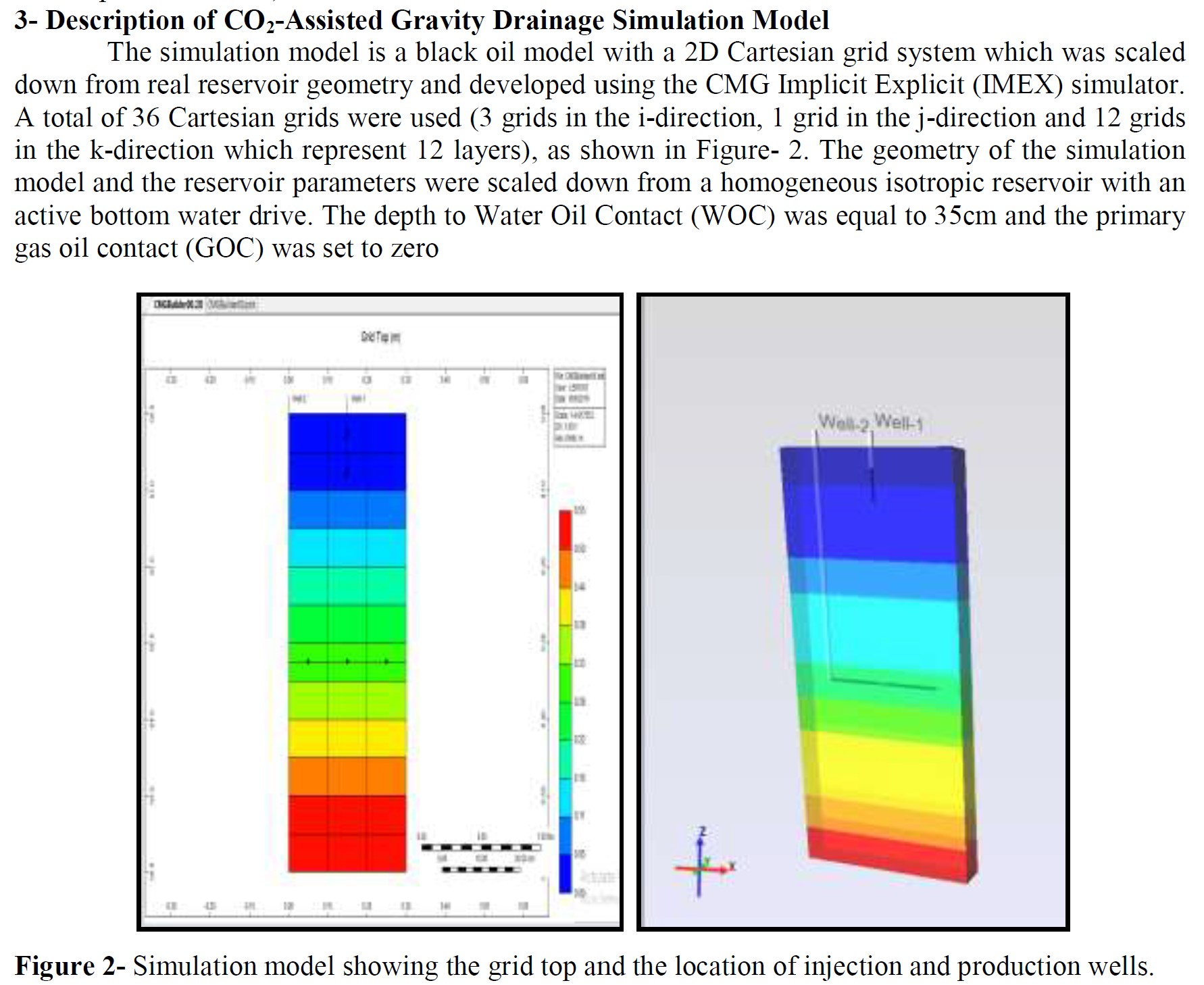
Numerical Simulation of Immiscible CO2-Assisted Gravity Drainage Process to Enhance Oil Recovery
CMG软件的应用情况
作者单位
ABSTRACT
The Gas Assisted Gravity Drainage (GAGD) process has become one of the most important processes to enhance oil recovery in both secondary and tertiary recovery stages and through immiscible and miscible modes. Its advantages came from the ability to provide gravity-stable oil displacement for improving oil recovery, when compared with conventional gas injection methods such as Continuous Gas Injection (CGI) and Water – Alternative Gas (WAG).
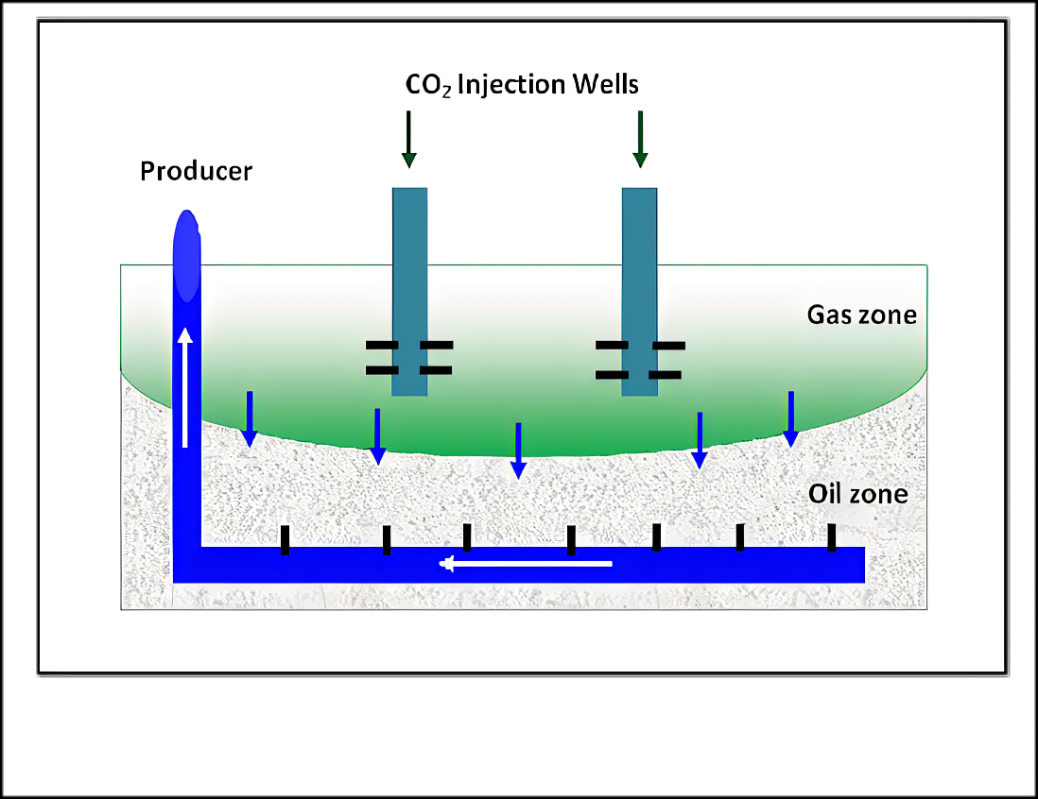
Vertical injectors for CO2 gas were placed at the top of the reservoir to form a gas cap which drives the oil towards the horizontal oil producing wells which are located above the oil-water-contact. The GAGD process was developed and tested in vertical wells to increase oil recovery in reservoirs with bottom water drive and strong water coning tendencies. Many physical and simulation models of GAGD performance were studied at ambient and reservoir conditions to investigate the effects of this method to enhance the recovery of oil and to examine the most effective parameters that control the GAGD process. A prototype 2D simulation model based on the scaled physical model was built for CO2-assisted gravity drainage in different statement scenarios. The effects of gas injection rate, gas injection pressure and oil production rate on the performance of immiscible CO2-assisted gravity drainage-enhanced oil recovery were investigated.
The results revealed that the ultimate oil recovery increases considerably with increasing oil production rates. Increasing gas injection rate improves the performance of the process while high pressure gas injection leads to less effective gravity mediated recovery.
Keywords: Gravity Drainage, Enhanced Oil Recovery, CO2 Injection, immiscible displacement.