Polymer Injectivity Test Design Using Numerical Simulation
本文聚焦于聚合物驱油过程中聚合物注入性测试设计,旨在探究如何通过数值模拟优化该测试,以深入理解聚合物在地层中的流变行为,进而辅助聚合物驱油项目设计。研究借助实验室径向流实验与数值模拟结合,以及构建油田规模模型模拟不同注入情形的方法,分析了注入井底压力(BHP)与聚合物原位流变学的关联,同时考察了地层非均质性及渗透率降低等因素的影响。研究结果表明,聚合物驱油与水驱的 BHP 压力建立时间存在差异,且可依据该时间区分不同流变模式;在油田现场测试中,采用速率变化方案并结合对压力稳定时间的评估,能够有效获取聚合物流变行为信息,此方法对均质和非均质油藏均具有一定适用性。
CMG 软件应用情况
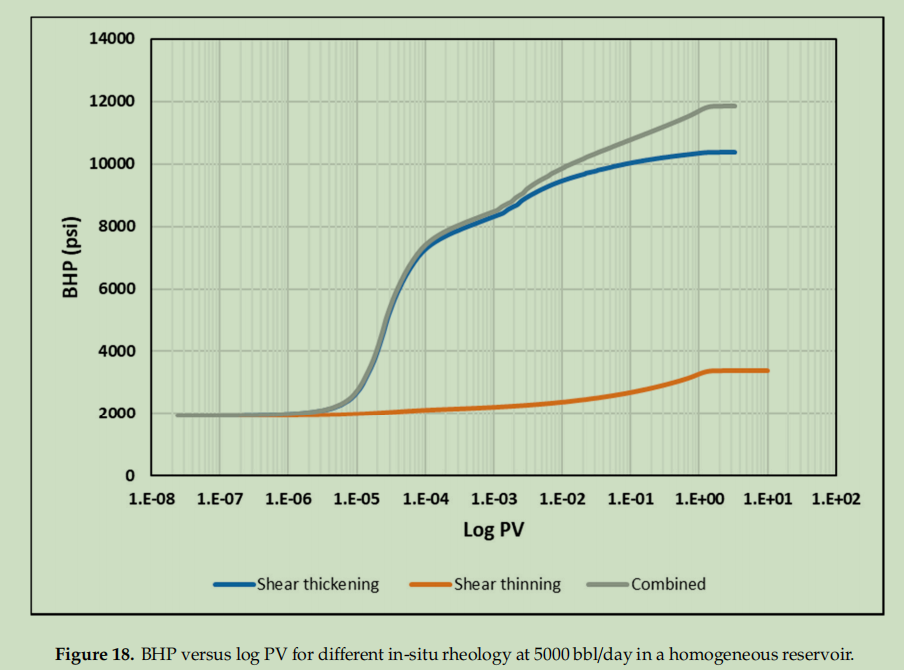
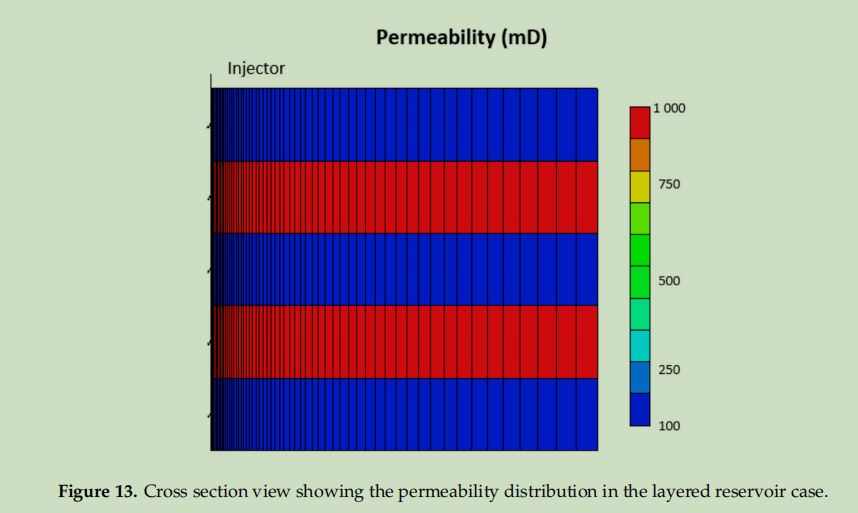
在油田规模模拟部分,使用了 CMG STARS 软件构建径向模型。通过该软件设置了特定的网格系统,包括采用指数增长的网格尺寸来精确捕捉近井区域速度变化,确定了如井型、厚度、孔隙度、渗透率等模型参数,并模拟不同注入速率下聚合物注入过程,分析不同流变行为下的 BHP 响应,以此研究聚合物在油藏中的注入特性及相关影响因素,为优化聚合物注入性测试提供依据。
作者单位:
穆罕默德・阿德尔・阿尔扎比(Mohamed Adel Alzaabi)、约根・高斯达尔・雅各布森(Jørgen Gausdal Jacobsen)、阿恩・斯考格(Arne Skauge):卑尔根大学化学系;挪威能源研究中心;挪威能源研究公司。
谢哈德・马萨尔梅(Shehadeh Masalmeh)、阿里・苏迈蒂(Ali Al Sumaiti):阿布扎比国家石油公司,阿联酋阿布扎比。
厄于斯泰因・彼得森(Øystein Pettersen):挪威研究中心。
Abstract:
Polymer flflooding is an enhanced oil recovery (EOR) process, which has received increasing interest in the industry. In this process, water-soluble polymers are used to increase injected water viscosity in order to improve mobility ratio and hence improve reservoir sweep. Polymer solutions are non-Newtonian flfluids, i.e., their viscosities are shear dependent. Polymers may exhibit an increase in viscosity at high shear rates in porous media, which can cause injectivity loss. In contrast, at low shear rates they may observe viscosity loss and hence enhance the injectivity. Therefore, due to the complex non-Newtonian rheology of polymers, it is necessary to optimize the design of polymer injectivity tests in order to improve our understanding of the rheology behavior and enhance the design of polymer flflood projects. This study has been addressing what information that can be gained from polymer injectivity tests, and how to design the test for maximizing information. The main source of information in the fifield is from the injection bottom-hole pressure (BHP). Simulation studies have analyzed the response of difffferent non-Newtonian rheology on BHP with variations of rate and time. The results have shown that BHP from injectivity tests can be used to detect in-situ polymer rheology.
Keywords: chemical EOR; polymer flflooding; in situ rheology; polymer injectivity; polymer modeling