Numerical Approach for Enhanced Oil Recovery with Surfactant Flooding using STARS (CMG)
本文探讨了化学增强石油回收(EOR)中的一个有前景的技术——表面活性剂驱油。表面活性剂能够降低油水之间的界面张力至超低值,从而提高油的流动性和相对渗透率,增加残余油的驱替效率。研究以利比亚一个油田为对象,使用CMG公司的STARS软件包进行数值模拟。通过模拟,确定了最佳的表面活性剂浓度、流速和驱油周期,结果表明,在最优条件下,额外回收了167,167桶油。
CMG软件的应用情况
CMG的STARS模拟器软件包在石油工业中被广泛使用,特别是在考虑复杂的化学行为时,它能够创建实验室和现场规模的模型。STARS软件能够模拟表面活性剂在驱油过程中的行为,并通过实验室规模的模拟优化现场规模的表面活性剂驱油事件。本文中,STARS软件被用来模拟从1987年至2010年的油田生产,包括自然能量驱油、水驱和表面活性剂驱油等不同阶段。

Abstract
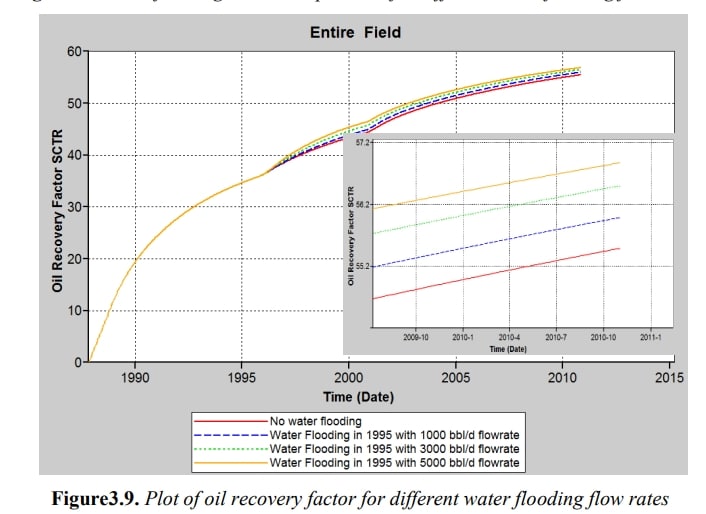
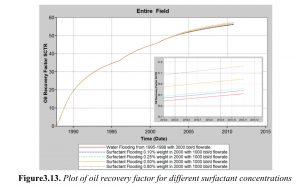
There is more than half of the original oil of the reservoir which is entrapped and immobile after orthodox recovery methods (primary and secondary recovery methods). Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) is essential to further extract the unrecovered residual oils. There are many EOR methods available to improve oil production by injecting fluids into the reservoir. In this thesis, the EOR method used is chemical injection and the specific chemical used is surfactant. Surfactant flooding utilises surface active agents (or surfactants) to adsorb onto oil-water interface and reduce their interfacial tension (IFT) to an ultralow value of 10-2 mN/m and below. Due to the low IFT, oil is readier to be mobilised and its relative permeability with water is increased and this in turn alters the wettability of the reservoir to become more water-wet. Henceforth, more residual oil can be displaced yielding a greater oil recovery. The reservoir used in this research is an oil field located in Libya. A numerical approach simulation is done on this field using STARS which is a software package by Computer Modelling Group (CMG). From the simulations executed, primary recovery is done from 1987 till 1995 using natural depletion as the reservoir has a strong water drive. Water flooding method is simulated as the secondary recovery method from year 1995. The optimum results are obtained when water is flooded at a rate of 3000 bbl/day and for 5 years till year 2000. From year 2000 onwards, the reservoir undergoes surfactant flooding. Sensitivity analyses are done for different surfactant concentrations, flow rates and flooding periods. From the results, surfactant is flooded for 6 years (2000-2006) with a flow rate of 3000 bbl/day and concentration of 0.8 % weight. It is proven that with optimum surfactant flooding conditions, an extra of 167,167 barrels of oil is recovered.
Keywords
Enhanced oil recovery, surfactant flooding, tertiary recovery, STARS, simulation, interfacial tension, EOR, IFT, and CMG.
作者单位
作者Brian Robin Stanislaus和Hisham Khaled Ben Mahmud均来自马来西亚科廷大学石油工程系。

