Comparative numerical study for polymer alternating gas (PAG) flooding in high permeability condition
Abstract
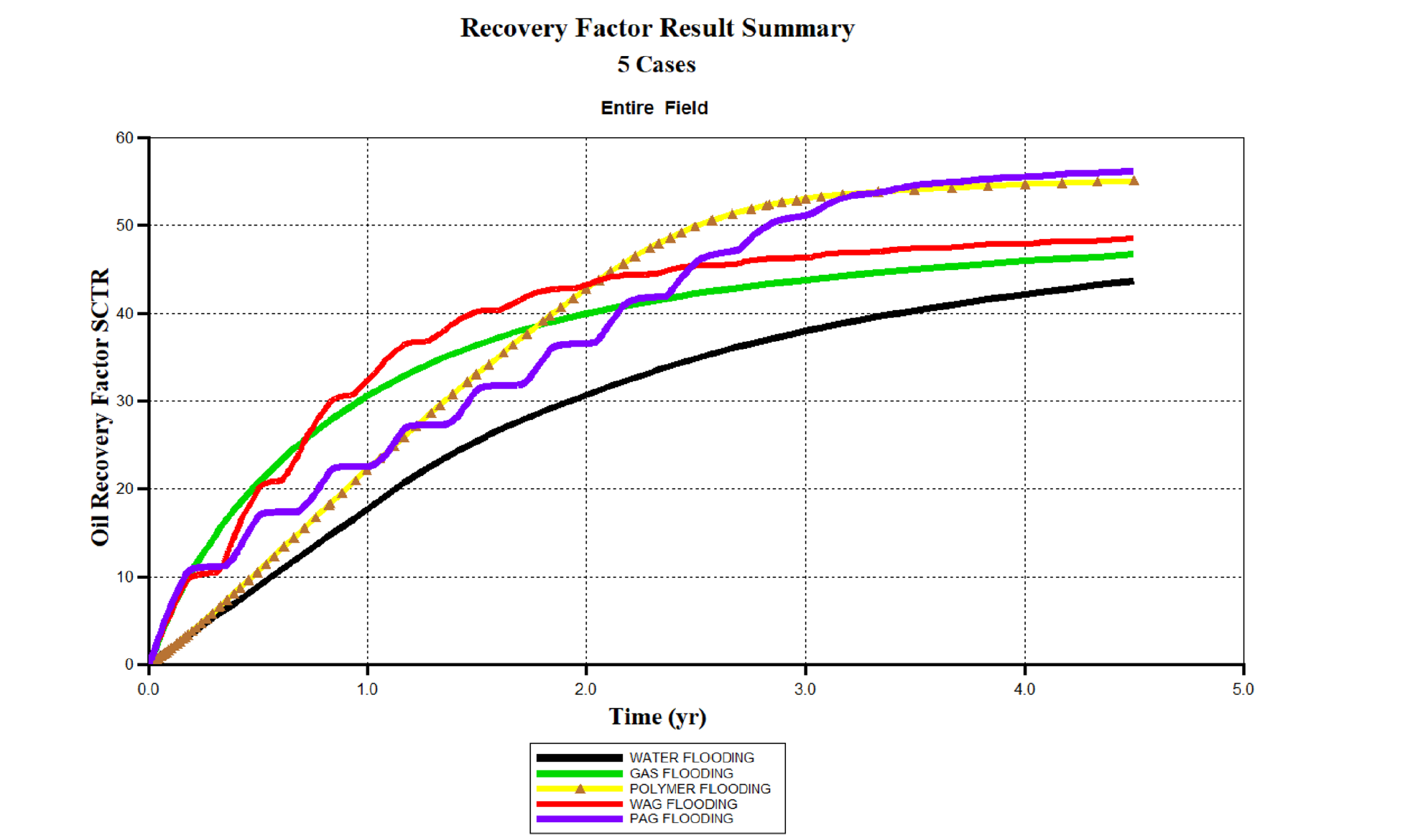
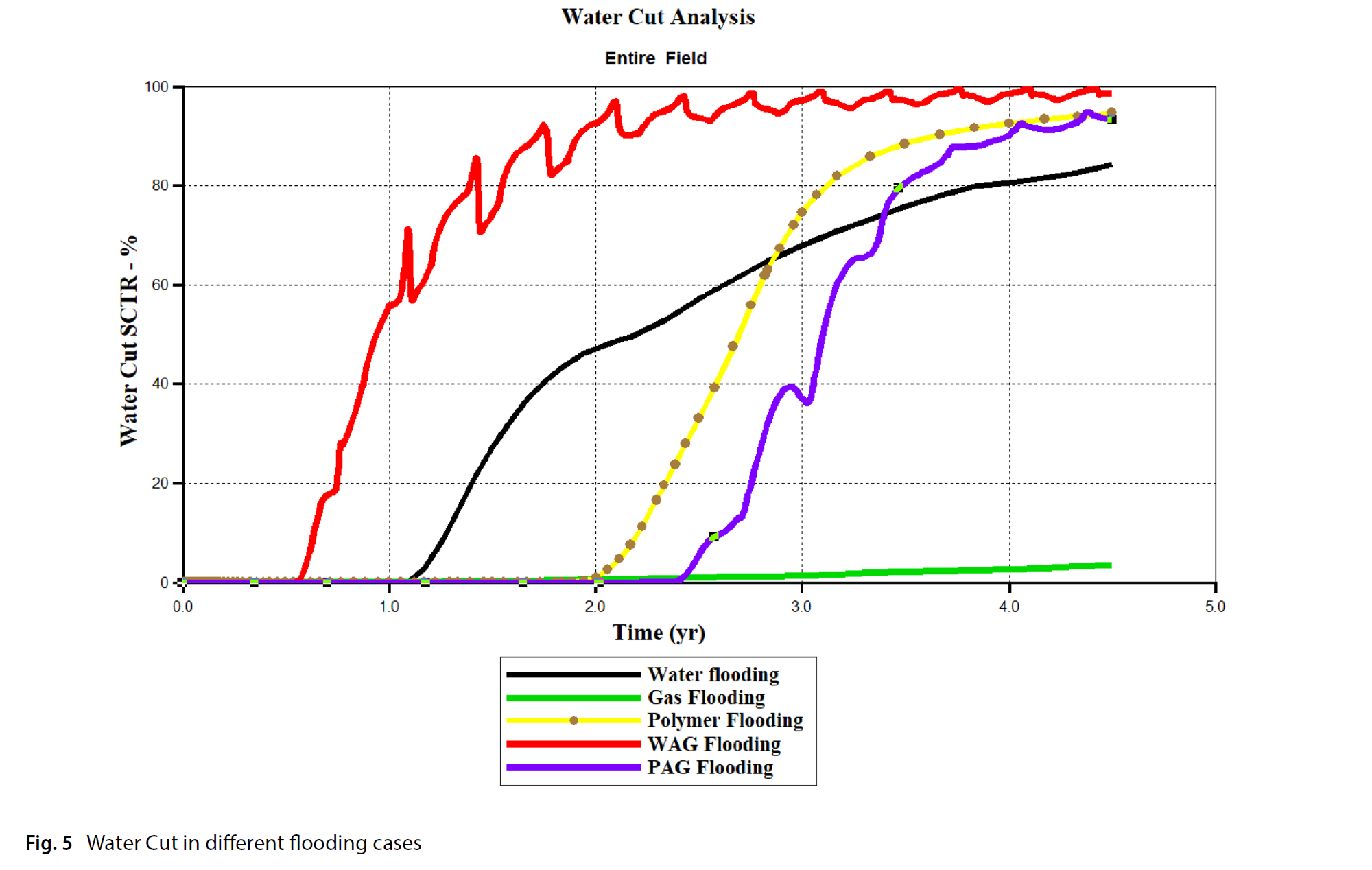
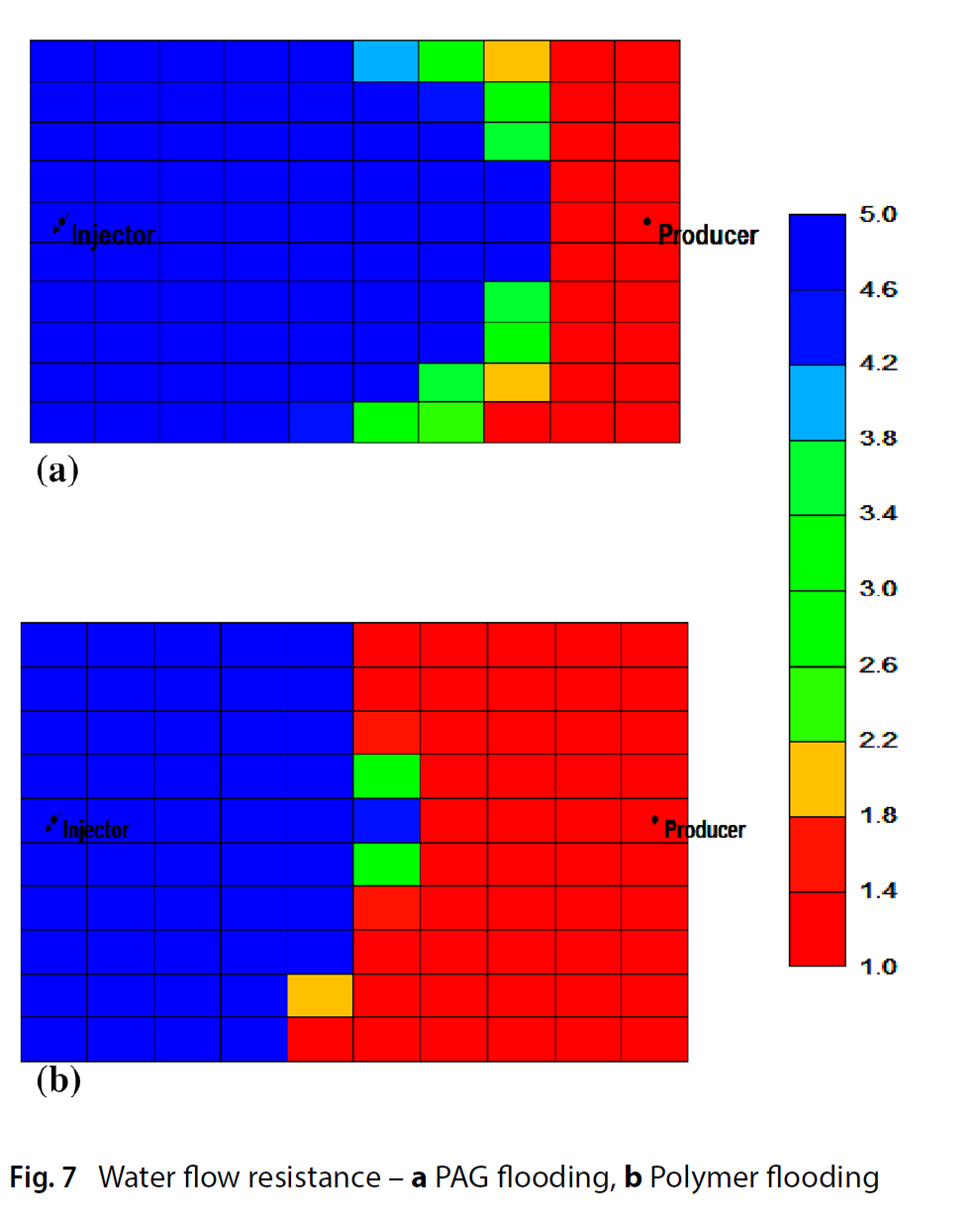
Polymers have been used in water alternative gas, to viscosify the water and improve the overall sweep efficiency. The use of polymer alternative gas was successful in increasing the oil production in high permeability zones. However, few practical factors affecting the field applicability have been overlooked. Therefore, this study is aimed at bridging the gap between the possibility of using several EOR such as water flooding, CO2 flooding, water alternative gas, polymer flooding and polymer alternative gas. The research based on progressive comparison considering constant constraint. The numerical simulation STARS-CMG was used to predict the characteristics and behaviour of the fluid in the reservoir. The designed flooding pattern chosen was a single producer-single injection (P-I) scheme in homogeneous high permeable reservoir. The results of oil incremental recovery showed the following order compared to Water flooding < (3%) CO2 flooding < (6.8%) < Water alternative gas (11.6%) Polymer flooding < (15%) Polymer alternative gas. The impact of polymer on enhancing the water alternative gas was mostly noticeable in the reduction of water cut% (83%). The controlled conformance by polymer aided in improving the sweep efficiency as indicated by the uninform U-shape. Moreover, the delayed gas breakthrough was significant and resulted in the lowest gas oil ratio of 5.17E + 04 ft3/bbl. The low gas oil ratio observation is indication of potential capturing of CO2 in the reservoir and thus, good evidence to further implementation of CO2 as green utilization.