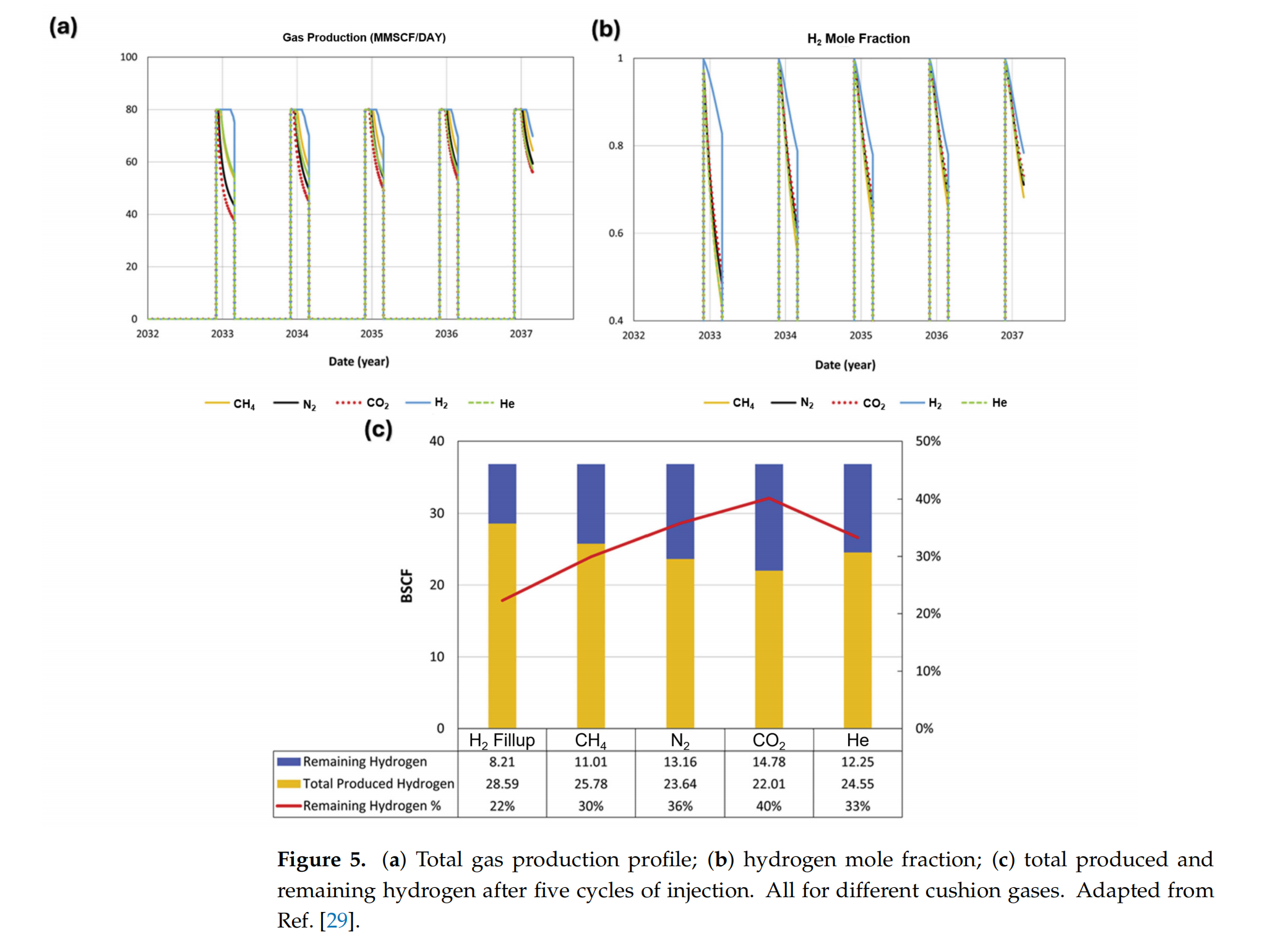
Cushion Gas Consideration for Underground Hydrogen Storage
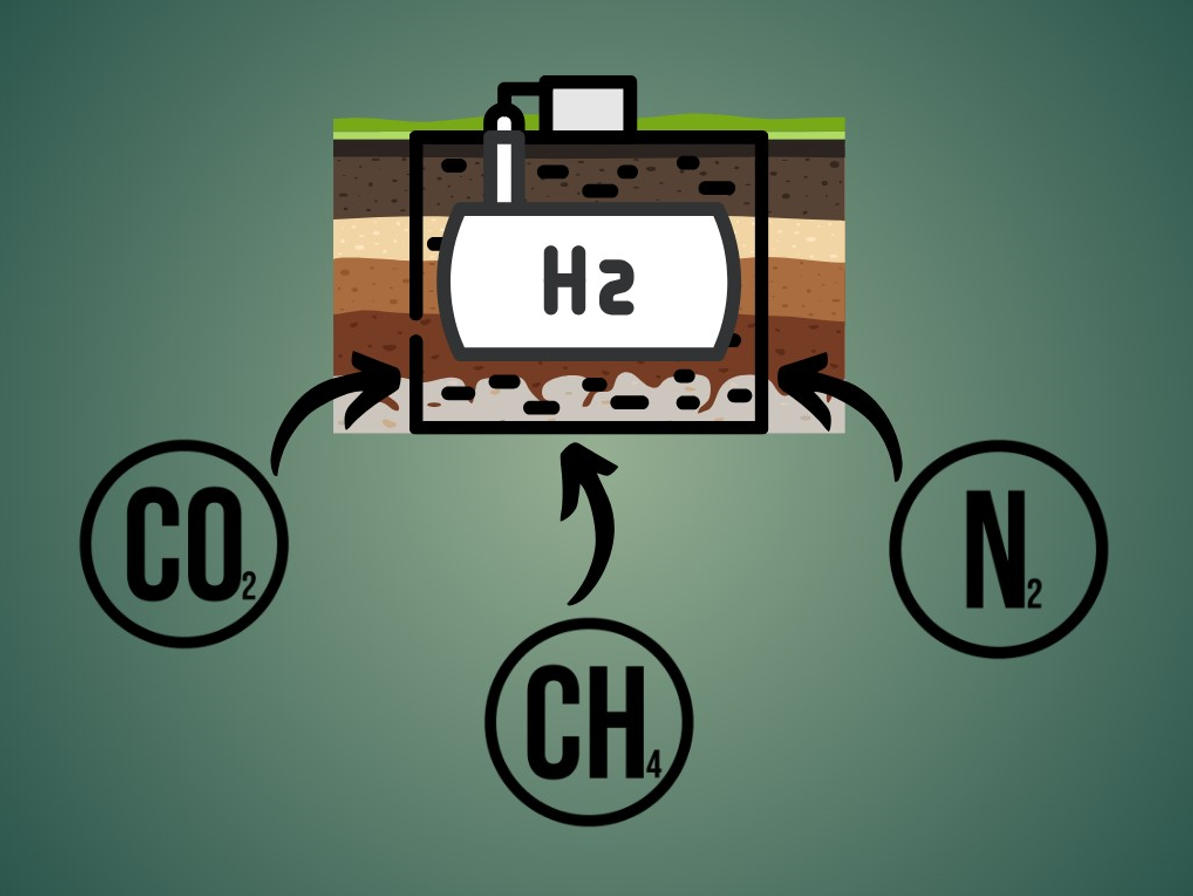
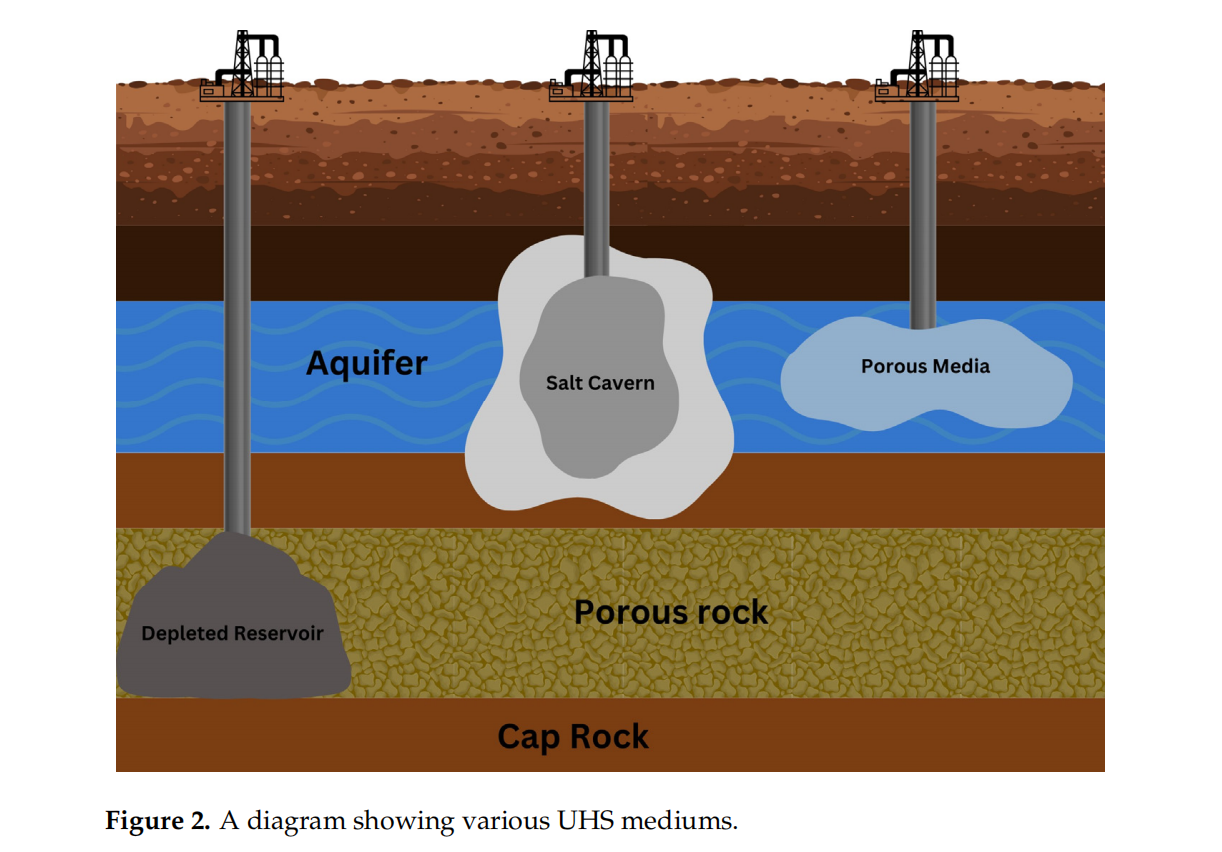
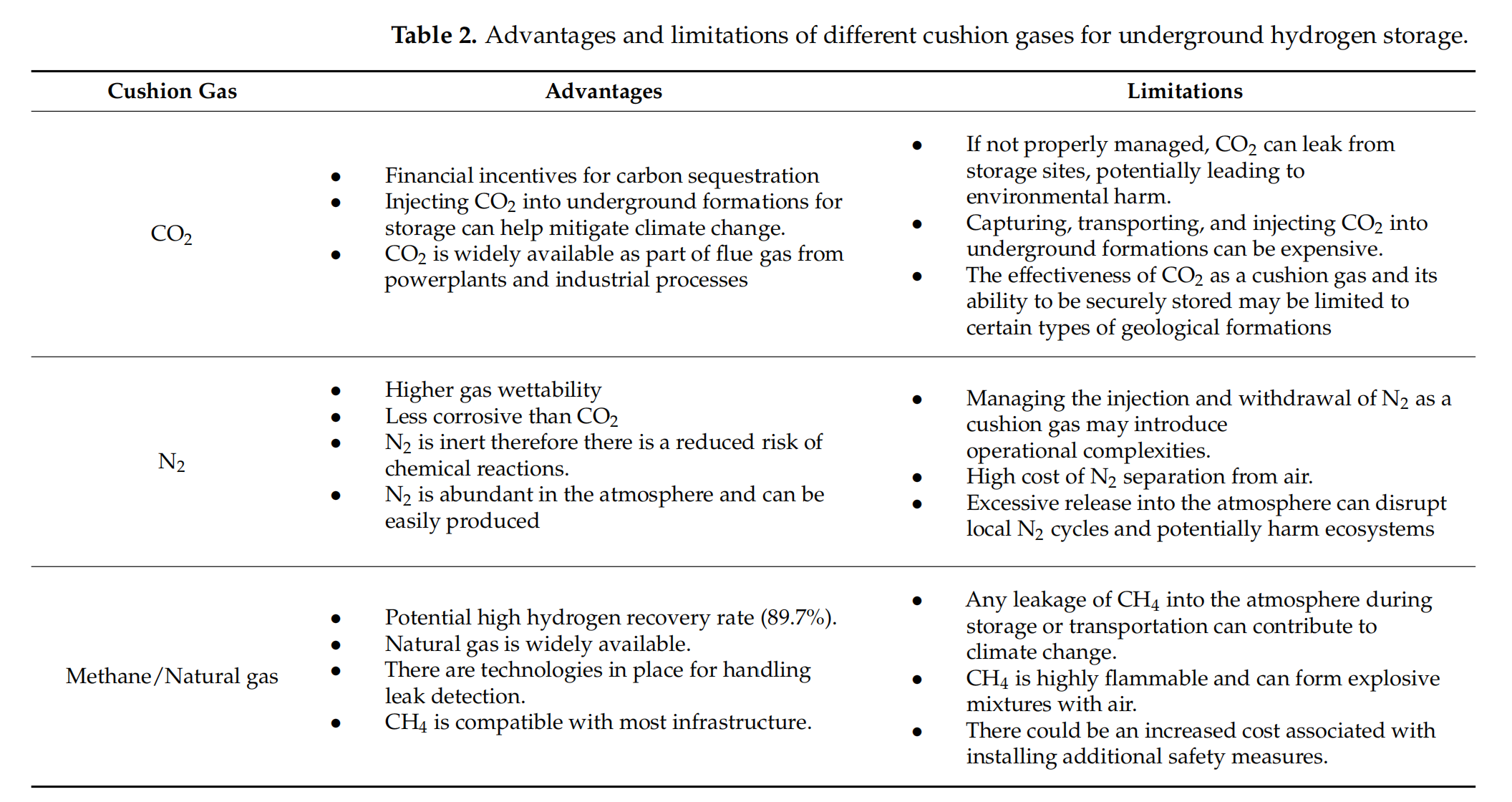
由于世界人口的增长和环境考量,人们对替代能源产生了巨大兴趣。氢气作为一种能源载体,因其环境友好性扮演着重要角色。氢气的燃烧释放出水蒸气,同时在航空、制药和冶金工业中有广泛的工业应用。尽管前景广阔,氢气面临储存挑战。地下氢储存(UHS)是一种安全储存氢气的方法。选择合适的UHS缓冲气体是确保储存系统安全性、效率和可靠性的关键方面。缓冲气体在维持储存库所需压力中起着关键作用,从而实现氢气的持续注入和提取速率。缓冲气体的一个关键功能是作为缓冲,确保储存压力在需求或供应波动时保持在所需范围内。这是通过在注入和提取周期中交替膨胀和压缩缓冲气体来实现的,从而有效调节储存设施内的整体压力动态。此外,垫气的选择对UHS系统的性能和长期稳定性有重要影响。在选择最合适的垫气时,必须仔细考虑与氢气兼容性、成本效益、可用性和环境影响等因素。本研究提供了UHS中常用的不同类型垫气的全面回顾,包括氮气、甲烷和二氧化碳。通过检查每种选择的优点、局限性和实际考虑,研究旨在提供有价值的见解,以优化UHS系统的性能和可靠性。最终,UHS的成功实施不仅取决于技术创新,还取决于缓冲气体选择和管理的战略决策。通过主动解决这些挑战,利益相关者可以充分发挥氢气作为清洁和可持续能源载体的潜力,从而为全球向低碳未来的转型做出贡献。
CMG软件应用情况
CMG软件,特别是CMG-GEMTM,被用于模拟和研究地下氢储存中作为垫气的二氧化碳的行为。该软件通过数值模拟支持对UHS中气体行为的理解和预测。
作者单位
加利福尼亚大学诺曼分校Gallogly工程学院,美国俄克拉荷马州诺曼市
尼日利亚联邦林业学院林业研究部,伊巴丹PMB 5054,尼日利亚
贝宁大学工程学院化学工程系,贝宁城PMB 1154,贝宁
菲律宾科技大学生物技术、微生物学和生物化学系,Kuje 903101,尼日利亚
煤炭城市大学生物科学系,埃努古400104,尼日利亚
墨西哥国立自治大学可再生能源研究所,特米斯科,莫雷洛斯62580,墨西哥
爱丁堡大学工程学院基础设施与环境研究所,罗伯特史蒂文森路,爱丁堡EH9 3FB,英国
Abstract
Due to the increasing world population and environmental considerations, there has been a tremendous interest in alternative energy sources. Hydrogen plays a major role as an energy carrier due to its environmentally benign nature. The combustion of hydrogen releases water vapor while it also has a vast industrial application in aerospace, pharmaceutical, and metallurgical industries. Although promising, hydrogen faces storage challenges. Underground hydrogen storage (UHS) presents a promising method of safely storing hydrogen. The selection of the appropriate cushion gas for UHS is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of the storage system. Cushion gas plays a pivotal role in maintaining the necessary pressure within the storage reservoir, thereby enabling consistent injection and withdrawal rates of hydrogen. One of the key functions of the cushion gas is to act as a buffer, ensuring that the storage pressure remains within the desired range despite fluctuations in hydrogen demand or supply. This is achieved by alternately expanding and compressing the cushion gas during the injection and withdrawal cycles, thereby effectively regulating the overall pressure dynamics within the storage facility. Furthermore, the choice of cushion gas can have significant implications on the performance and long-term stability of the UHS system. Factors such as compatibility with hydrogen, cost-effectiveness, availability, and environmental impact must be carefully considered when selecting the most suitable cushion gas. The present study provides a comprehensive review of different types of cushion gases commonly used in UHS, including nitrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide. By examining the advantages, limitations, and practical considerations associated with each option, the study aims to offer valuable insights into optimizing the performance and reliability of UHS systems. Ultimately, the successful implementation of UHS hinges not only on technological innovation but also on strategic decisions regarding cushion gas selection and management. By addressing these challenges proactively, stakeholders can unlock the full potential of hydrogen as a clean and sustainable energy carrier, thereby contributing to the global transition towards a low-carbon future.
Keywords:
hydrogen; cushion gas; reservoir; sustainability; aquifer; natural gas
