Optimizing underground hydrogen storage in aquifers: The impact of cushion gas type
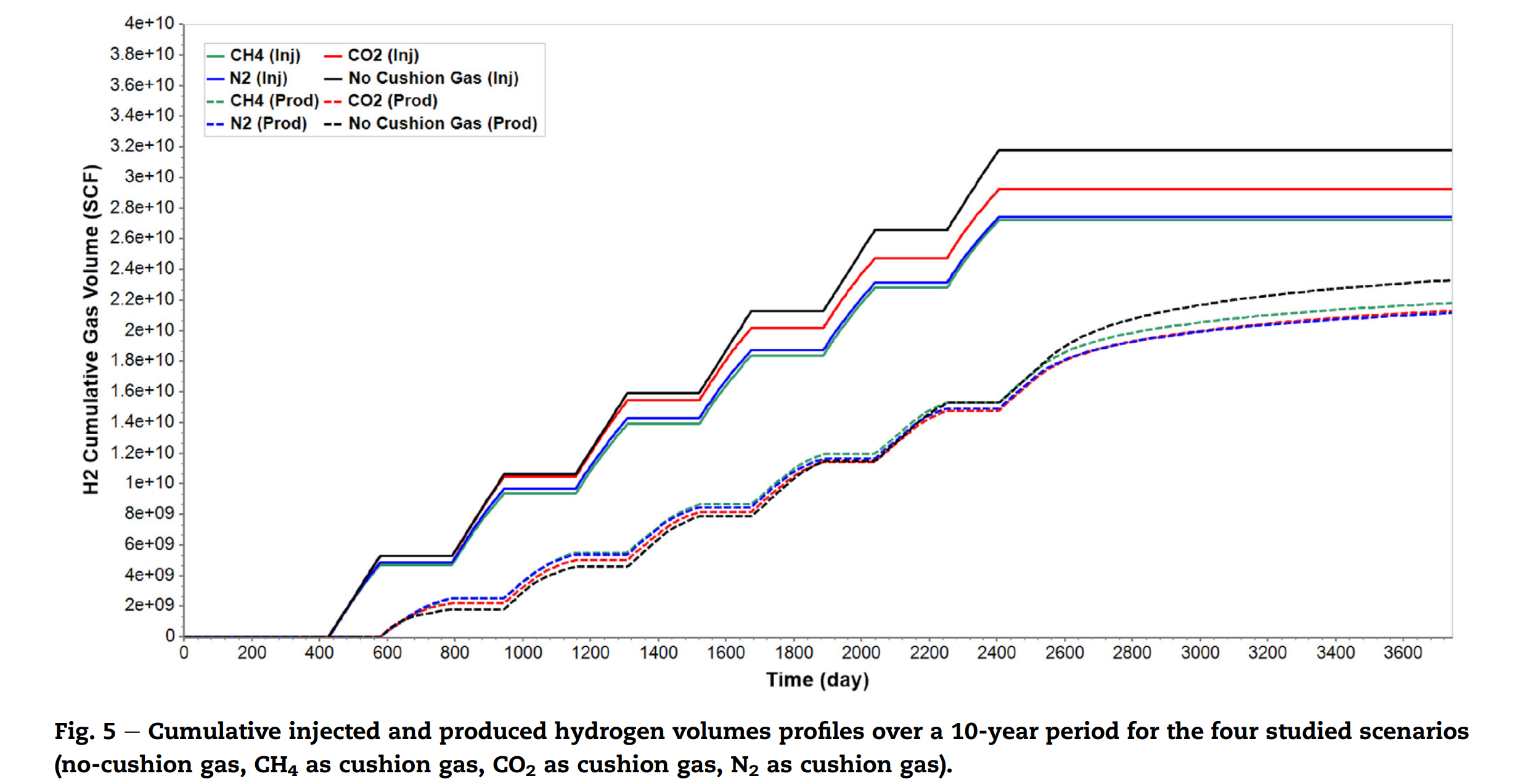
本研究调查了垫层气体类型及存在对北海含水层地下氢气储存(UHS)性能的影响。通过数值模拟,全面评估了垫层气体类型与UHS性能之间的关系,为设计高效UHS项目提供了宝贵见解。研究结果表明,垫层气体类型可以显著影响过程的回采效率和氢气纯度。CO2具有最高的储存能力,而像N2和CH4这样的轻气体表现出更好的回采效率。使用CH4作为垫层气体可以实现高达80%的回收效率,最小化侧向扩散和粘性指进。垫层气体密度决定了地下氢气储存方案的效率。
CMG软件的应用情况:
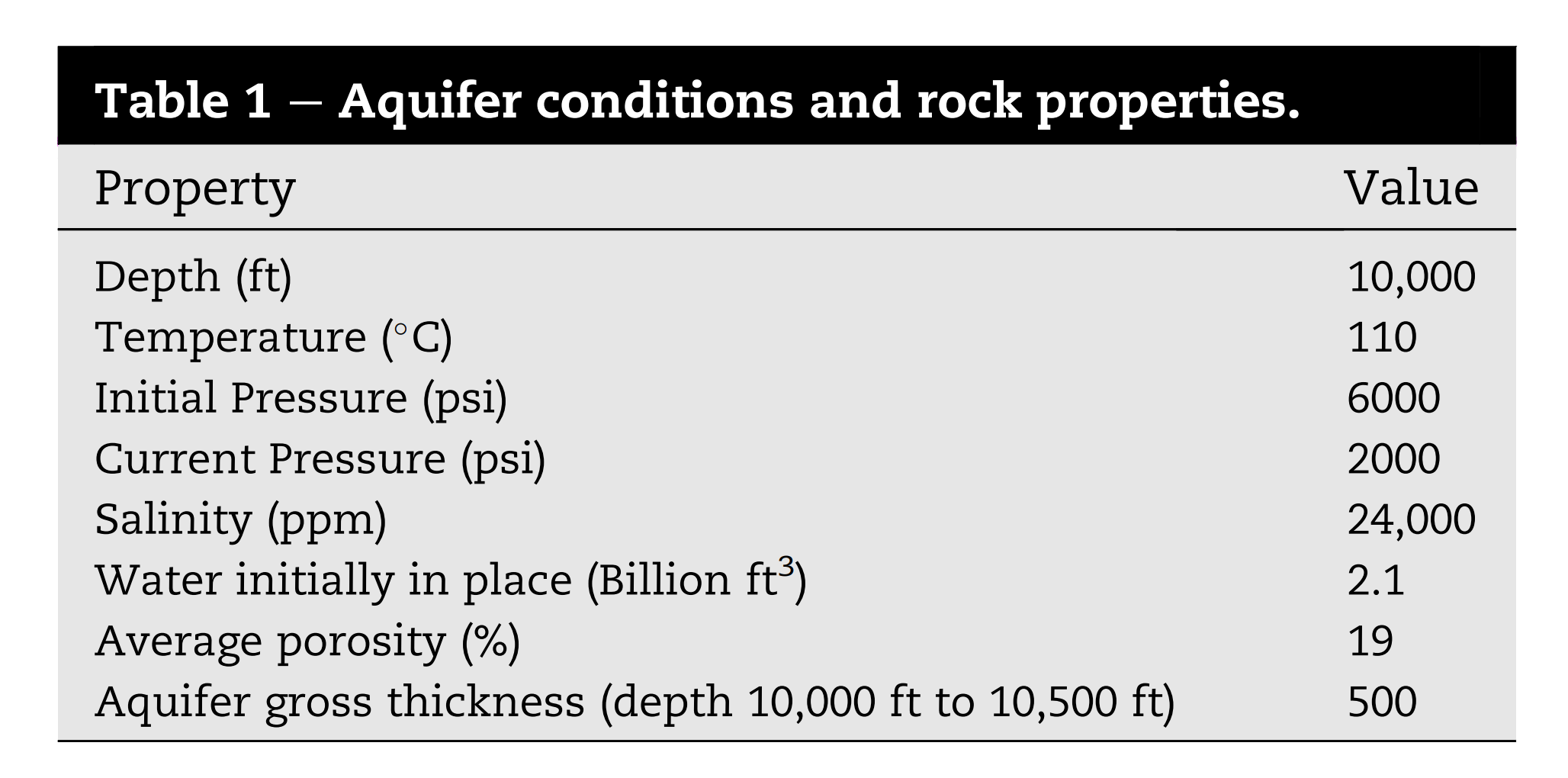
在这项研究中,使用了CMG-GEM™组成模拟软件来调查垫层气体类型对北海含水层地下氢气储存性能的影响。模拟包括了六周期的氢气注入和生产阶段,以及在氢气注入前的一年零两个月内以最大速率40 MMscf/d注入垫层气体。模拟研究使用位于含水层中心的单井进行。
This study investigated the impact of cushion gas type and presence on the performance of underground hydrogen storage (UHS) in an offshore North Sea aquifer. Using numerical simulation, the relationship between cushion gas type and UHS performance was comprehensively evaluated, providing valuable insights for designing an efficient UHS project delivery. Results indicated that cushion gas type can significantly impact the process’s recovery efficiency and hydrogen purity. CO2 was found to have the highest storage capacity, while lighter gases like N2 and CH4 exhibited better recovery efficiency. Utilising CH4 as a cushion gas can lead to a higher recovery efficiency of 80%. It was also determined that utilising either of these cushion gases was always more beneficial than hydrogen storage alone, leading to an incremental hydrogen recovery up to 7%. Additionally, hydrogen purity degraded as each cycle progressed, but improved over time. This study contributes to a better understanding of factors affecting UHS performance and can inform the selection of cushion gas type and optimal operational strategies.
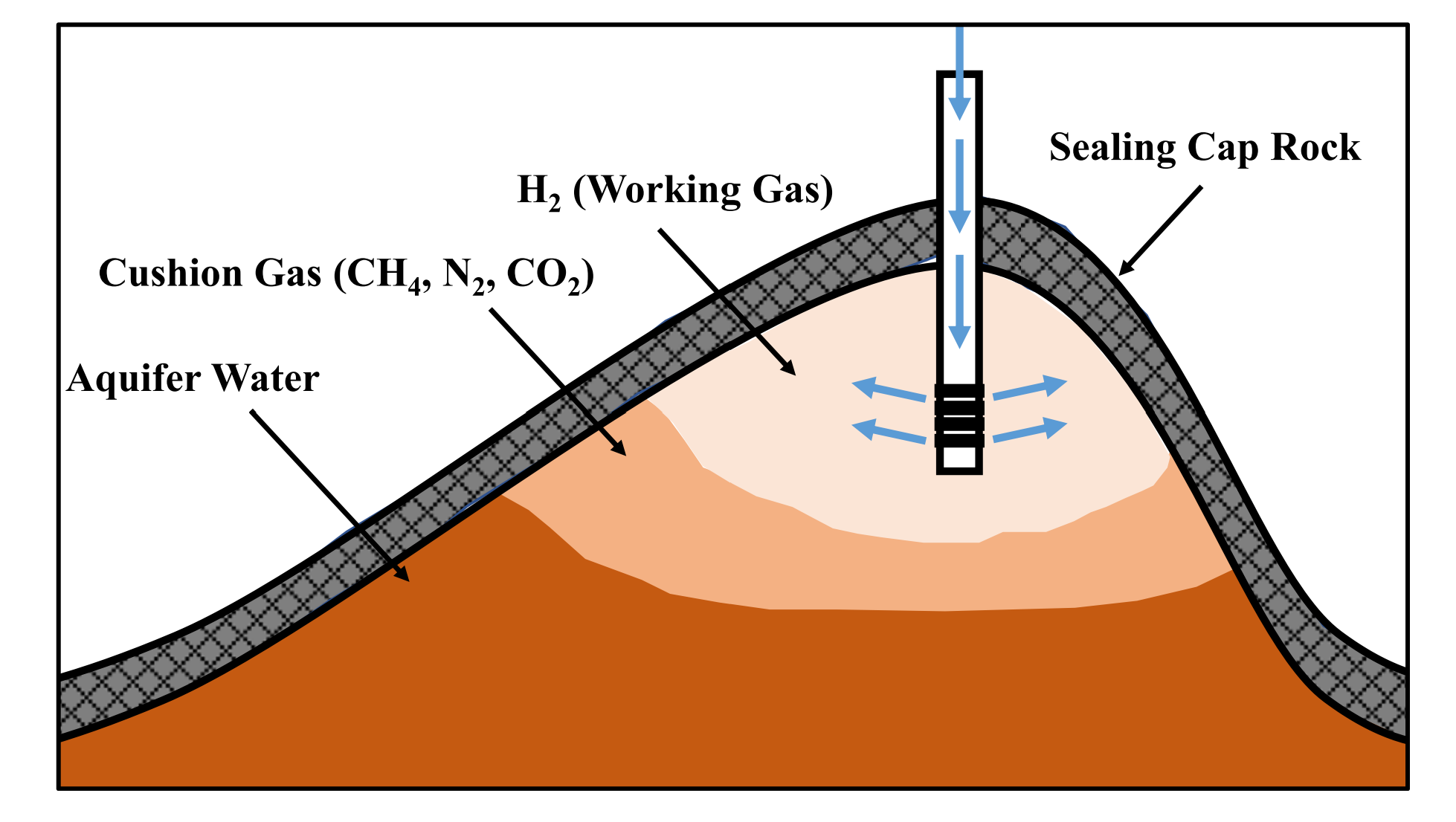
Fig. 1 e Schematic of underground hydrogen storage in an aquifer.

作者单位:
Motaz Saeed 和 Prashant Jadhawar 均来自苏格兰阿伯丁大学阿伯丁工程学院。
