Flow Behavior through Porous Media and Displacement Performance of a SILICA/PAM Nanohybrid: Experimental and Numerical Simulation Study
本研究通过实验和数值模拟研究了一种硅酸盐/聚丙烯酰胺(SiO2/PAM)纳米复合物(CSNH-AC)在多孔介质中的流动行为和驱油效率。研究结果表明,纳米复合物在较低浓度下展现出比HPAM溶液更好的流变行为。此外,纳米聚合物溶液的吸附和不可进入孔隙体积(IPV)以及残余阻力因子(RRF)均高于HPAM溶液,这归因于实验室测试中使用的岩石渗透率的差异。
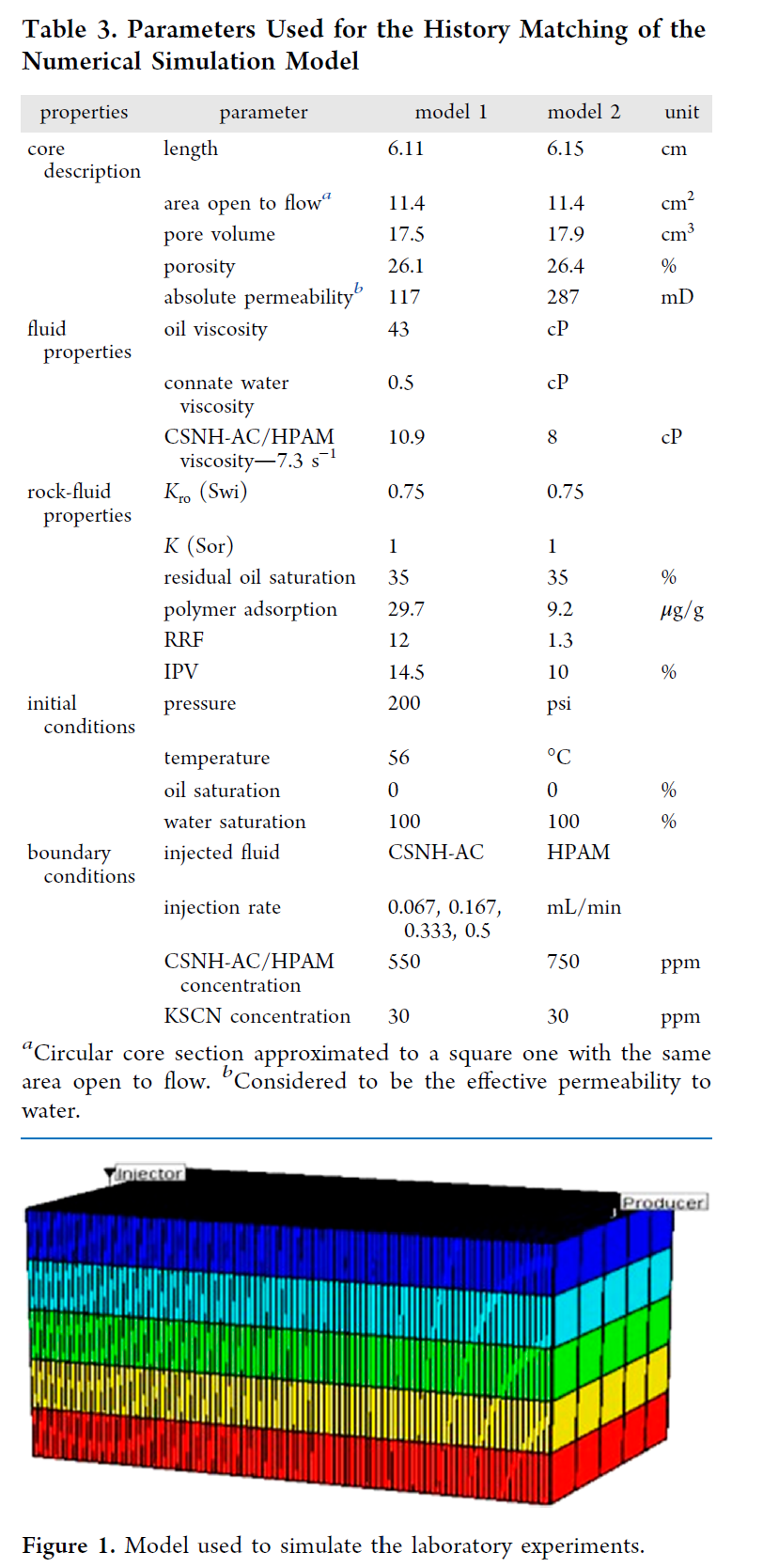
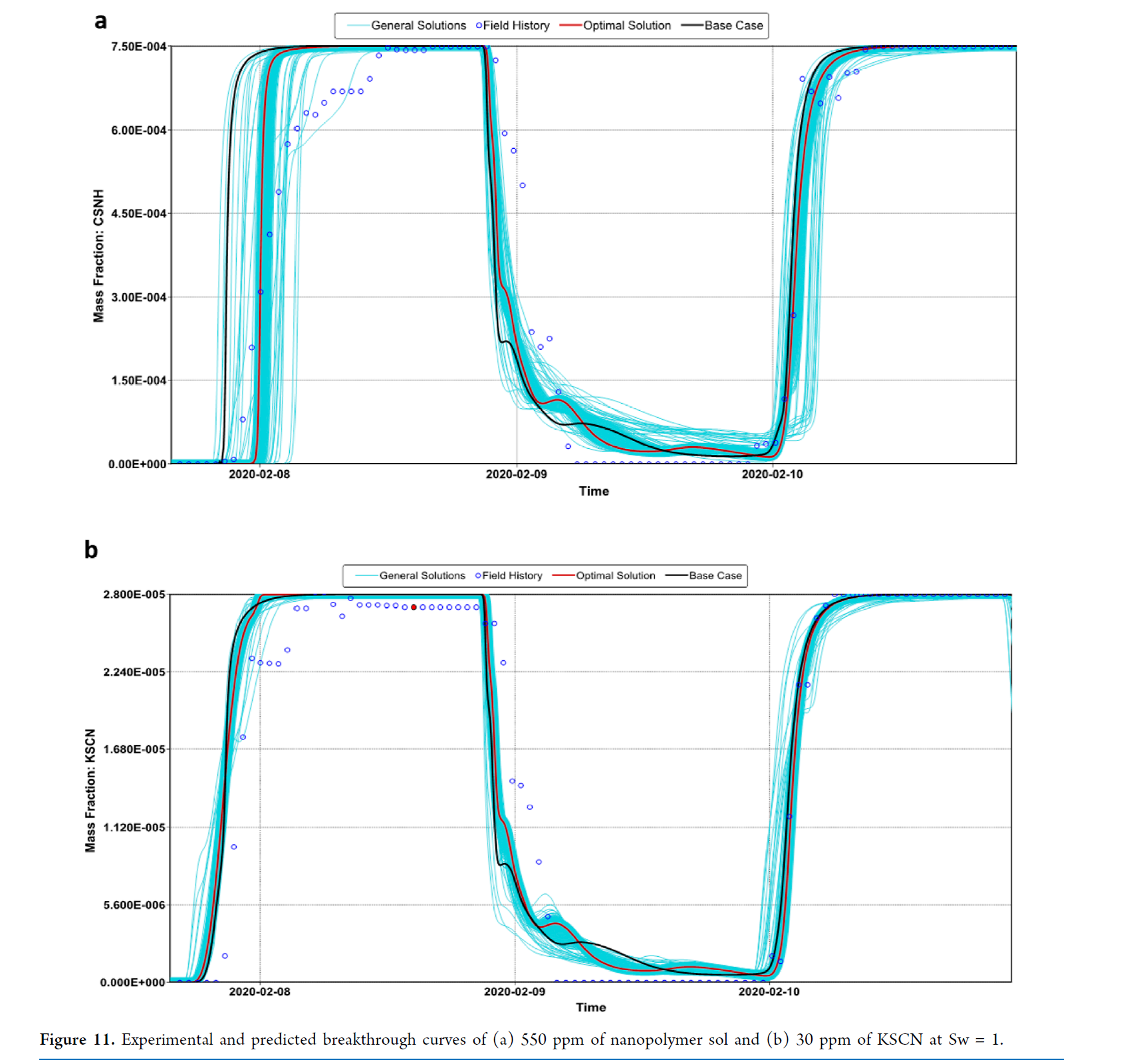
在CMG应用方面,研究使用了商业软件CMG STARS进行数值模拟。通过实验室尺度模型的建立和历史拟合,结合先进的统计分析和机器学习,对实验室数据进行了模拟。模拟结果与实验室数据的最小差异表明,模型输入数据已成功调整以正确反映在岩心驱替测试中发生的传输机制。
在数值模拟的历史拟合过程中,调整了渗透率降低因子、动态吸附和IPV等参数,这些参数对历史匹配过程中的目标函数影响最大。一旦获得最佳拟合,使用新的拟合参数来预测CSNH-AC和HPAM溶液在相同实验室尺度模型中的驱油效率。
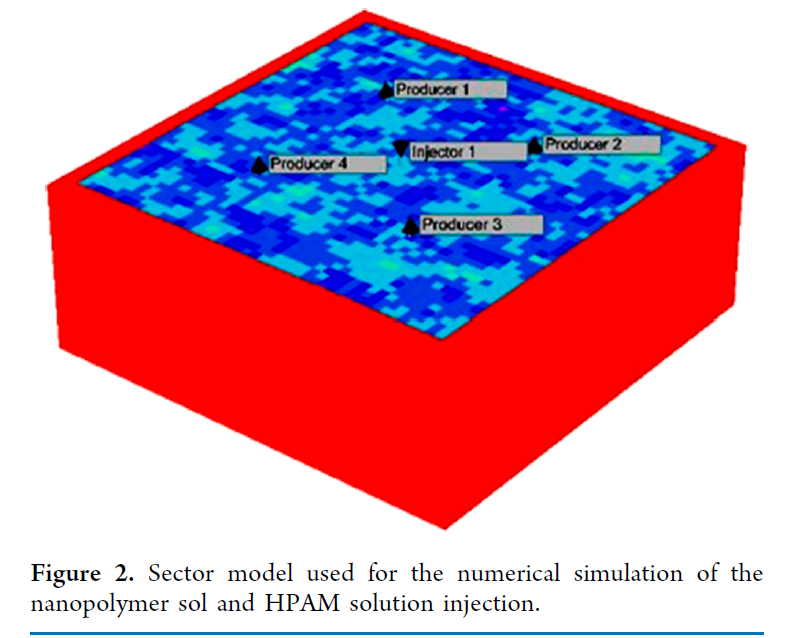
此外,为了评估CSNH-AC和HPAM注入在矿场规模上的体驱油效率,使用了一个反5点井网机理模型中进行了模拟。模拟结果表明,与水驱相比,纳米聚合物溶液和HPAM溶液分别增加了11.3%和6.7%的采收率。
综上所述,CMG在本研究中的应用成功地模拟了实验室条件下的多孔介质流动和驱油效率,并通过历史拟合方法优化了模型参数。这些模拟结果对于理解纳米复合物在多孔介质中的行为和提高采收率具有重要意义。此外,CMG的应用还为矿场规模的化学驱油项目提供了重要的指导和预测,有助于优化化学驱油的设计和实施。
Abstract
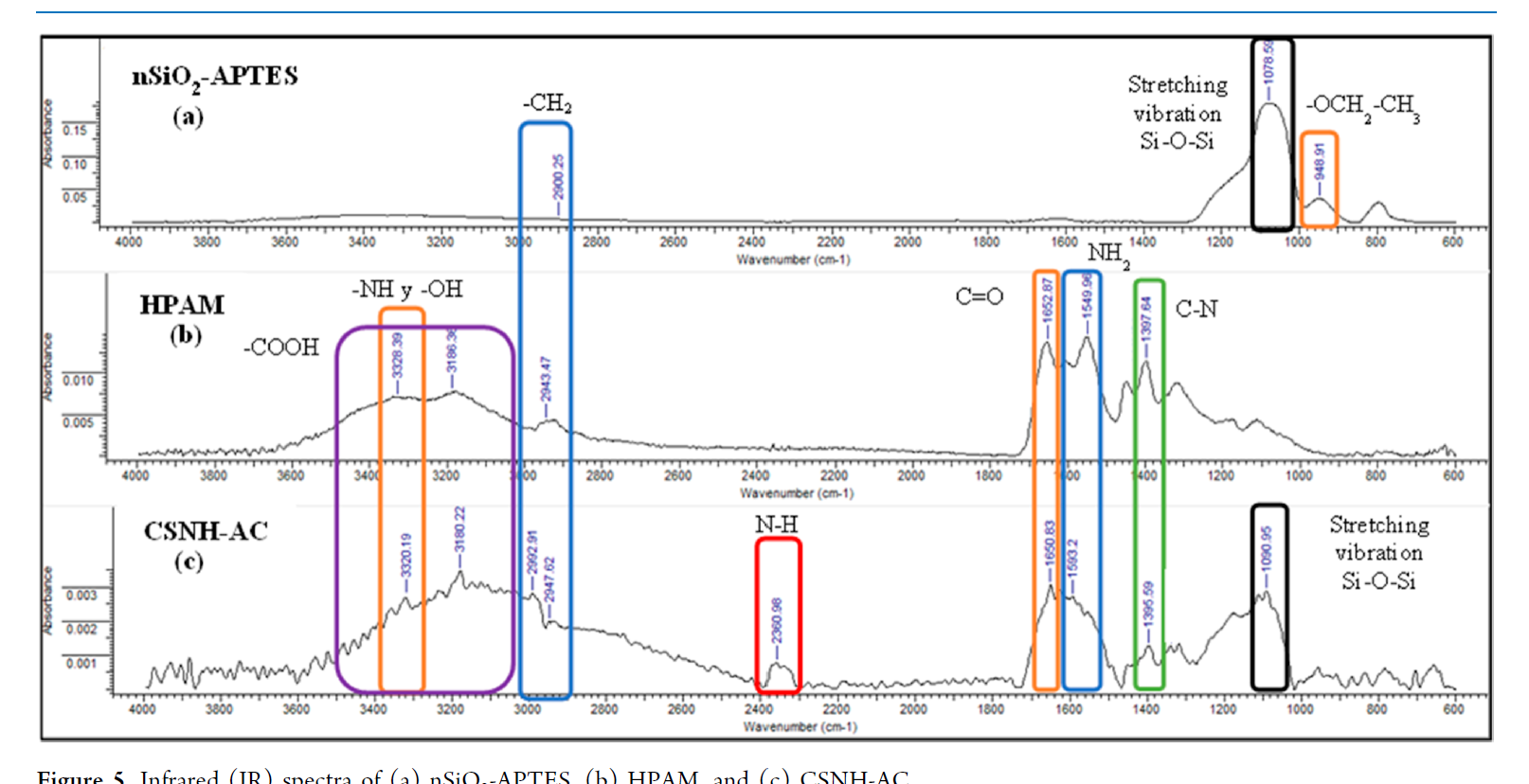
Nanoparticles (NPs) have been proposed as additives to improve the rheological properties of polymer solutions and reduce mechanical degradation. This study presents the results of the retention experiment and the numerical simulation of the displacement efficiency of a SiO2/hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) nanohybrid (CSNH-AC). The CSNH-AC was obtained from SiO2 NPs (synthesized by the Stöber method) chemically modified with HPAM chains. Attenuated total reflection–Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, field emission gun–scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and thermogravimetric analysis were used to characterize the nanohybrid. The injectivity and dynamic retention tests were performed at 56 °C in a sandstone core with a porosity of ∼26% and a permeability of 117 and 287 mD. A history matching of the dynamic retention test was performed to determine the maximum and residual adsorption, IPV, and residual resistance factor (RRF). A laboratory-scale model was used to evaluate the displacement efficiency of CSNH-AC and HPAM through numerical simulation. According to the results, the nanohybrid exhibits better rheological behavior than the HPAM solution at a lower concentration. The nanopolymer sol adsorption and IPV (29,7 μg/grock, 14,5) are greater than those of the HPAM solution (9,2 μg/grock, 10), which was attributed to the difference between the rock permeabilities used in the laboratory tests (HPAM: 287 mD and CSNH-AC: 117 mD). The RF of both samples gradually increases with the increase in shear rate, while the RRF slightly decreases and tends to balance. However, the nanopolymer sol exhibits greater RF and RRF values than that of the polymer solution due to the strong flow resistance of the nanohybrid (higher retention in the porous media). According to the field-scale simulation, the incremental oil production could be 295,505 and 174,465 barrels for the nanopolymer sol and the HPAM solution, respectively (compared to waterflooding). This will represent an incremental recovery factor of 11.3% for the nanopolymer sol and 6.7% for the HPAM solution.