Deep Learning-Based Investigation of Multiphase Flow and Heat Transfer in CO2–Water Enhanced Geothermal Systems
为应对全球变暖与日益增长的能源需求,本文提出一种融合地质参数、温度梯度及井控方案的“多模态-Transformer”代理模型,用于快速、准确预测 CO₂–水增强型地热系统(EGS)中的多相流动与传热行为。
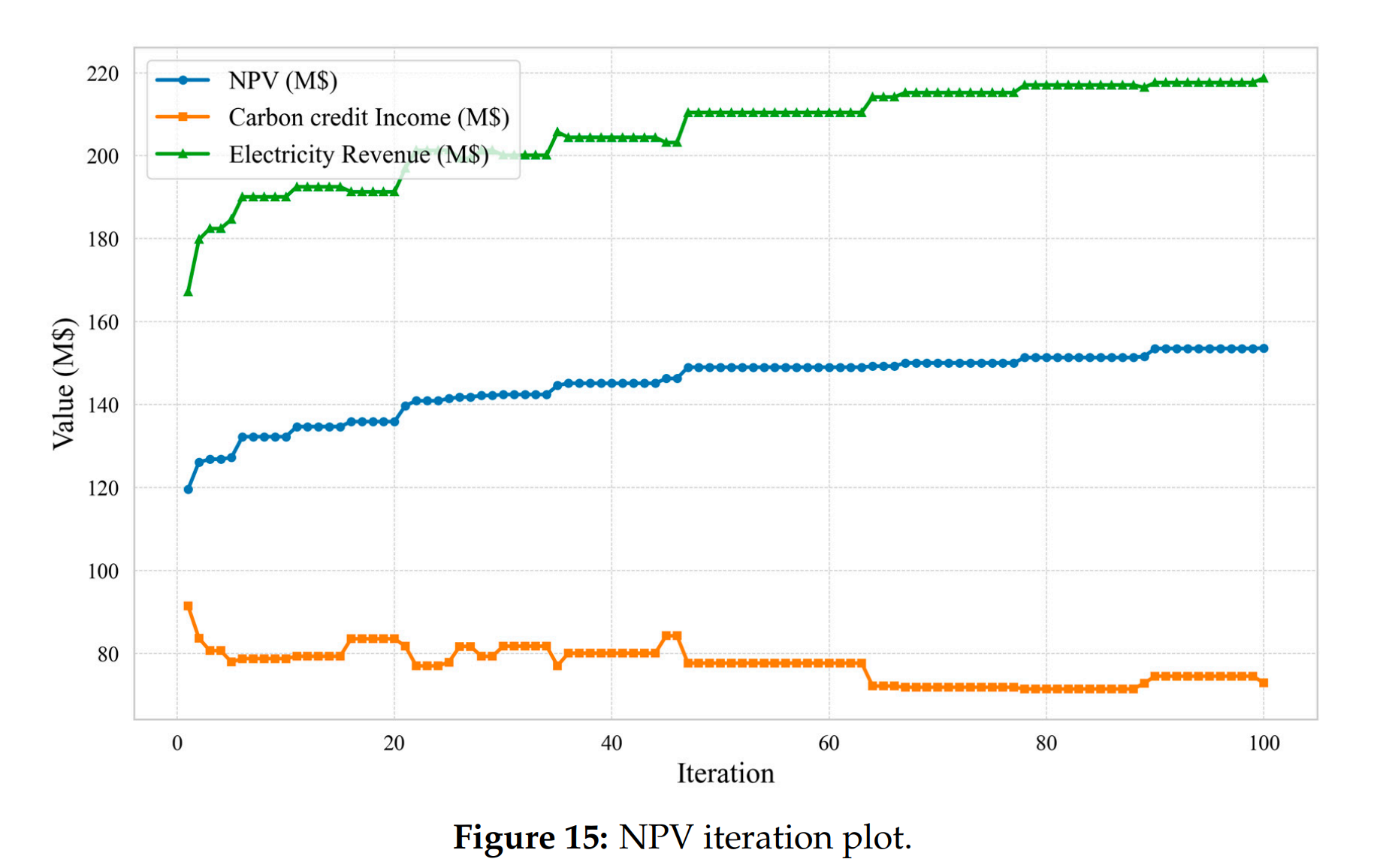
研究首先利用 CMG-STARS 建立三维双孔双渗地质模型,生成涵盖 25 年、1000 套随机渗透率-井控序列的高保真训练数据;随后构建物理引导的 Transformer 网络,将质量守恒、能量守恒及边界约束嵌入损失函数,实现对井口温度、压力、产量及 CO₂封存量的高精度映射(RMSE 3–5 %,MAE <4 %,R²>0.95)。与常规 GRU/LSTM 相比,代理模型预测误差降低 40 % 以上,单轮推理耗时仅 0.53 s。进一步耦合差分进化(DE)算法进行闭环优化,结果表明:在电价为 0.09 /t 条件下,优化后的 CO₂-水注入比例与注采压力组合可将净现值(NPV)提高 15–20 %;电价与碳价是影响经济效益的最敏感因素。研究为地热开发实时预测与井控优化提供了一种可扩展的深度学习框架。
CMG 软件应用情况
- 使用模块:CMG-STARS(热-流-化学耦合模拟器)。
- 模型设定:
– 双孔双渗、29×29×9 网格,尺寸 1770×1770×110 m³;
– 基质渗透率 10–30 mD,裂缝渗透率 80–200 mD;
– 9 口注入井、16 口生产井,注水量 200–400 m³/d,CO₂-水比例 0–1 可调;
– 局部热平衡、忽略化学反应与力学效应,模拟时长 25 年、每年 1 个控制步。 - 功能与输出:
– 批量计算 1000 组方案,获取温度场、压力场、产热量、CO₂溶解量等训练样本;
– 为代理模型提供高保真标签数据,并用于验证神经网络预测精度(误差<5 %)。
主要结论
- 代理模型精度高:Transformer 架构在测试集上 RMSE 3–5 %,R²>0.95,显著优于 GRU/LSTM/传统降阶模型。
- 物理约束有效:引入质量-能量守恒损失函数后,预测误差再降 10–12 %。
- 经济收益提升:耦合差分进化优化后,最佳井控策略使 NPV 提高 15–20 %。
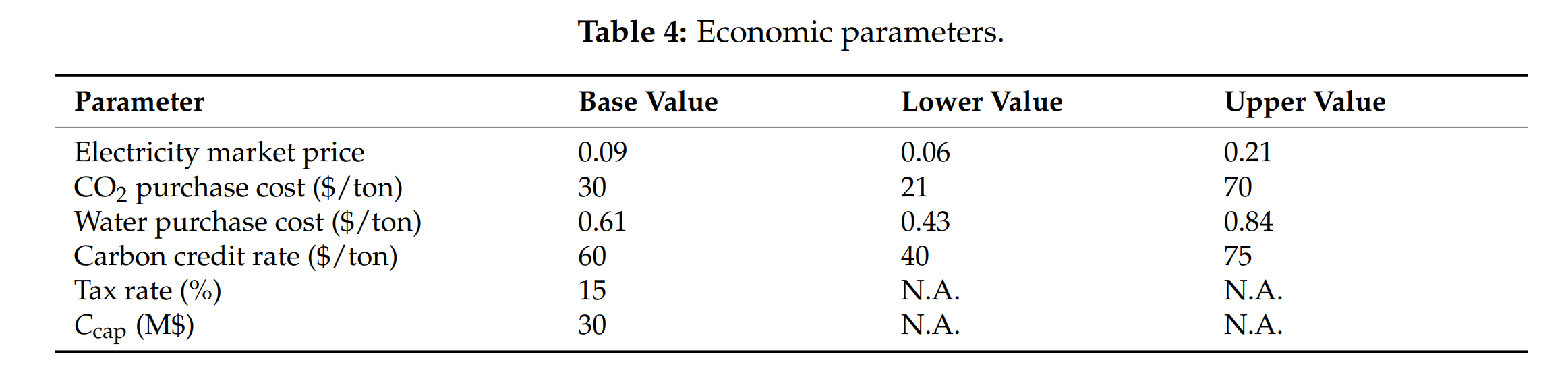
- 敏感因素识别:电价与碳价波动对净现值影响最大,水/CO₂采购成本影响有限。
- 研究局限:当前假设局部热平衡、忽略化学反应与力学耦合,后续将扩展非热平衡、反应-应力耦合模型。
作者单位
中国石油川庆钻探工程有限公司
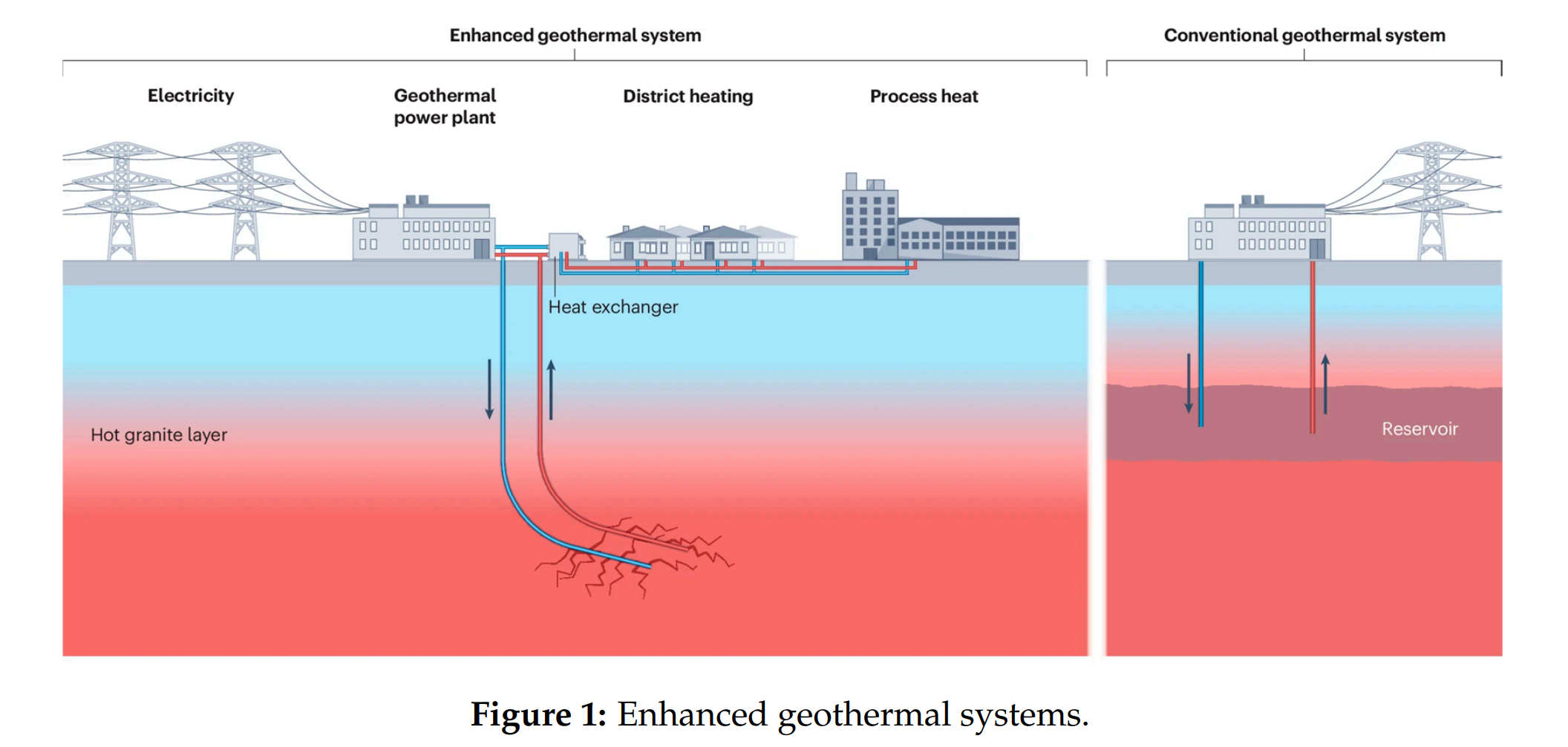
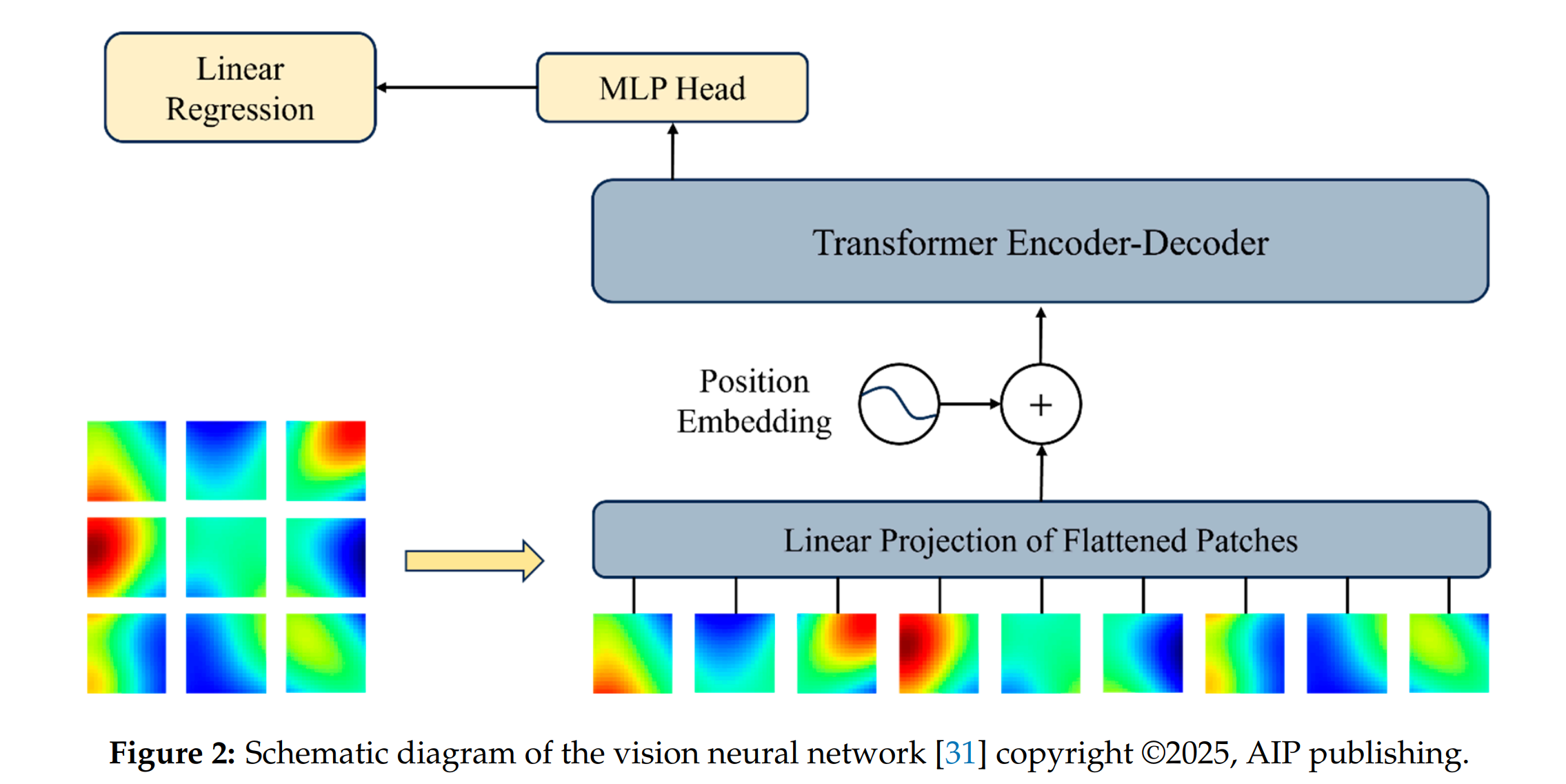
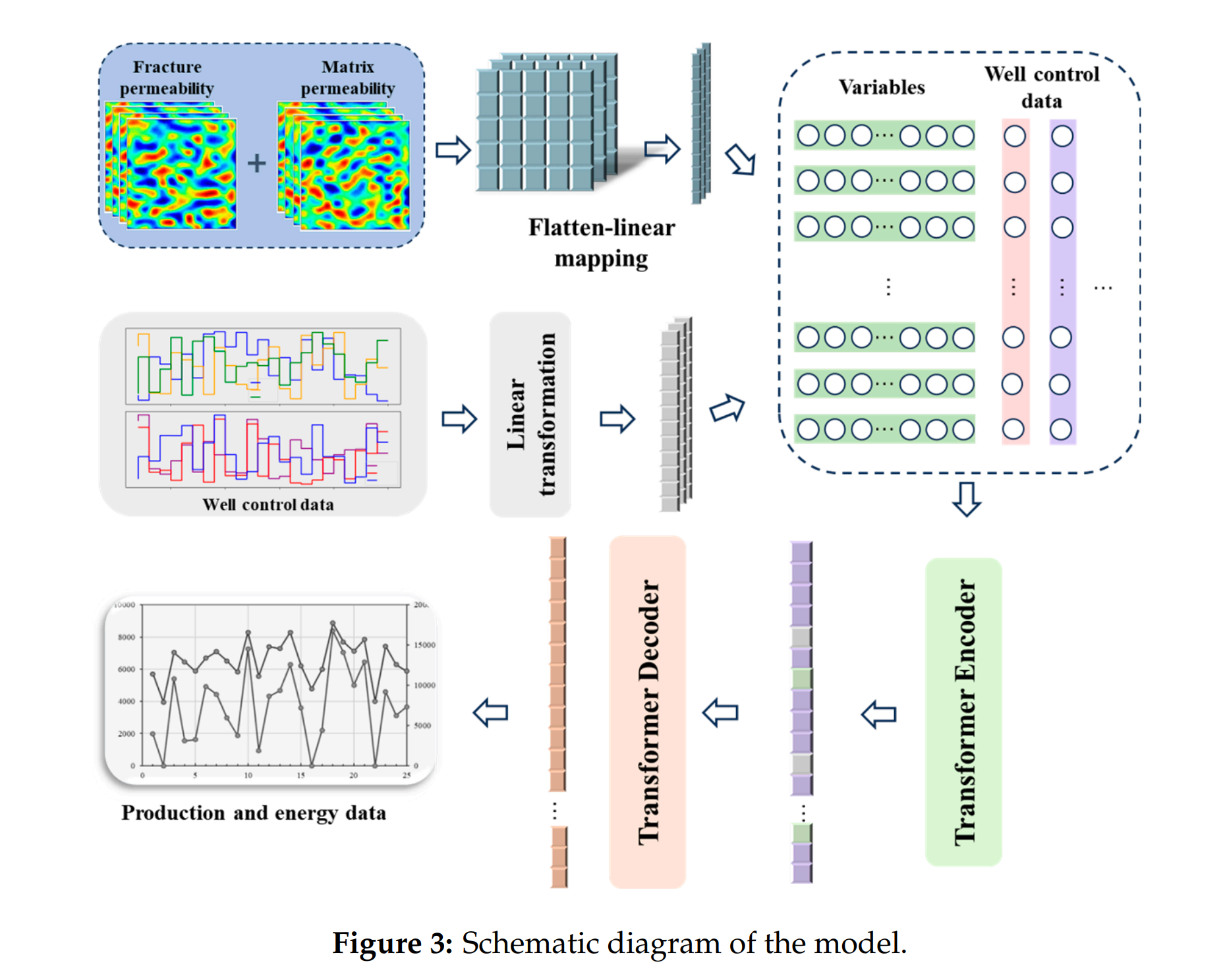
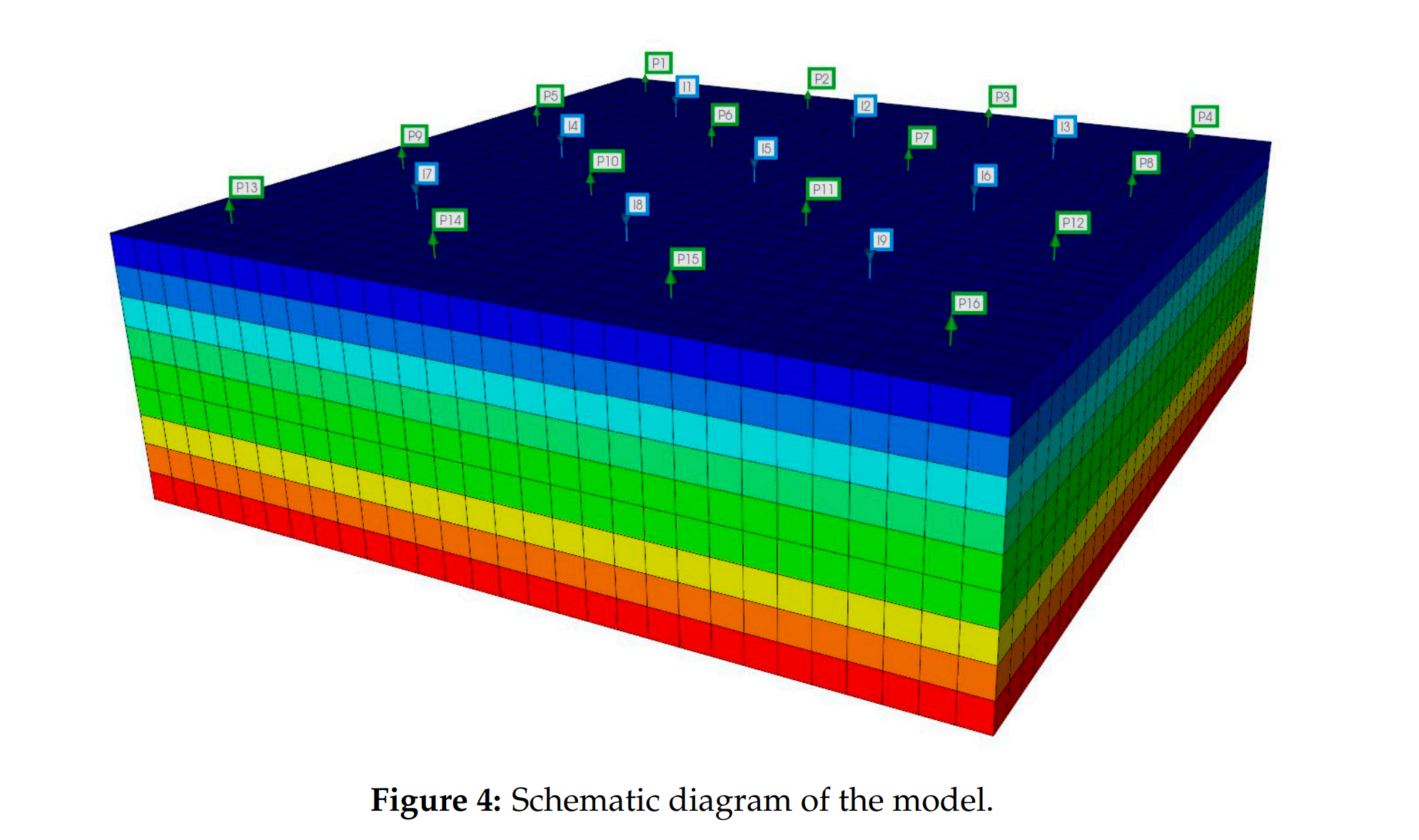
Abstract
This study introduces a Transformer-based multimodal fusion framework for simulating multiphase flow and heat transfer in carbon dioxide (CO2)–water enhanced geothermal systems (EGS). The model integrates geological parameters, thermal gradients, and control schedules to enable fast and accurate prediction of complex reservoir dynamics. The main contributions are: (i) development of a workflow that couples physics-based reservoir simulation with a Transformer neural network architecture, (ii) design of physics-guided loss functions to enforce conservation of mass and energy, (iii) application of the surrogate model to closed-loop optimization using a differential evolution (DE) algorithm, and (iv) incorporation of economic performance metrics, such as net present value (NPV), into decision support. The proposed framework achieves root mean square error (RMSE) of 3–5%, mean absolute error (MAE) below 4%, and coefficients of determination greater than 0.95 across multiple prediction targets, including production rates, pressure distributions, and temperature fields. When compared with recurrent neural network (RNN) baselines such as gated recurrent units (GRU) and long short-term memory networks (LSTM), as well as a physics-informed reduced-order model, the Transformer-based approach demonstrates superior accuracy and computational efficiency. Optimization experiments further show a 15–20% improvement in NPV, highlighting the framework’s potential for real-time forecasting, optimization, and decision-making in geothermal reservoir engineering.
