A critical review of cushion gas in underground hydrogen storage: Thermophysical properties, interfacial interactions, and numerical perspectives
随着全球能源转型加速,地下氢气储存(UHS)被视为大规模、长周期氢储能的重要方式。在UHS中,注入垫气(如CO₂、CH₄、N₂等)可维持地层压力、抑制氢气上浮、提高回采率。
本文系统综述了不同类型垫气的热物性(密度、粘度、压缩因子、溶解度)及其与岩石/盐水系统的界面行为(润湿性、界面张力、相对渗透率)对UHS性能的影响,并总结了垫气类型、组成、注入量及生物甲烷化过程对氢气采收率、产出纯度、水产量等关键指标的影响。文章还指出当前数值模拟中存在的知识空白,并提出了未来研究方向。
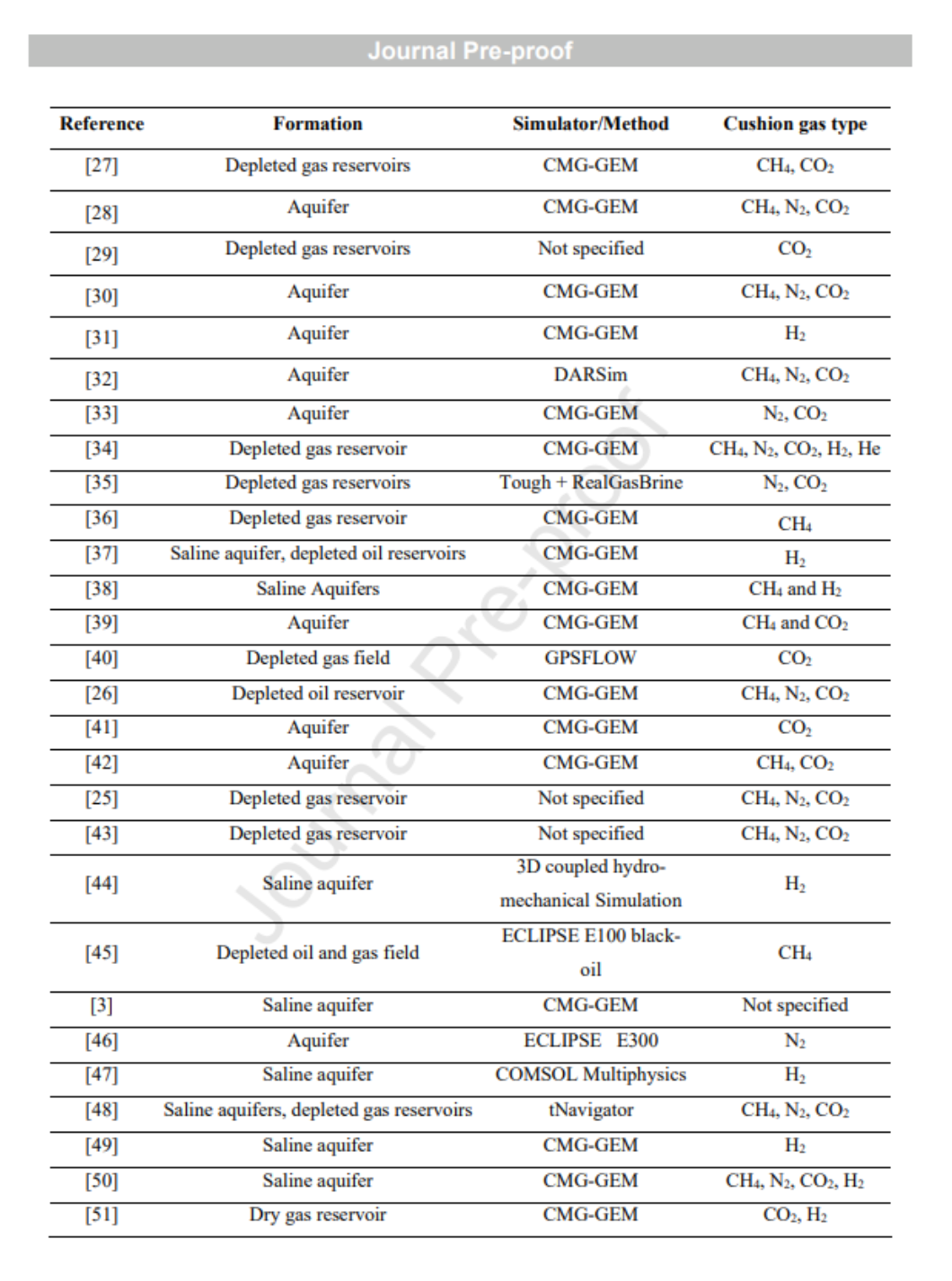
CMG软件应用情况
- 软件平台:CMG(Computer Modeling Group)系列模拟器,如GEM、STARS、IMEX等,在多篇研究中被广泛用于模拟地下氢气储存过程中的多相流动、气体混合、界面反应等复杂过程。
- 主要应用:
- 模拟不同缓冲气体(CO₂、CH₄、N₂)对氢气采收率、产出纯度、水产量的影响;
- 模拟气体混合区形成与扩散过程;
- 分析垫气注入量对储层压力、氢气分布及回采效率的影响;
- 模拟CO₂作为垫气时的生物甲烷化反应及其对氢气损失的贡献;
- 模拟不同注入策略(如注采周期、注入速率、井位布置)对UHS性能的影响。
结论
- 气体性质方面:
- H₂密度和粘度最低,易上浮,需通过垫气抑制重力分异;
- CO₂密度和溶解度最高,易溶解于地层水,缓冲效果好但可能引发生物甲烷化反应;
- N₂和CH₄在密度、润湿性等方面与H₂更接近,有利于提升H₂纯度。
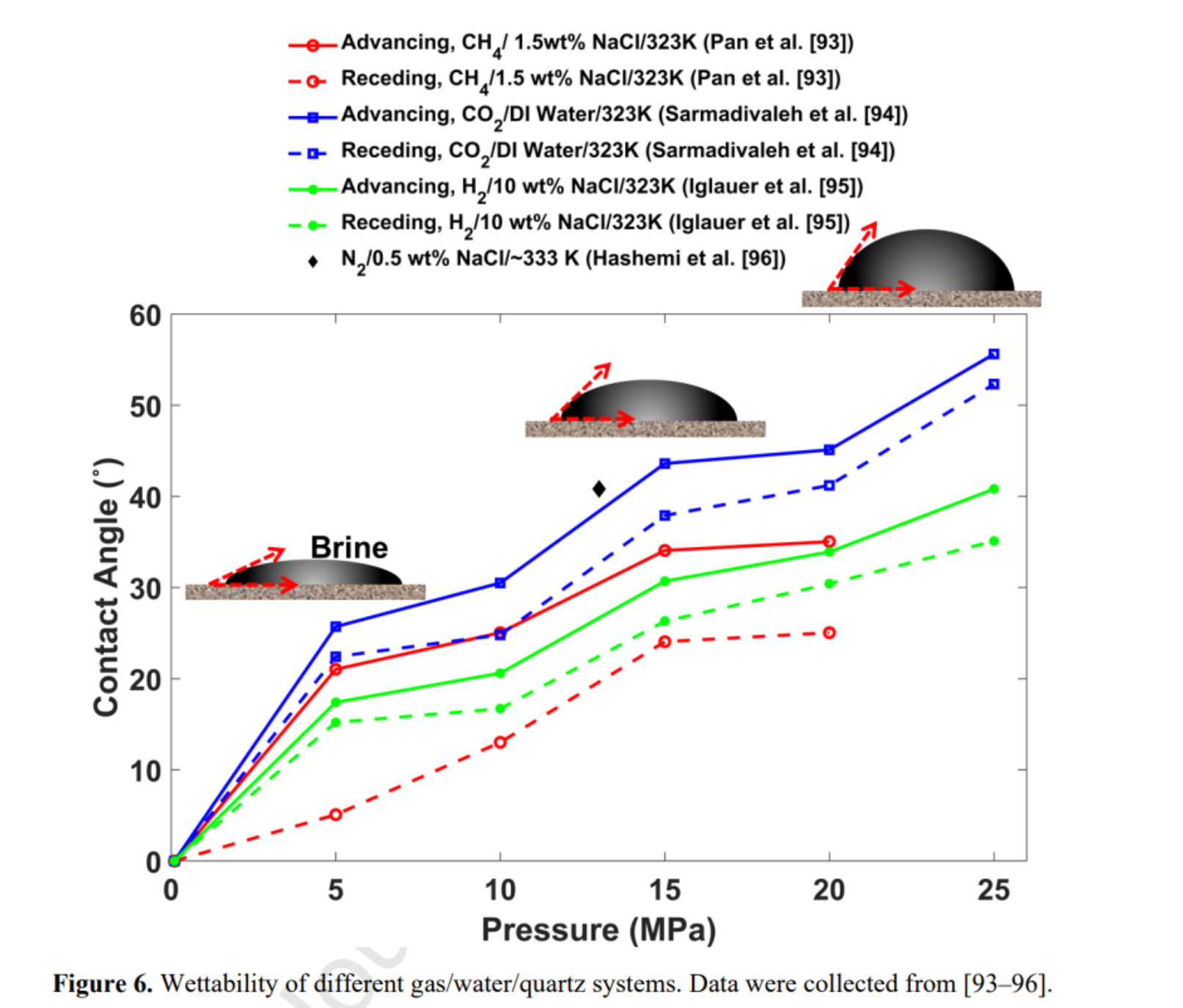
- 界面行为方面:
- H₂-盐水系统具有最高的界面张力,有利于残余捕集;
- 混合气体的润湿性、相对渗透率与纯气体不同,需单独模拟;
- 气体混合区扩散程度:H₂-N₂ > H₂-CH₄ > H₂-CO₂。
- 数值模拟方面:
- 垫气可提高氢气采收率,但效果受限于注入量、气体类型及地质条件;
- CO₂作为垫气时,若存在产甲烷菌,会导致H₂被消耗,降低采收率;
- 多数模拟未区分“垫气H₂”与“工作气H₂”,建议引入“c-H₂”标签进行区分。
- 研究空白与展望:
- 缺乏系统对比不同气体在多矿物岩石上的润湿性;
- 混合气体相对渗透率实验数据稀缺;
- 需进一步研究垫气在循环注采过程中的动态行为与长期稳定性;
- 模拟中应更精细地刻画气体混合、微生物反应、应力变化等耦合过程。
作者单位
阿联酋哈利法大学化学与石油工程系
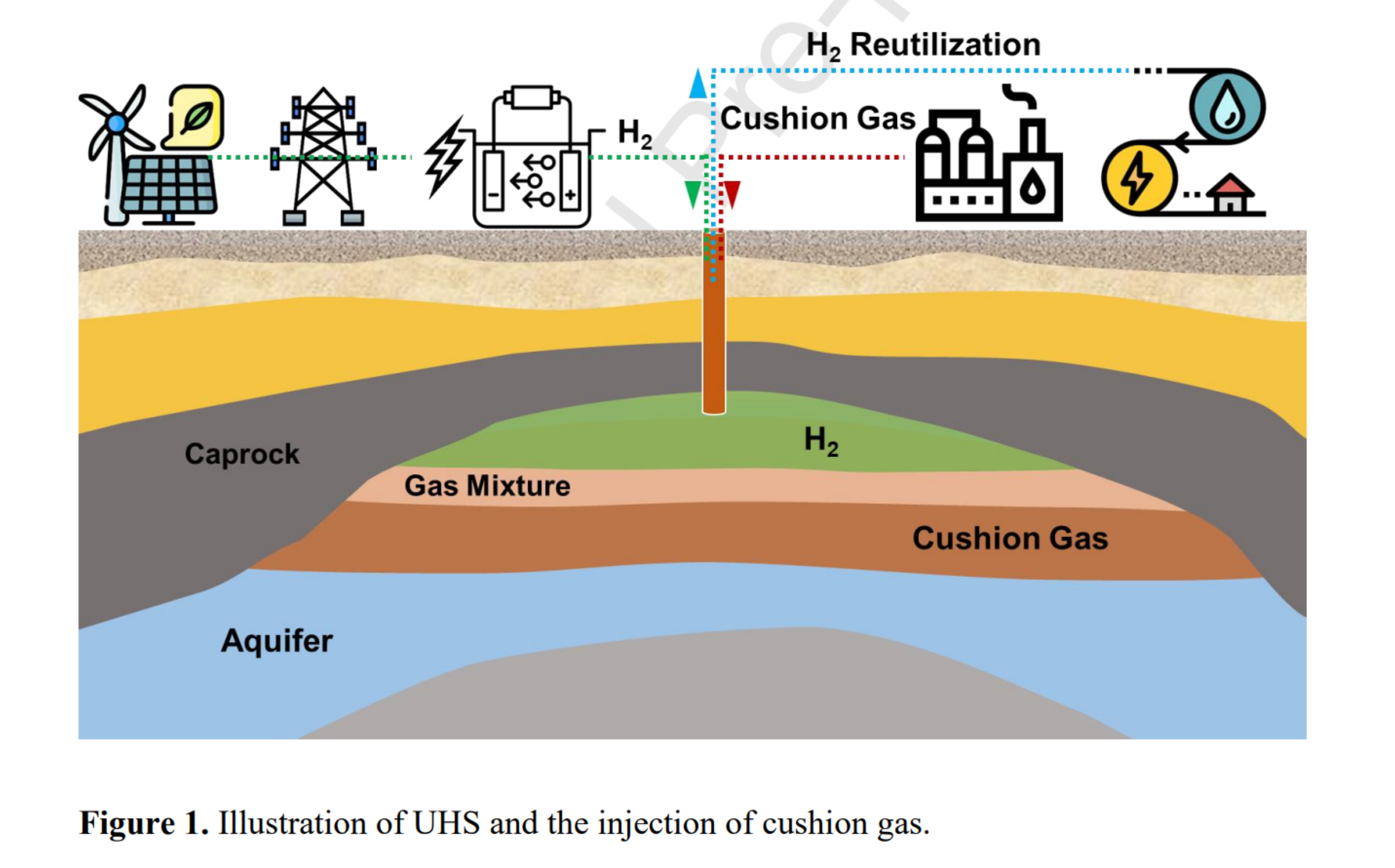
Abstract
Increased greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel consumption have significantly contributed to global warming, promoting the transition toward renewable energy sources. Underground hydrogen storage (UHS) represents a large-scale energy storage system, aiming to ensure a consistent supply by storing hydrogen generated from surplus energy. In the practice of UHS, cushion gas is generally injected into the formation to retain the reservoir pressure for efficient hydrogen withdrawal. This paper reviews the impact of cushion gas on the performance of UHS from both experimental and numerical simulation perspectives. The thermophysical (e.g., density, viscosity, compressibility, and solubility) and petrophysical (interfacial tension, wettability, and relative permeability) properties of different cushion gases, as well as the mixing and diffusion behavior of different cushion gases, were compared. The corresponding impact of different cushion gases on plume migration and trapping potential is then discussed. Furthermore, this review critically analyzes and explains the impact of various factors on the performance of UHS, including the type of cushion gas, the composition of cushion gas mixtures, the volume of injected cushion gas, and the effects of bio-methanation processes. The corresponding analysis specifically focuses on key performance indicators, including H2 recovery factor, formation pressure, brine production, and H2 outflow purity. Thus, this review provides a comprehensive analysis of the role of cushion gas in UHS and provides an understanding of the effective management and optimization of cushion gas injection in field-scale UHS operations.
